Answer
advertisement

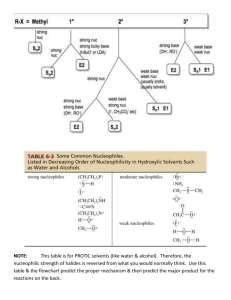
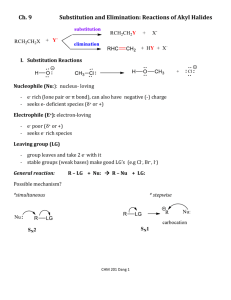
Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) 533562652 1 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) Single Jeopardy Answers 1. SN2 Rxns Answer 50 SN2 reactions proceed best with this type of substrate. 100 SN2 reactions are much faster in these types of solvents. 150 SN2 reactions are only possible with carbons that have this type of hybridization. 200 SN2 reactions are faster when this component of the reaction mixture is small. 250 SN2 substrates undergo this unique phenomenon during their transition states. 2. SN1 Rxns Pts Answer 50 SN1 reactions are fastest with this type of substrate. 100 SN1 reactions form these as part of their mechanism. 150 SN1 reactions are faster in this type of solvent. 200 SN1 reactions are often undesirable because they destroy this desirable quality in the starting material. 250 This is the term used to describe SN1 product mixtures, in which both enantiomers of the product molecule are present. Questions Questions 3. E2 Rxns Pts Answer Questions 50 The rate of E2 is highest when a nucleophile has this quality. 100 E2 reactions are characterized by this type of reaction order. 150 This type of carbon hybridization is found in the product molecules of E2 reactions. 200 Mechanisms of the type found in E2 reactions, in which the entire process happens in one step, are said to be this. 250 E2 reactions normally, but not always, depend on the following stereochemical relationship. 533562652 2 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) 4. E1 Rxns Pts Answer Questions 50 E1 reactions convert alkyl halides to this functional group. 100 The rate determining step in E1 reactions is the same as that in this type of reaction. 150 E1 reactions are characterized by this type of reaction order. 200 The rate of E1 is highest when the solvent present has this quality. 250 The nature of this component has no effect on the rate of E1 reactions. 5. Between Us Pts Answer 50 Increasing the concentration of a strong base in the reaction mixture will cause the mechanism to shift from an E1 to this type of reaction. 100 Use a polar protic solvent, a good leaving group, and limit the basicity of the nucleophile to shift the product mixture to this type of product rather than an SN2. 150 Big, bulky bases are likely to make a reaction proceed by this mechanism rather than an SN2. 200 A tertiary substrate with beta carbon branching in the presence of a weak, bulky nucleophile should favor this mechanism rather than SN1. 250 This is the most important predictor of whether a reaction proceeds primarily by SN1 or SN2. 6. Solvents Pts Answer 50 Polar protic solvents are necessary for E1 and SN1 reactions because they facilitate this initial step. 100 A change in solvent can alter this quality of the halides. 150 These two types of substrates can not react with the solvents in which they are placed (i.e. they do not undergo solvolysis reactions). 200 Acetone, DMF, and DMSO are solvents which favor this type of reaction. 250 These types of solvents are very poor ionizers. 533562652 3 Questions Questions 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) Double Jeopardy Answers 1. Solvents Pts Answer Questions 100 An example of a common polar protic solvent is _____. 200 Polar protic solvents are necessary for E1 and SN1 reactions because they facilitate the initial step. 300 A change in solvent can alter this quality of the halides. 400 The absence of a solvent means these 2 types of reactions do not occur in the gas phase. 500 An example of solvent in which an SN1 reaction will never occur is ______. 2. Why N.R.? Pts Answer 100 Questions Cl CH3OH CH3CH2 200 CH3CH2 OCH3 CH3CH2 NaBr C OCH3 CH3CH2 300 CH3CH2 CH3OH C Br CH3CH2 NaBr CH3 CN CH3 Br CH3OH 400 Me4N Br OTs 500 Br Br hexane + HC CH CH + 533562652 4 HBr 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) 3. Rxn Types Pts 100 200 300 400 500 Answer Is an example of this type of reaction, in which a substrate reacts with its solvent. When this type of reaction is exothermic, it will proceed before any others. The stereochemical consequence of this type of reaction is likely to be a racemic mixture. This type of reaction results is stereochemical inversion. This type of reaction can occur with primary, secondary, and tertiary substrates. Questions 4. Carbocations Pts Answer 100 When you see a carbocation, the three things you must immediately consider. 200 Writing this type of carbocation on an exam is suicide. 300 Of secondary, allylic, and benzylic substrates, this substrate forms the most energectically favorable carbocation. 400 Saturated carbocations are stabilized by this phenomenon. 500 Questions The reason the first carbocation is lower in E than the other two. 533562652 5 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) 5. Well, Poor, N.R. Pts Answer 100 CH3 Questions H3C C CH2CH2CH2CH2OH CH3SO2O CH3NO2 O 200 Br OH NaOH O 300 I SCH3 NaSCH3 CH3OH 400 NaOEt Cl 500 EtOH CH3I O O I 533562652 6 2/16/2016 Organic Chemistry, Game 17: Substitution and Elimination Reactions (based on Volhardt and Schore, 3rd edition, Chapter 7) 6. Kinetics Pts Answer 100 Questions The figure is a reaction coordinate diagram that belongs to this type of reaction. 200 The figure is a reaction coordinate diagram that belongs to this type of reaction. 300 The SN2, E2, SN1, and E1 reactions undergo this type of control, which means that, when a reaction can go by more than one mechanism, the major product forms from the mechanism whose transition state energy is the lowest. 400 Reactions that follow this kinetic order, in which the concentration of only one reagent determines the entire rate law, are said to be this. 500 A reaction with a transition state energy higher than this amount is unfavorable under normally available laboratory conditions. 533562652 7 2/16/2016