Text
advertisement

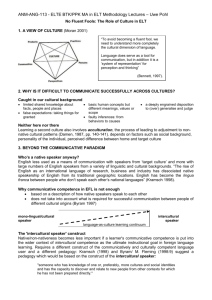
International Extension Curriculum: Strengthening Extension’s Capacity for International Engagement http://www2.ces.purdue.edu/iec/default.htm UNIT 2: INTRODUCTION OF THE SIX STAGE BENNETT MODEL OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE TIME FRAME: (90 MINUTES) Using the Bennett Model (30 minutes) Introduction to the Cross Model (30 minutes) Knowledge and Skills for a Diverse Workplace (15 minutes) Ten Fundamental Aspects of Intercultural Competence (15 minutes) WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT TO KNOW? It is important that individuals and organizations gain an understanding of how certain attitudes and behaviors impact relationships with others. OBJECTIVES/PURPOSE: 1. Individuals will explore and compare the six stage developmental Bennett and Cross cultural competence models. 2. Individuals will identify personal biases and gain an understanding of how these may affect their interactions with others. 3. Individuals will identify those areas that we as individuals need to work on and those we need to address in the workplace. HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: There are many developmental models of cultural competence in the field. The Bennett and the Cross models are two models that are commonly referred to and used to help individuals understand how attitudes and behaviors affect relationships with others. Comparison of both models will serve as a springboard for discussion and insight into dimensions of diversity. In this unit facilitator should introduce the Bennett model by using lecture (2) for the discussion. Next use lecture (3) to introduce the Cross model. Lead a discussion on the comparison of the two models. Then use exercise (4) for discussion and to draw conclusions followed by lecture (4). SUPPORTING MATERIALS: Introduction to a Cultural Competence Models Lecture 2 (30 minutes) – Using the Bennett Model Lecture 3 (30 minutes) -- The Cross Model Exercise 4 (15 minutes) – Knowledge and Skills for a Diverse Workplace Lecture 4 (15 minutes) – Ten Fundamental Aspects of Intercultural Competence Materials may be reproduced in electronic or print form for use in educational or training activities. Authors should be credited for their work in all instances. All other reproduction or use of materials requires prior electronic or written permission by contacting cameronselby@purdue.edu International Extension Curriculum: Strengthening Extension’s Capacity for International Engagement http://www2.ces.purdue.edu/iec/default.htm BIBLIOGRAPHY OF ADDITIONAL RESOURCES, if applicable: Anand, R. (2000). Teaching Skills and Cultural Competency: A Guide for Trainers. Fourth Edition. Washington, DC: NMCI Publications. Bennett, M. J. (1993) Towards Ethnorelativism: A developmental model of intercultural sensitivity. In R. M. Paige (Ed.) Education for the intercultural experience. Yarmouth, ME: Intercultural press. For futher information, contact Dr. Milton Bennett. The Intercultural Communication Institute, 8835 S.W. canyon Ln, Suite 238, Portland OR. 97225. Website: http://www.intercultural.org Cross, T. (1998, Fall). Services to minority populations: Cultural Competence continuum. Focal Point, 3. Materials may be reproduced in electronic or print form for use in educational or training activities. Authors should be credited for their work in all instances. All other reproduction or use of materials requires prior electronic or written permission by contacting cameronselby@purdue.edu