F3 optic SWB

F3 Optic Fibre Transmission – Student Work Book
1). (a) Explain what is meant by the term Refraction .
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Define refractive index in terms of:-
(i) the velocities of the waves in the different media.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d)
Calculate the velocity of light in water which has a refractive index of 1.33.
Light travels from air into this water. Calculate the angle of refraction for the following angles if incidence:-
(i) the angles of incidence and refraction.
30°
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii)
(iii)
50°
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
70°
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2). (a) A rod is made from glass with a refractive index of 1.5.
Calculate the critical angle in air.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) The glass rod is now placed in water of refractive index 1.33.
Calculate the critical angle for light passing through the glass rod when in water.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
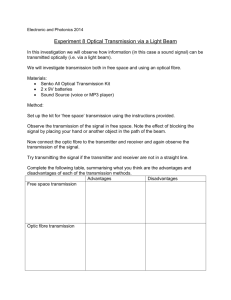
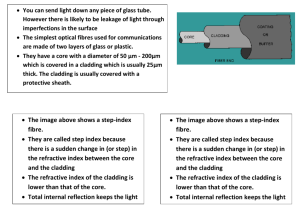
3). (a) Explain the principle of operation of an optical fibre.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Give two reasons why optical fibres make better communications media than copper cables.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
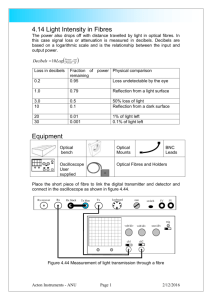
4). (a) Define the decibel in terms of input and output power to a system.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Two computers, 10km apart, are to be connected by optical fibre which has a loss of
0.5dB/km. The connectors on the ends of the optical fibre each have a loss of 3.5dB.
Calculate the total loss, in dB, for the signals traveling between the two computers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
5). (a) State and explain two reasons why a signal becomes attenuated as it passes along an optical fibre.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) As well as becoming attenuated, a signal will also become an optical fibre.
(i) Explain what is meant by the term noise.
'noisy' as it passes along
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) State and explain two sources of noise within an optical fibre communications system.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) The signal emerging from an optical fibre communications system is both attenuated and noisy.
(i) Explain why amplifying the signal is likely to have little effect on the quality of the signal.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Describe how the quality of the received signal can be improved.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
6). An optical fibre communications system has a maximum operating speed of 1Gb/s.
(a) (i) Explain the term 1Gb/s.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) A DVD contains 2.5GB of data in the form of a feature film.
Estimate how long it would take to transfer the contents of the DVD along this optical fibre system.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(iii) Explain what limits the maximum operating speed of an optical fibre.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) (i) A digital phone produces data at a rate of 8kB/s.
Describe the method by which multiple digital signals can be sent along a communications system.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Estimate how many different telephone signals could be sent along the 1Gb/s fibre each second.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
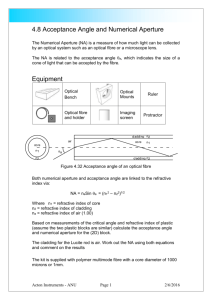
7). (a) A polymer optical fibre has a core of refractive index 1.489 and a cladding of refractive index 1.452. Calculate the critical angle for light passing through the optical fibre.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c)
Light enters the optical fibre from the air. What is the largest angle of incidence that a ray of light can enter the optical fibre and still pass along the fibre?
If an optical fibre is bent through too much, the light will hit the cladding at less than the critical angle and pass into the cladding. Estimate the maximum radius of curvature for the optical fibre to be bent for light to be able to pass along it if the core has a diameter of 1mm.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
F3 Optic Fibre Transmission – Student Work Book – Responses
1). (a) Change of direction of light resulting from the change in velocity as light passes from one medium to another.
(b) (i) refractive index
n
velocity in incident medium velocity in refracted medium
(ii) refractive index
n
sin i sin r
(c) 2.25 x 10
8 m/s
(d) (i)
22°
(ii) 35°
(iii) 44.8
2). (a) 41.8°
(b) First calculate the refractive index of water to glass = 1.15
Then calculate the critical angle using this refractive index = 62.46°
3). (a) TIR occurring at the boundary between the fibre and the cladding
(b) e.g. greater bandwidth, lighter, less attenuation, more secure etc
4). (a) attenuatio n = 10
log
Input
Output power power
( P
1
)
dB
(b) Sum the losses = 3.5 + 10 x 0.5 + 3.5 = 12dB
5). (a) Two from:- Absorption, Scattering, Radiation plus explanations
(b)
(c)
(i)
(ii)
(i)
Unwanted, random signals that are added to information signals
Two from:- Laser, fibre materials, photo detector plus explanations
Noise amplified as much as the signal => no improvement in S/N ratio
(ii) Use a Regenerator which reshapes the signal and restored the logic levels
6). (a) (i) 10
9
bits of data sent every second
(ii) 2.5GB = 20Gb
> takes 20s
(iii) Explanations of Material and Modal dispersion
(b) (i) Time Division Multiplexing plus explanation.
(ii) Each phone gives 64kb/s => 15625 concurrent signals.
7). (a)
Refractive index of cladding to core is 1.0255. => critical angle is 77.20°
(b)
Angle of refraction is 90° - 77.20° = 12.80°. => angle of incidence is 19.26°
(c) 40.24mm