FIRST GRADE MATH CURRICULUM
advertisement

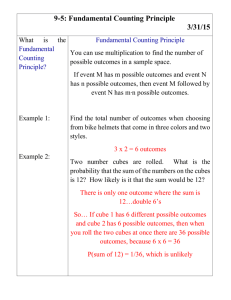
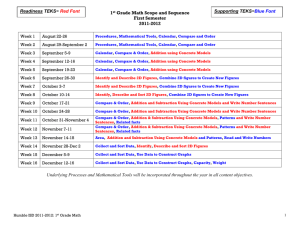
FIRST GRADE MATH CURRICULUM The primary focus of Math in the Archdiocese of Kansas City in Kansas is to promote in our students their problem solving abilities, which are among God’s many gifts. Standard 1: Number and Computation The student will: 1. ◊Read, write, represent, and sequence numbers to 100 using concrete objects. 2. Identify place value of ones, tens, and hundreds. 3. Read and write 0-100 in numerical form. 4. Define positions using ordinal terms to ten. (Peter was the first pope). 5. Recognize and determine even and odd numbers 1-30. 6. Write in words the numbers 0-10. 7. Solve addition problems to the sum of 20 horizontally and vertically. 8. Solve subtraction problems to the difference of 20 horizontally and vertically. 9. Memorize addition and subtraction facts to ten. 10. Use repeated addition with whole numbers (multiplication) e.g. 5+5+5=15 (nickels). 11. Use repeated subtraction with whole numbers (division) e.g. 9-3-3-3 with none left over or 9-2-2-2-2. 12. Use two-digit addition without regrouping or renaming through 99. 13. Subtract 2 digits without regrouping. 14. Use the concepts of these properties: a. Commutative 3+2=2+3 b. Zero property 4+0=4 15. Separate whole figures into equal parts. 16. Identify and write fractions ½, 1/3, ¼, and whole. 17. Identify and count like coins to one dollar. 18. Count mixed coins to fifty cents. 19. ◊Identify and state the value of coins and currency $1, $5, and $10. 20. Use estimation techniques to find whole numbers 0-100. 21. Use skip counting with 2’s, 5’s, and 10’s to 100. 22. ▲Solve real-world one-step addition or subtraction problems with various groupings of two-digit numbers without regrouping. (religion outcome: family members. Create realworld problems about family) 23. ◊Compare and order numbers 0 through 100 and fractions with like denominators (halves and fourths) using concrete objects. Standard 2: Algebra The student will: 1. Recognize patterns found in Church. 2. Identify, continue, and create a pattern in a variety of formats (numerical, visual, oral, written, kinesthetic, pictorial, tabular, graphical). 3. Use attributes to generate patterns (calendars, geometric shapes, money, time, parents/brothers/sisters as attributes). 4. Explain and use symbols to represent unknown numbers to solve basic facts e.g. ▲ cubes = 2 cubes + 2 cubes. 5. Describe and compare two numbers as equal, less than, or greater than. 6. Plot whole numbers 0-100 on a number line. 7. ◊State numerical relationships 0-50 in both horizontal and vertical function table (inputoutput machine, T-table). 8. Know, explain, and use models to represent math concepts with concrete objects such as unifix cubes, place value mats, fraction strips, base 10 blocks, T-tables, geoboards, and number cubes. 9. ◊Know, explain, and use symbols to represent unknown whole numbers from 0 – 20. Standard 3: Geometry Teacher note: The term “geometry” comes from the Greek words meaning, “earth measure.” The process of learning to measure at the early grades focuses on what property (length, width, height) is to be measured and to make comparisons. The student will: 1. Recognize geometric shapes in the Church. 2. ◊Recognize solids (sphere, cone, cube, cylinder, pyramid, rectangular prism). 3. Use geometric terms: sides and corners, open and closed figures, symmetrical and congruent. 4. Identify faces of a solid. 5. ◊Recognize attributes of circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, and ellipses. 6. Compare two measurements using these attributes: longer/shorter, taller/shorter, heavier/lighter, hotter/colder. 7. Select appropriate measuring tools (ruler, measuring cup, scale, etc.). 8. State the number of days in a week, and months in a year. 9. Develop foundation for spatial sense using concrete objects (behind, above, on, under, over, etc.). 10. Recognize that changing an object’s position does not change its name, shape, or size. 11. ◊Give and follow directions to move concrete objects from one location to another using appropriate vocabulary (slide/translation, flip/reflection, and turn/rotation). 12. Describe a whole number 0-100 as before or after another number. 13. Use a number line to model addition. 14. Measure and compare length and width using inches and feet. 15. Read and write time to the hour and half hour using analog and digital clocks. 16. Read, write, and position calendar dates. 17. ◊Demonstrate how several plane figures can be combined or separated to make a new shape. Standard 4: Data The student will: 1. Understand that God gave us a gift to interpret data. 2. Display and read data displays (simple graphs, pictographs, bar graphs, Venn diagram, and frequency table). 3. Recognize and predict outcomes as possible, impossible, or certain. 4. Identify minimum and maximum value in a set. 5. Determine the mode (most) after sorting by one attribute. (e.g. bowl of 7 red apples and 3 green apples. Mode is 7. 6. ◊Sort and record qualitative (non-numerical and numerical) data sets using one attribute. 7. ◊Recognize whether a simple event in an experiment or simulation including the use of concrete objects can have more than one outcome. ◊ Essential prerequisite skill ▲Assessed math indicator for KSDE