TRAIT - SemOneAPBioFinalExamReview
advertisement

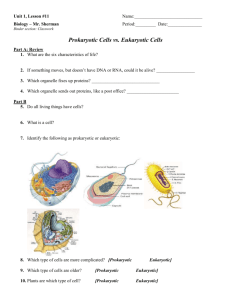
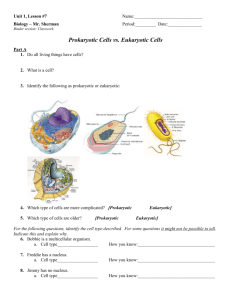
TRAIT Method of reproduction? VIRUS Viruses need the host cell in order to reproduce Glycoproteins on the viral envelope of animal viruses promotes entry into the host Phages reproduce either through the lytic or lysogenic cycle Type of nucleic acid? Contains either DNA or RNA, but never both Usually RNA Can be single-stranded or doublestranded Outer layer? Capsid (protein shell) determines the shape of the virus, and protects the viral genome Some viruses have viral envelopes, (may be derived from host cell membrane); helps facilitate entry into host cell; glycoproteins from virus, phospholipids from host Independent CANNOT EXIST ON ITS OWN existence? Lacks ability to make proteins, reproduce, store/generate energy Needs host cell Ability to generate Cannot store energy (ATP) own energy? Must derive energy from host cell No metabolic functions either Size? Much smaller than prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Tiniest are only 20 nm in diameter, which is smaller than a ribosome! Can they make their own proteins? CANNOT SYNTHESIZE OWN PROTEINS! Lacks ribosomes! Uses ribosomes of host cell to translate viral messenger RNA into viral proteins CELL Eukaryotic cells go through the cell cycle, which includes mitosis, cytokinesis, etc. Prokaryotic cells go through a much simpler process, binary fission Both generate identical daughter cells CAN REPRODUCE ON ITS OWN DNA Phospholipid bilayer with proteins makes up the plasma membrane Plant cells and prokaryotic cells also have cell walls made of cellulose Prokaryotic cells may have a capsule (jellylike coating) on the outside Can exist as one cell; for example, Paramecium Cellular respiration! ATP! Able to harvest chemical energy Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, but still much bigger than viruses Diameters range from 1-100 micrometers Ribosomes used for protein synthesis