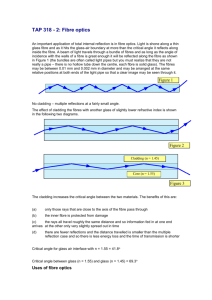
in the refractive index between the core and the
advertisement
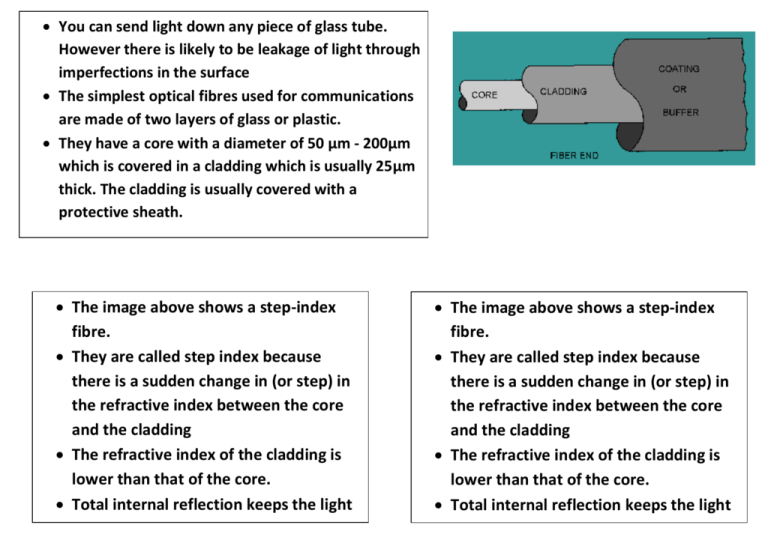
You can send light down any piece of glass tube. However there is likely to be leakage of light through imperfections in the surface The simplest optical fibres used for communications are made of two layers of glass or plastic. They have a core with a diameter of 50 µm - 200µm which is covered in a cladding which is usually 25µm thick. The cladding is usually covered with a protective sheath. The image above shows a step-index fibre. They are called step index because there is a sudden change in (or step) in the refractive index between the core and the cladding The refractive index of the cladding is lower than that of the core. Total internal reflection keeps the light rays inside the core. The image above shows a step-index fibre. They are called step index because there is a sudden change in (or step) in the refractive index between the core and the cladding The refractive index of the cladding is lower than that of the core. Total internal reflection keeps the light rays inside the core. Step index fibres have the disadvantage that light rays travel different distances along the fibre, depending on the angle that the light enters. As a result the parts of a signal transmitted at the same moment arrive spread out over time (see Fig 1A) A sharp square wave signal becomes degraded – this is called multimode or multipath distortion. Figure 2 a) a square wave signal as it enters a fibre b) a degraded signal as it emerges from a step index fibre Figure 1 A graded index fibre helps reduce multipath distortion by gradually reducing the refractive index from the core to the cladding (Fig 1B) This gradual change makes the rays of light follow a curved path All the rays of light arrive at the same time and this helps to reduce the distortion