Mutations and Chromosomal
Abnormalities
Higher Human Biology
Mutations
• A mutation is a change in the structure or
amount of an organisms genetic material
• When a change in genotype produces a
change in phenotype, the individual is
called a mutant
Gene Mutations
• POINT MUTATIONS – substitution, inversion;
bring about only a minor change (ie one different
amino acid); sometimes the organism is affected
only slightly or not at all
• FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS – insertion ,
deletion; leads to a large portion of the gene’s
DNA to be misread; the protein produced differs
from the normal protein by many amino acids and
is usually disfunctional
Substitution
Inversion
• Inversion of two or more nucleotides
Insertion
Insertion
Deletion
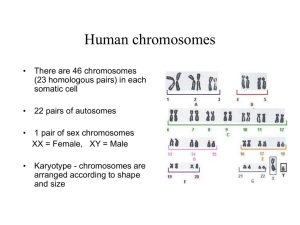
Chromosomal Abnormalities
• During meiosis in humans unusual gametes
can be formed which contain 22 or 24
chromosomes
• These abnormal gametes are formed when a
spindle fibre fails and one of the pair of
homologous chromosomes fail to become
separated
• This is called non-disjunction
Non-disjunction
Down’s Syndrome
• Due to non-disjunction of chromosome 21
• An extra copy of chromosome 21 is seen in the
karyotype of someone with Down’s syndrome
• The affected individual is characterised by mental
retardation and distinctive physical features
• Egg mother cells of older women tend to be more
prone to non-disjunction at meiosis
Down’s Syndrome Karyotype
Non-disjunction of Sex
Chromosomes
• If human sex chromosomes are affected by
non-disjunction during meiosis then unusual
gametes are formed
Turner’s Syndrome
Turner’s Syndrome
• Chromosome complement 2n = 44 + XO
• Individuals are always female and short in
stature
• Their ovaries do not develop so they are
infertile and fail to develop secondary
sexual characteristics e.g. breast
development and menstruation
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
• Chromosome complement 2n = 44 + XXY
• Individuals are always male and possess male sex
organs
• They are infertile since their testes only develop to
half the normal size and fail to produce sperm
• Testes produce low levels of testosterone so facial
hair, deepening of voice are only weakly
expressed