File
advertisement

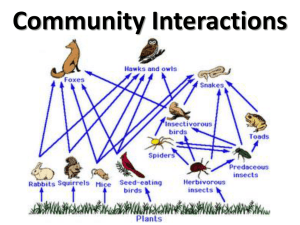
Ecosystems and communities Weather and Climate Weather Day-to-Day variations in conditions Climate Year-after-Year Factors patterns of temperature and precipitation that affect CLIMATE? The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Water Vapor, CFCs Why is this important? Where do Organisms Live? Tolerance: the range of conditions under which an organism can survive and reproduce. Habitat: the general place where an organism lives Niche: An organism’s role in an ecosystem, including how it interacts with biotic and abiotic factors, plus the resources it uses Competition in Ecosystems Definition: When organisms attempt to use the same resource Intraspecific – between members of the same species Interspecific – between members of different species Competitive Exclusion Principle No two species can occupy exactly the same niche at the same time If two species attempt to occupy the same niche at the same time, one will lose out Predation and Herbivory Predation: One animal (predator) captures and feed on another animal (prey) Herbivory: One animal (herbivore) feeds on primary producers (i.e. plants) *BOTH affect the population size and distribution of what is eaten What is going on here?? Keystone Species Definition: A species that can cause dramatic changes in ecosystem and/or community structure Symbiosis Definition: Relationship in which 2 organisms live closely together Types: Mutualism, Parasitism, Commensalism Mutualism: Both organisms benefit Parasitism: One organism benefits and the other is harmed Commensalism: One organism benefits and the other is unaffected Is it Mutualism, Parasitism, or Commensalism? Clownfish and Sea Anemone Whale and Barnacles Tick and Human Caterpillar and Wasp (larvae) Ants and Acacia Populations Describing Populations Geographic Range: Area inhabited by population Density: Number of individuals per unit area Distribution: How individuals are spaced within a population Random Uniform Clumped Growth Rate: population numbers changing Age Structure: Number of males and females of each age Why is this important? Random, Uniform, or Clumped?? Population Growth Rate What factors affect growth rate?? Birthrate Death rate Immigration Emigration Exponential Growth Definition: The larger a population gets, the faster it grows When does this occur? Under ideal conditions, unlimited resources Logistic Growth Definition: When a population’s growth slows and then stops, following a period of exponential growth. Carrying Capacity: The maximum number of individuals of a species that a particular environment can support Limiting Factors Definition: Factors that control the growth of a population and determine the carrying capacity Density-Dependent Factors: Affect populations significantly only when population reaches a certain size Density-Independent Factors: Affect all populations in similar ways, regardless of size and density