Hawaii Pacific University
advertisement

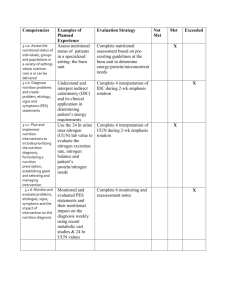
Hawaii Pacific University BIOL 1300 Nutrition: Eat Smarter Section ____ Semester and year, meeting times Instructor: Name, contact information and other relevant information about the instructor. Course description: This is a one semester introductory nutrition course designed to provide comprehensive nutrition information in a clear and concise manner by demonstrating how nutrition relates to the student’s health, including an assessment of the eating habits of each of the students. Students will learn how to evaluate information provided by government, media and advertising in order to make healthy choices, as well as to understand how these cultural forces shape diet and nutritional decisions at the local, national and international level. Course prerequisite: None General Education Requirement: This course is classified under the Values and Choices Theme and meets the requirement for a course in Values and Choices B: Social Choice. General Education Student Learning Outcomes and the Five Themes: HPU’s general education curriculum is focused around five themes. This course emphasizes the Values and Choices Theme and provides students with opportunities to achieve the following related general education student learning outcomes. In the course, students will: Understand and analyze the range of consequences that follow from a choice, policy, or course of action. A necessary step in bringing about the critical evaluation of one’s self and one’s personal life choices is the introduction of a spectrum of different health and nutritional choices. Students examine the consequences of their personal dietary choices—( e.g. What changes could you make in your diet to improve the health of your GI tract? What changes can you make in your diet to more closely meet carbohydrate and sugar recommendations? What changes can you make in your diet to more closely meet fat and cholesterol recommendations?)-- and of national policies such as changes to school lunch programs or nutritional labeling requirements. Recognize and value multiple perspectives and develop skills for mediating among conflicting claims. Students will be encouraged to read sources with differing opinions and philosophies and to cultivate healthy degrees of skepticism regarding information that is encountered. They will develop an appreciation that truth can be obscured by personal, political or commercial interests, and that the interests of those who are providing nutritional information may determine the content. Articulate various ethical and moral questions and explore their own system of values through examination and analysis of examples drawn from . . . current events and controversies. The food industry is huge, global and often controlled by companies that either own print or broadcast media. Politics of trade, regulation, and advertising influence what people choose to eat. This course is aimed at helping student develop an understanding of global issues that impact them or on which they may have an impact. One aim is to develop the ability to critically evaluate his/her own personal life choices in this light, thereby enabling a new perspective from which they may be able to make better, more informed decisions both as a citizen and as a consumer. The course also addresses the Global Systems Theme by providing students with opportunities to achieve the following related general education student learning outcomes: Students will utilize various systems approaches or theories to comprehend natural global processes. Human nutrition is a global issue that affects individuals, communities, countries and the planet as a whole. Furthermore this is a biology course which examines the role of nutrition in maintaining proper functioning of human body systems. For instance, students will learn to describe the process of digestion and the function of enzymes, vitamins, minerals, electrolytes and so on. Note: Purple text shows places where specific course information must be filled in. Red text provides explanatory notes to the instructor which should be deleted before using the syllabus. Blue explanations above may be rephrased by the individual instructor to reflect the specific approach in that section. Course-specific outcomes below are an example and may also be rephrased or modified by the instructor. Course-Specific Student Learning Outcomes for BIOL 1300 Nutrition: Eat Smarter By the end of the course, students will be able to: Discuss why daily nutrition choices are important to health. Identify classes of nutrients essential for health and how you choose foods containing these nutrients. Differentiate between appetite and hunger, describing what stimulate each. Describe how food passes through the gastrointestinal tract and the interaction of organs and enzymes in breaking down the food. Describe the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates, which is a better choice? Identify foods that are good sources of carbohydrate, proteins, and/or fats; and how you choose foods containing these nutrients. Explain the functions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in our bodies. Compare the differences between fat- and water-soluble vitamins and their functions; and how you choose foods containing these nutrients. Recall the vitamins that have antioxidant properties. Describe what a mineral is, how they are classified and describe their functions. Describe how electrolytes function. Identify physiological changes that occur with aging and describe how these changes affect the nutrient needs of older adults Describe the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, and discuss how these guidelines can be used to design a healthful diet. Describe how www.MyPyramid.gov, food labels and use the Nutrition Facts Panel can be used to design a healthful diet. Identify the potential health risks associated with diets high in simple sugars. Define the recommended dietary intakes for total fat, saturated fat, and the two essential fatty acids. Calculate his or her recommended dietary allowance for protein, carbohydrates and fats. List the deficiency disorders of vitamins. Describe how our body maintains its fluid balance. Identify three problems with fluid imbalances. Identify and discuss the three components of energy expenditure. List health benefits of being physically active on a regular basis and compare and contrast the concepts of physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness. Explain why maintaining a nutritious diet is important for prospective parents even before conception, as well as after. Compare and contrast the nutrient requirements of pregnant and lactating women. Describe strategies for preventing food-borne illness at home, while eating out, and when traveling to other countries. Describe malnutrition and nutrient deficiencies, as well as what factors contribute to them. Identify the potential health risks associated with fad diets. Define what is meant by a healthful weight. Describe factors that influence our body weight. List at least three methods that can be used to assess your body composition or risk for overweight. Identify two beneficial and two detrimental effects of alcohol. Discuss reasons why food safety is an important concern. Analyze and comment on current debates or controversies related to nutrition (For example, school lunch reform, eating disorders, food advertising, government regulation of transfats or nutritional labeling, genetically modified food, benefits and risks of supplements; ethics of eating fast food etc.) Recognize sources of reliable and accurate nutrition information. Be able to distinguish between reliable and unreliable sources of information (especially on the internet.) For the rest of these required syllabus items see the details in the faculty handbook. Delete this note once the syllabus is complete. For online courses there are some additional requirements given at this link. Texts List textbooks with ISBN’s and include this language as well All textbook information (pricing, ISBN #, and e-books) for this course can be found on the HPU Bookstore website: hpu.edu/bookstore. If you have any questions regarding textbooks, please contact the HPU Bookstore at: Phone: 808-544-9347 Or e-mail: jyokota@hpu.edu mmiyahira@hpu.edu Assignments and mode of evaluation Summary of important dates and deadlines (if the schedule is a separate document and due dates are not given with the description of the assignments). Class rules and policies (including regarding attendance, late work and academic dishonesty) Schedule of events (may be attached separately)