Examination of the Breast
advertisement

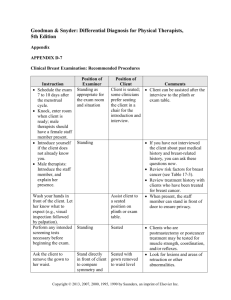
Examination of the Breast Inspection: Inspection is initially from the foot of the bed. Patient stripped to the waist. Patient sitting comfortably at 450 with arms by sides. Note size, symmetry, contour, colour, venous pattern and scarring. Nipples: note symmetry, eversion, flattening, and inversion. Ask the patient to raise arms above head. (?tethering of a mass to skin) Ask patient to press hands against hips. (?fixation of a mass to muscle) Abnormalities that may be seen: Lumps. Nipple retraction or deviation. Prominent veins. Oedema, with or without skin dimpling. Reddening, thickening or ulceration of the areola. Palpation: Patient lying on the couch with hands by sides, or arms above head. Use the palmar surface of the middle three fingers. Palpation of the Breast: Concentric: begin at the axilla, end at the nipple. Parallel: each half, from side-to-side, top-to-bottom. If a mass is palpated, again ask the patient to Raise arms above head, and assess for tethering to the skin Press hands firmly against the hips to assess for fixity to deep muscles (Pec. Major) Axillary tail: arms above head. Use thumb and forefinger. Palpation of the nipple: Hold gently between thumb and finger. Gently compress: to express any discharge. Palpation of the Lymph nodes: Axillary nodes: lying or sitting; apical, anterior, posterior, lateral chest wall, medial border of the humerus. Infraclavicular nodes. Supraclavicular nodes. Abnormal Palpation: Lumps: benign or malignant. Abscess: mastitis. Nipple and areola: blood stained discharge implies intraductal carcinoma. Retraction or distortion in malignancy. Red crusty scaling in Paget’s disease. Lymphadenopathy: can be seen in infection, malignancy, and fibrocystic disease. Complete the Examination: Palpate the liver (as per abdominal examination) for hepatomegaly secondary to metastasis. Ask the patient about bone-pain and inspect any sites for swelling, tenderness, deformity etc (bony metastasis) Bloods: FBC, U+E, LFT, Coag, G+S. Xrays: Chest/Any bones USS: to assess breast mass, also check liver for metastasis Refer: breast surgeon for FNAC or biopsy.