Chapter9
advertisement

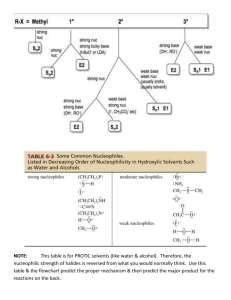
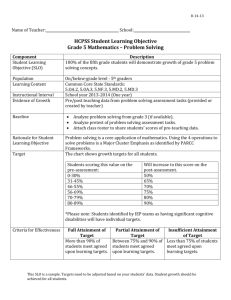
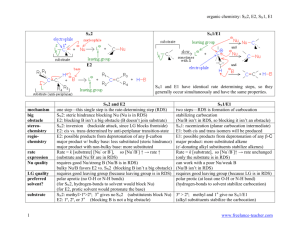
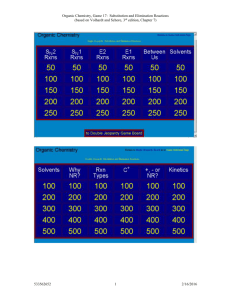
Ch. 9 Substitution and Elimination: Reactions of Akyl Halides I. Substitution Reactions Nucleophile (Nu:): nucleus- loving - e- rich (lone pair or π bond), can also have negative (-) charge - seeks e- deficient species (δ+ or +) Electrophile (E+): electron-loving - e- poor (δ+ or +) - seeks e- rich species Leaving group (LG) - group leaves and take 2 e- with it - stable groups (weak bases) make good LG’s (e.g Cl-, Br-, I-) General reaction: R – LG + Nu: R – Nu + LG: Possible mechanism? *simultaneous * stepwise CHM 201 Dang 1 SN2: Substitution Nucleophilic Biomolecular Reaction (9.2) E.g Mechanism: one step SN2 Kinetic Rate = k [CH3O-] [CH3Cl] Rate depends on both Nu: and E+ Biomolecular rxn Sterics affect rate of SN2 R Group Abbreviation MeX X = Cl, Br, I Carbon type EtX Methyl 1o 2o IPrX TBuX 3o CHM 201 Dang 2 Relative rate 30 1 0.02 0.004 Relative stabilities of alkyl halides (Fastest) Methyl > 1o > 2o > 3o (NR) SN2 E vs. POR diagram *if LG is too sterically hindered (3o) - T.S is high energy - Ea is high - reaction is too slow (N/R) SN2 summary 1 – step mechanism Backside attack inversion of stereochemistry requires an unhindered LG and good Nu: (-charge or NH3) Rate (RX) Methyl > 1o > 2o > 3o (slowest or NR) CHM 201 Dang 3 E.g Predict the major product and show the mechanism CHM 201 Dang 4 SN1 Substitution Nucleophilic Unimolecular (9.4) Could this be an SN2 ?........................ SN1 mechanism (2 key steps but usually 3 steps) (9.4) 1. Loss of LG 2. Addition of Nu: CHM 201 Dang 5 SN1 Kinetic Rate = k [tBuCl] Rate determining step involves E+ only Rate is independent of [Nu:] A more stable carbocation will be formed faster Rate of SN1: benzylic/allylic > 3o > 2o >> 1o, methyl Stereochemistry of SN1 SN1 result in racemization SN1 Summary Stepwise mechanism via carbocation More stable carbocation, faster reaction Racemization occurs Requires no strong Nu (usually with solvent: H2O or ROH) CHM 201 Dang 6 E.g Predict the major product(s) and show the mechanism E.g Predict all possible products for the following reactions and identify whether which approach (SN1 or SN2) would be possible for the reactions to occur. CHM 201 Dang 7