Quarterly Sequence
advertisement
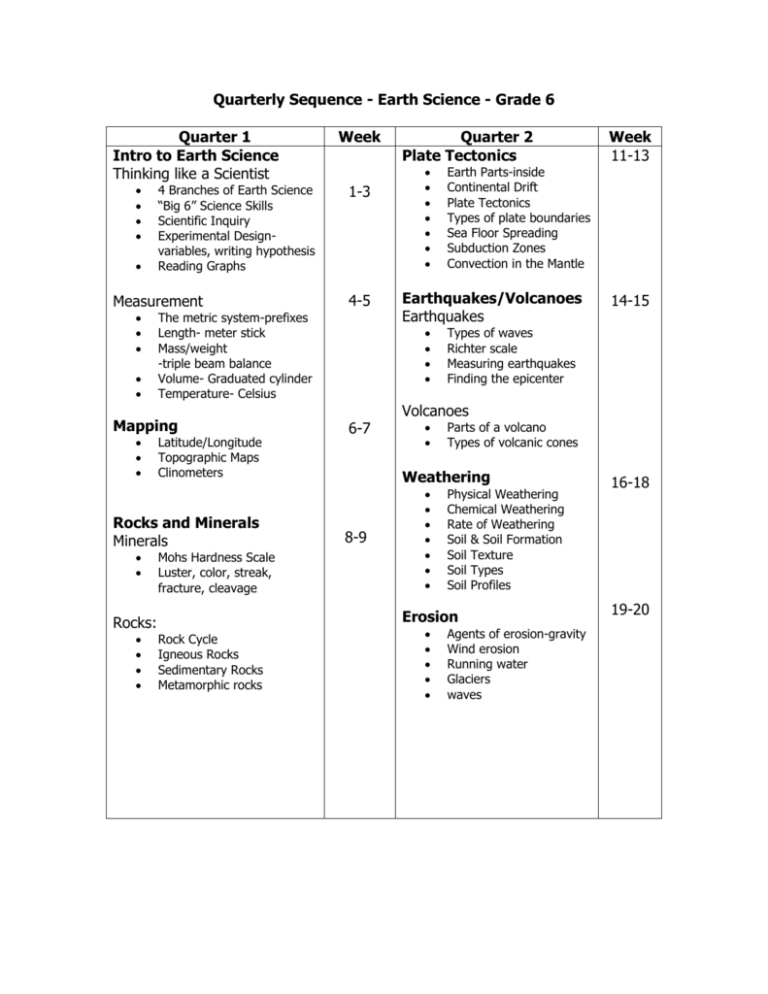
Quarterly Sequence - Earth Science - Grade 6 Quarter 1 Intro to Earth Science Thinking like a Scientist 4 Branches of Earth Science “Big 6” Science Skills Scientific Inquiry Experimental Designvariables, writing hypothesis Reading Graphs Measurement Latitude/Longitude Topographic Maps Clinometers Rocks and Minerals Minerals Mohs Hardness Scale Luster, color, streak, fracture, cleavage 4-5 Quarter 2 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes/Volcanoes Earthquakes 6-7 Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic rocks 14-15 Types of waves Richter scale Measuring earthquakes Finding the epicenter Volcanoes Parts of a volcano Types of volcanic cones Weathering 8-9 Week 11-13 Earth Parts-inside Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Types of plate boundaries Sea Floor Spreading Subduction Zones Convection in the Mantle Physical Weathering Chemical Weathering Rate of Weathering Soil & Soil Formation Soil Texture Soil Types Soil Profiles Erosion Rocks: 1-3 The metric system-prefixes Length- meter stick Mass/weight -triple beam balance Volume- Graduated cylinder Temperature- Celsius Mapping Week Agents of erosion-gravity Wind erosion Running water Glaciers waves 16-18 19-20 Quarter 3 Fossils mold, cast, imprint preservation Why study fossils? Relative age absolute age Geologic time scale Oceanography Water cycle Ground water Wells, springs, geysers Ocean floor Ocean Currents Ocean Waves Ocean sediments Ocean life/Coral reefs Weather Week 21-22 Air gasses Earth’s heat Atmosphere Humidity Dew point Air pressure Fronts/air masses Reading weather maps Quarter 4 ASTRONOMY Earth Movement 23-25 Rotation & Revolution Eclipses High & Low Tides Spring and Neap Tides Sun and Other Stars 26-30 Parts of the Sun H-R Diagram Relative/Actual Magnitude Life Span Solar System 31 Rotation & Revolution Perihelion & Aphelion Seasons- Solstice/Equinox Moon and Moon Motions Week Galaxies/Solar Systems Planets-Dwarf Planets Asteroids- Asteroid Belt Comets Meteors Review- Final 32-33 34-35 36-38 39-40