1930`s Research Paper and oral presentation
advertisement

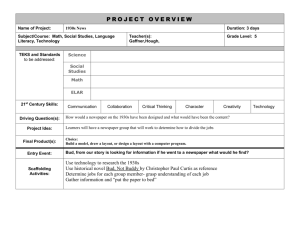
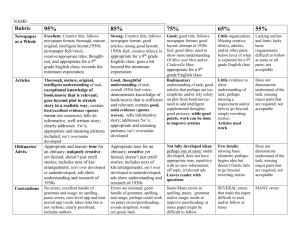
The 1930s Research Oral and News Article Introduction of Setting in To Kill a Mockingbird Your task is to research a particular area of American cultural history in the 1930s in order to give some background to the book To Kill a Mockingbird. You have two library lessons to research your topic before completing two graded tasks: o Prepare a 200-300 word news article on your chosen topic. o Present a 3min informative oral presentation to the class on your topic. You must use at least three sources of information and one of these must be a print resource (book, encyclopaedia, newspaper article). All information needs to be written in your own words. Do not cut and paste from the internet. You will be assessed on the inclusion of a bibliography according to the requirements written in your diary. Possible topics: Most topics relate to the United States in the 1930s. Women of the 1930s Description/details about traditional "Southern Belles" Fashion, careers, family roles, taboos for women, the work place, wages Gertrude Stein, Mrs. Wallis Simpson, Margaret Mitchell, Jane Addams, Pearl S .Buck, Amelia Earhart Education in the 1930s Educational Reforms: John Dewey - "Experience and Education" Level of education - State Laws Colleges and Agricultural colleges, trade schools Literacy The Headlines of the 1930s: What and Who Made the News Sports, disasters, "big" events, 21st amendment. Science/Technology/ Innovation during 1930s President Hoover Television, radio, President Roosevelt’s "New Deal," World’s Fair (1933) social security U.S. Nobel Prize Wall Street winners Statistics: population, wages and Glenn Curtiss, salaries, costs of home, food, cars, Sigmund Freud, rent T.A. Edison, Thomas Hunt Morgan Golden Gate Bridge, Boulder Dam Economic Concerns of the 1930s Status of African -Americans Jim Crow laws, voting rights, civil rights, education, occupations in North and South Discrimination, treatment by white people. Housing, neighbourhoods W.B. Dubois, George Washington Carver, Booker T. Washington. Marian Anderson, Langston Hughes, Zora Neale Hurston, Richard Wright, Bessie Smith, Lena Horn Political Concerns of the 1930s International Relations Relationships with other world leaders League of Nations Hitler, Churchill, Stalin, MacArthur 1950s-1960s: Civil Rights Movement Rosa Parkes Martin Luther King Sit-ins March on Washington etc The 1930s: News Article Student Checklist and Evaluation Use the Checklist column during and after writing your newspaper article to ensure you have considered each of the specific requirements and expectations for the task. Use the Evaluation columns for peer and/or self assessment, to evaluate areas where your article can be revised and improved prior to submission for graded assessment. Your teacher will consider these same items in determining the grade for your final finished piece. Name: ____________________________ Checklist Check Evidence of research Detailed notes Bibliography: at least 3 sources listed (1 print resource) and formatted correctly as per information in diary. Content Headline: eye catching, interest-grabbing and relevant. Relevant information Synthesis of research: ability to incorporate information researched effectively into the article. Attention to a specific newspaper text type Photographs: relevant, add something to text of article or reinforce a key point. Structure Logical sequence of ideas/content. Adherence to a text type (e.g. standard news article, special feature, etc). Effective Orientation: Who/what/when/where Effective Conclusion Language and Presentation Fluent and clear Accurate Spelling Accurate Punctuation Sentence Structure Effective Paragraphing Presentation: well set out as a news article; composition of text and picture/s. Student Self or Peer Evaluation High Medium Low Not Evident The 1930s: Research Oral Graded Assessment The oral component of this assignment will be graded according to the criteria below: Content (40%) Evidence of research: e.g. bibliography, notes, speech draft as required by teacher. Quality of content: knowledge, relevance and coverage of the topic. Structure (20%) Structure of presentation: clear introduction, organisation of ideas and conclusion. Delivery (40%) Quality of verbal aspects of presentation: voice pitch, expression, language, pace, tone, fluency, volume. Quality of non-verbal aspects of presentation: eye contact, stance, body language, use of visual aids, etc. Level of preparedness: fluency, timing and use of cue cards.