Chromosome Disorders
advertisement

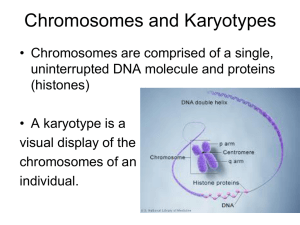
Chromosome Disorders Prenatal Diagnosis Amniocentesis • A small sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby is removed using a syringe. • The fluid contains skin cells from the baby. • The skin cells are grown in the lab. • The chromosomes from the cells are magnified under a microscope and a picture is taken. • The chromosomes are cut out and arranged in homologous pairs in decreasing size order. • This is called a karyotype. Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) • Extra chromosome 21 in every cell of the body • Causes mental retardation, heart defects • Karyotype = 47,XX+21 or 47,XY+21 • As a woman gets older, her chances of having a baby with a chromosome abnormality increases ***remember, a woman is born with all of her egg cells, but meiosis is not yet complete (egg development stops in prophase I until the follicle matures prior to ovulation) • Most cases of Down syndrome are caused by nondisjunction during meiosis • Nondisjunction: homologous chromosomes do not separate properly http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/biolink/j _explorations/ch10expl.htm Turner Syndrome 45,X Characteristics • • • • • short stature ovaries do not develop (infertile) cardiovascular problems kidney and thyroid problems skeletal disorders such as scoliosis Klinefelter Syndrome 47,XXY Characteristics • Infertility (cannot produce a lot of sperm) • Learning disability Trisomy 13 • severe birth defects • mental retardation Trisomy 18 • severe birth defects • mental retardation