ELECTROPHORESIS
advertisement

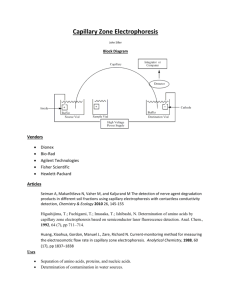
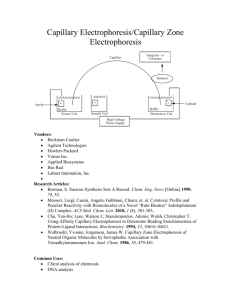
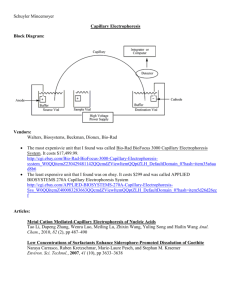
ELECTROPHORESIS = an analytical method based on a movement of charged particles because of an external electric field electrophoretic mobility - mobility of a substance (i.e. how quickly an ion moves in an electric field) - it depends on the: a) size, shape and charge of the substance b) given applied voltage anion - negatively charged ion, it moves to the anode (+) cation - positively charged ion, it moves to the catode (-) amphoteric - a substance that can have a positive, zero, or negative charge, depending on conditions (e.g. proteins) classification of electrophoresis 1) free-boundary e. - separation is carried out entirely in a liquid phase, i.e. no support is used (capillary electrophoresis) 2) e. in a supporting medium - paper, gel (agarose, polyacrylamide) - it can be done horizontally or vertically effects of electrophoretic parameters on separation pH - changes charge of analyte and hence its mobility - can affect structure of analyte (denaturing, dissociating) ionic strength - changes voltage or current: increased ionic strength usually reduces migration velocity and increases heating temperature - overheating can denaturate (precipitate) proteins - lower t. reduce diffusion but also reduce migration velocity, no effect on resolution current - too high current causes overheating voltage - migration velocity is proportional to voltage time - resolution (separation of bands) increases linearly with time, but dilution of bands (diffusion) increases with the square root of time medium - major factors are endosmosis and pore-size effects, which affect migration velocities process of electrophoresis 1) sample application 2) adjustment of voltage or current (!!direct current !!) (gel-electrophoresis about 70 volts, capillary electrophoresis about 20,000 volts) 3) separation time: minutes (e.g. gel-electrophoresis of serum proteins 30 min.) 4) electrophoresis in supporting medium: fixation, staining 5) evaluation: * qualitative (standards) * quantitative (densitometry) application examples: * separation of serum proteins, isoenzymes, nucleic acids * imunoelectrophoresis (immunoglobulins)