The fleet manager of a major UK cosmetics company has to make a
advertisement
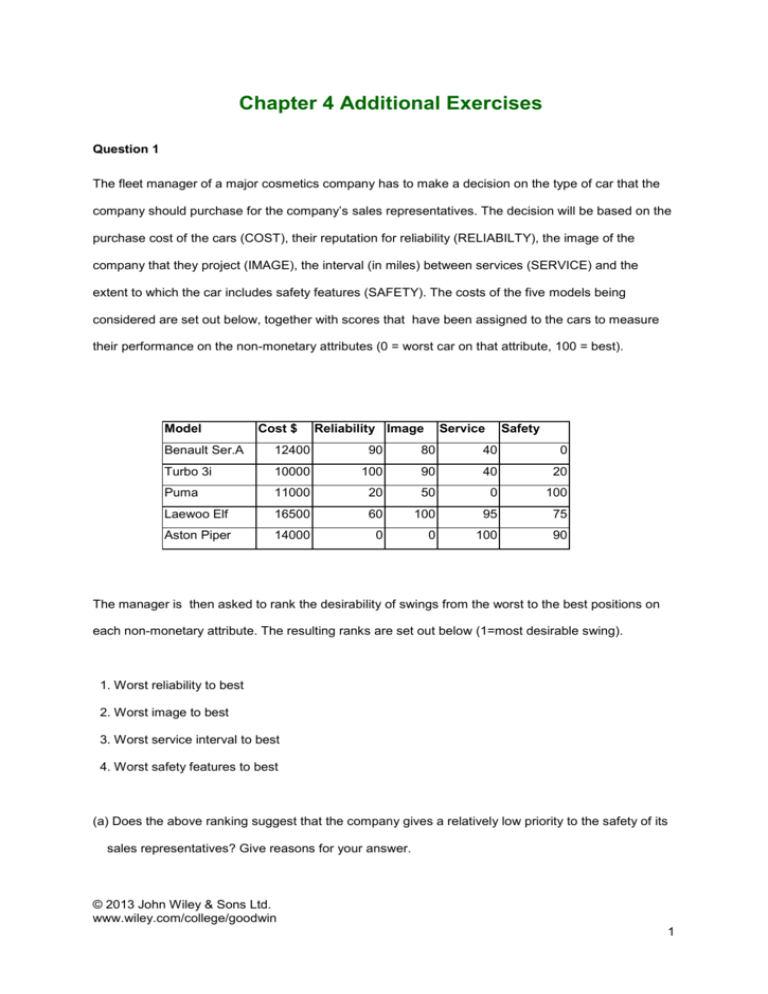
Chapter 4 Additional Exercises Question 1 The fleet manager of a major cosmetics company has to make a decision on the type of car that the company should purchase for the company’s sales representatives. The decision will be based on the purchase cost of the cars (COST), their reputation for reliability (RELIABILTY), the image of the company that they project (IMAGE), the interval (in miles) between services (SERVICE) and the extent to which the car includes safety features (SAFETY). The costs of the five models being considered are set out below, together with scores that have been assigned to the cars to measure their performance on the non-monetary attributes (0 = worst car on that attribute, 100 = best). Model Cost $ Reliability Image Service Safety Benault Ser.A 12400 90 80 40 0 Turbo 3i 10000 100 90 40 20 Puma 11000 20 50 0 100 Laewoo Elf 16500 60 100 95 75 Aston Piper 14000 0 0 100 90 The manager is then asked to rank the desirability of swings from the worst to the best positions on each non-monetary attribute. The resulting ranks are set out below (1=most desirable swing). 1. Worst reliability to best 2. Worst image to best 3. Worst service interval to best 4. Worst safety features to best (a) Does the above ranking suggest that the company gives a relatively low priority to the safety of its sales representatives? Give reasons for your answer. © 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.wiley.com/college/goodwin 1 (b) SMARTER was used to obtain the following aggregate scores for the non-monetary attributes. Model Aggregate score Benault Ser.A 74.41 Turbo 3i 83.59 Puma 30.27 Laewoo Elf 76.96 Aston Piper 20.27 Demonstrate and explain how the aggregate score for the Benault Series A model was obtained. (c) Identify the model or models that appear on the efficient frontier and interpret your result. (d) If the weights for the non-monetary attributes had been obtained using the rank-sum method what would these weights have been? © 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.wiley.com/college/goodwin 2 Question 2 A new road is to be built to bypass a busy country town and two possible routes, referred to as North and South, have been shortlisted. The choice between these routes will be based on three attributes: construction cost (Cost), environmental impact (Environment), and the average travel time it will take to drive along the new route (Time). The Analytic Hierarchy Process will be used to support the decision makers. When asked to compare the attributes, the decision makers agree on the following. -Environment is ‘weakly more important’ than Cost and ‘strongly more important’ than Time -Cost is ‘between weakly and strongly more important’ than Time. The decision makers’ relative preferences for the two routes are then compared on each attribute. -On Environment the South route is ‘strongly preferred’ to the North. -On Cost the North is ‘weakly preferred’ to the South -On Time the North is ‘very strongly preferred’ to the South. (a) Construct a hierarchy to represent the decision problem. (b) Use an appropriate software package, or the approximation method, to calculate the weights for each table in the hierarchy and hence determine which route should be chosen (c) Calculate the Inconsistency Ratio for the decision makers’ comparisons of the importance of the three attributes and interpret your result (use either your software or the approximation method here). © 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd. www.wiley.com/college/goodwin 3