Chapter 2: Living Things in Ecosystems Name: 2.2 How Species
advertisement

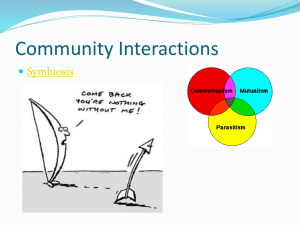
Chapter 2: Living Things in Ecosystems Name: __________________________________ 2.2 How Species Interact with each other Ecosystems are made up of biotic and abiotic components The biotic components – organisms – affect one another The five major types of interactions are: predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism and commensalism Predation In predation, one organism kills and eats another organism The organism that is eaten is called the prey The organism doing the eating is called the predator Examples: lions feeding on zebras; cougars eating deer; snakes consuming mice; birds eating insects; blue whale feeding on tiny krill Predators tend to feed on young and weak individuals; as prey decline, predators either feed on other organisms or die Competition Competition occurs when two or more organisms of the same or different species attempt to use the same limited resource Examples: Lions and hyenas fighting over the same carcass; two plants fighting for a limited amount of sunlight Species can fight over the same resource and never see one another, ex: one insect feeding on a certain plant during the day and another who feeds on that same plant during the night; because they use the same food source, the two species are competitors Parasitism Parasites are organisms that live in or on another organism and feed on it without immediately killing it; parasitism is the relationship between the parasite and its host Examples: ticks, fleas, tapeworms, viruses, blood-sucking leeches, mistletoe Organism the parasite takes nourishment from is known as the host The difference between parasitism and competition is that the parasite does not immediately kill their host; it lives in or on the host most of its life; and the parasite weakens its host making it more vulnerable for predators Mutualism Mutualism is the cooperative partnership between two species in which both species benefit Examples: clownfish and the sea anemone; bacteria in your intestines; acacia tree covered in ants in Central America (when the ants were removed, the tree suffered) Commensalism Commensalism is the rarest and strangest type of species interaction It is the relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither harmed or helped Example: sharks and remoras