Grammar tips for graduation report
advertisement

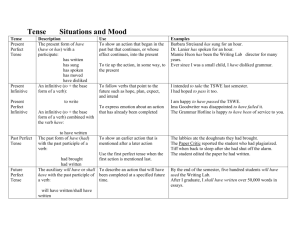
Grammar tips for graduation report Tenses Present Simple – form and use One of the most common tenses in English. Third person singular has ending –s, questions and negatives are formed with auxiliary verb do, does. It is used to express habits, facts that are always true and states (facts which stay the same for a long time) (timetable future) Examples: He goes to work by car. / My daughter has brown eyes. / I live in a flat. Present Continuous Form: present simple of the verb to be + verb + ending –ing; questions – inversion Use: action that is happening now, temporary activity, future arrangement Examples: I'm revising English grammar at the moment. I'm living with my grandparents (temporary; my parents went somewhere for two weeks). I'm going to the cinema tomorrow. Past Simple Form: ending –ed or –d for all persons, questions and negatives with did Use: finished action in the past, actions which follow each other in a story, past habits Examples: Yesterday I came late to school. It wasn't my fault. I collected model cars when I was a child. Past Continuous Form: past simple of the verb to be + verb + ending –ing, Q & N - inversion Use: longer, background activities, something that was going on in the past, unfinished past actions etc. Examples: When I came to the party people were dancing, some of them were drinking. She was wearing a red dress… When I was crossing the street I stepped on a banana skin and fell heavily. Present perfect Form: have/has + p.p.; Q & N – inversion Use: it means “before now” and it does not express when the action happened. (action which began in the past and still continues, experience and present result) Examples: I have been teaching English for 10 years. I have travelled a lot. I can't give you a lift because I have crashed my car (It's still being repared). Past perfect Form: had + p.p.; Q & N – inversion Use: Used to look back to a time in the past and refer to an action that happened “before then”. Example: When I came to the shop I realized that I had left my wallet at home. Future tenses Will + infinitive; Use: decision made at the moment of speaking, future fact or prediction Examples: I think it will be sunny tomorrow. Will you help me with these bags? Going to Use: intention that is thought about before the moment of speaking (plan) and when we can see the evidence that something is certain to happen. Example: I'm going to study medicine. What are you going to do with all that paint? / Watch out! You're going to fall! / Look at the clouds. It's going to rain. Passive Use: Passive sentences move the focus from the subject to the object of active sentence (because it is more important to us). Football is watched every day. Telephone was invented in the 19th century. Form: verb to be (in the same tense as the predicate) + p.p. Reported Speech Statements: When the reporting verb is in past tense, it is usual to move the verb “one tense back”. Example: "I'm going to redecorate my room". - She told me she was going to redecorate her room. Questions: The word order is the same as in the statement (no inversion, no do/does/did); and if the reported verb is in past tense, it is usual to move the verb “one tense back”. Example: "Why haven't you read this book?" She asked why I hadn't read that book. / "Are you hungry?" He wondered if I was hungry. Commands, requests, offers etc. They are formed with a verb + person + to/not to + infinitive. Eg. "Don't leave the window open!" She told me not to let the window open. Conditionals Zero conditional – for conditions that are always true (if+present, present) Eg. If you heat ice it melts. First conditional – for conditions that are possible to happen (if+present, will+infinitive) Eg. If you don't go away, I'll call the police. Second conditional – imaginary about the present, possible in theory, but not in practice (if+past, would+infinitive) Eg. If I were you, I wouldn't listen to him. Third conditional – imaginary about the past, impossible (if+past perfect, would + have + p.p.) Eg. If you had stopped on time, you wouldn't have crashed into that fence. Sentences with wish – I wish... the same as second and third conditional (unreal situation, therefore it goes one tense back). Eg. I wish I had someone to talk to (but I don't). Modal verbs of probability They are used to express the degrees of certainty about present and past. Different from other modal verbs expressing obligation (must, have to), ability (can) etc. Eg. She might be cooking dinner. It can't be true! Past tense is formed with perfect infinitive. I must have forgotten his number.