Section 1 - Viruses
advertisement

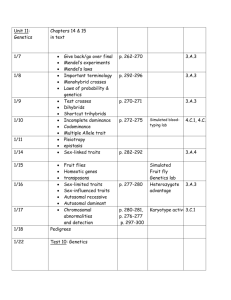
Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 1 - Viruses - Pages 48 – 55 What is a Virus? 1. Define the following terms: virus _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ parasite _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ host _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Viruses are considered to be nonliving because: a. ______________________________________ b. ______________________________________ c. ______________________________________ d. ______________________________________ 3. How are viruses similar to living organisms? _________________________________ 4. Besides humans what are some other organisms that viruses can infect? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 5. When you are sick with a cold, are you the host or the parasite? __________________ Naming a Virus 6. How are viruses named? a. _____________________ b. _____________________ c. _____________________ d. _____________________ Example of virus for each _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 1 - Viruses - Pages 48 – 55 (continued) Shapes and Sizes of Viruses 7. Define Bacteriophage: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 8. List four different shapes of viruses: a. _______________________________ b. _______________________________ c. _______________________________ d. _______________________________ 9. Viruses are ________________than cells and are measured in _________________. Structure of Viruses 10. Label the two basic parts of the virus: 11. The function of A: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 12. The function of B: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 13. Why does a virus only invade a specific type of cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 1 - Viruses - Pages 48 – 55 (continued) How Viruses Multiply 14. How do viruses multiply? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 15. Two types of viruses: a.____________________ infects a cell immediately b. ____________________ becomes part of the cell's genetic material and remains silent for a while. These types of viruses can become suddenly active. 16. Give and example of a hidden virus ______________________. Viruses and the Living World 17. Most viruses are harmful but some are useful. Give an example of each: Harmful: ______________________________________________________________ Helpful:_______________________________________________________________ Thinking Critically: 18. Scientist Hypothesize that viruses could not have existed on Earth before living organisms, such as bacteria, appeared. Use what you have learned about viruses to support this hypothesis. Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 2 - Bacteria - Pages 56 – 65 The Bacterial Cell 1. Bacterial cells were first discovered in the late 1600's by Anton van Leewenhoek. How did he discover them?___________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Bacterial cells are considered ____________________ because they lack a nucleus. 3. Where is the genetic material located in a bacterial cell? ________________________ 4. What are the three basic shapes of a bacterial cell? a. __________________________ b. __________________________ c. __________________________ 5. Describe these basic structures of the bacterial cell then label on the diagram below: a. cell wall ____________________________________________________________ b. cell membrane _______________________________________________________ c. cytoplasm _________________________________________________________ d. ribosomes___________________________________________________________ e. genetic material ______________________________________________________ f. flagellum____________________________________________________________ Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 2 - Bacteria - Pages 56 – 65 (continued) Two Kingdoms of Bacteria 6. List three characteristics of Archaebacteria: a. ___________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________ c. ___________________________________________ 7. List three characteristics of Eubacteria: a. ___________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________ c. ___________________________________________ 8. Why are Eubacteria and Archaebacteria placed in separate kingdoms? _____________________________________________________________________ Reproduction in Bacteria Define the following terms: 9. asexual reproduction _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 10. binary fission _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 11. sexual reproduction: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 12. conjugation: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 13. Bacterial reproduction can result in two different types of offspring: a. _____________________ produces offspring genetically identical to the parents. b. _____________________ produces offspring genetically different than the parents. Chapter 2 Notes: Viruses and Bacteria November 2010 Section 2 - Bacteria - Pages 56 – 65 (continued) Survival Needs 14. Bacterial cells can obtain food from a variety of sources. a. _________________ bacteria that make their own food. b. __________________bacteria that obtain food by consuming other autotrophs or heterotrophs. 15. The process of breaking down food to obtain energy is called ___________________. 16. endospore: _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 17. Why do bacterial cells form endospores? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Bacteria and the Living World: 18. List five positive roles of bacteria in today's society: a. _____________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________ c. _____________________________________________ d. _____________________________________________ e. _____________________________________________ Thinking Critically: 19. Why do you think different types of bacteria are shaped differently?