Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences

Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
59-191
Lecture 11
In the presence of excess alcohol hemiacetal reacts further to form acetal. An alkoxyl group replaces the hydroxyl group of the hemiacetal. This looks like the formation of ether. The difference between the formation of an acetal and ordinary ether is that acetals form and break more readily. When two functional groups are very close to each other in a molecule each modifies the properties of the other in some way. The OR group makes the OH group attached to the same carbon much more reactive toward the splitting out of water with an alcohol. Hemiketals give identical kind of reaction, but the products are called ketals.
In a structural sense, an acetal is a 1,1 diether., but “1,1” does not refer to the numbering of the chain. The “1,1” means only two OR groups come to the same carbon. Hemikatals are also “1,1” diethers. The molecules of many carbohydrates, like sucrose, lactose and starch also have the 1,1 diether system.
Ordinary ethers, R-O-R
/
, do not break up in dilute acid or base, but acetals and ketals are stable only if they are kept out of contact of aqueous acids. In water acid catalyze the hydrolysis of acetals and ketals to their parent alcohols and aldehydes. In aqueous base, however the acetal (ketal) system is stable.
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS:
In carboxylic acids carbonyl carbon holds an OH group and either another C or a H atom.
Those with long straight alkane like chains are called fatty acids, because they are products of the digestion of butterfat, oliveoil, and similar fatty substances in the diet.
All carboxylic acids are weak acids. Both in basic solutions and in their salts carboxylic acids exist in their anionic form. In living cells and body fluids also mostly anionic form is found.
Carboxylic acids are polar compounds. They form strong hydrogen bond to each other.
The carbonyl group has planar geometry.
IUPAC RULES TO NAME CARBOXYLIC ACIDS:
The parent acid is that of the longest chain that includes carboxyl group.
To name the parent chain, change the name ending of the alkane having the same number of carbons from -e to –oic acid.
To number the chain of the parent acid, always give position 1 to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group.
To name the anion of the carboxylic acids, the carboxylate anion, change the ending of the name of the parent acid from –ic to –ate, and omit the word acid.
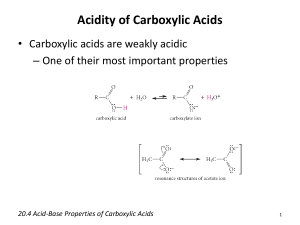
Carboxylic acids are weak acids toward water, and their percentage ionization is low.
Aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids have following ion in equilibrium
But they are several billion times stronger acid than alcohols and roughly 100,000 times stronger than phenols. The greater stability of carboxylate ion relative to that of the anions of alcohols and phenols is responsible for greater acidity of carboxylic acids.
Strong bases like hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ion neutralize carboxylic acids.
The bicarbonate ion in body fluids helps neutralize carboxylic acids produced by normal metabolism. Otherwise the pH of the body fluids, like blood, would fall too low to sustain life.
RCOOH + OH RCOO + H
2
O
RCOOH + HCO
3
-
RCOO
-
+ H
2
O + CO
2
CH
3
COOH + OH CH
3
COO
-
+ H
2
O
C
6
H
5
COOH + HCO
3
-
C
6
H
5
COO
-
+ H
2
O + CO
2
Carboxylate ions are more soluble in water than their parent acids. Carboxylate ions are strong bases (good proton acceptors), especially toward water. Water insoluble carboxylic acids dissolve almost instantantly, when base is added and RCOOH changes to RCOO
-
. Similarly a water soluble carboxylate anion, RCOO
-
, instantly changes to its much less soluble form when we add a strong acid.
So by suitably adjusting the pH of an aqueous solution, we can make a substance with a -
COOH group more soluble or less soluble in water.
Carboxilic acids are parents for several families that collectively are called acid derivatives. They include acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, and amides. They are called acid derivatives because they can be prepared from the acids and they can be hydrolyzed back to acids.
Esters and other related compounds:
The functional group of ester is the central structural feature of all of the edible fats and oils. It is also found in a number of constituents of body cells.
NAMING OF ESTERS:
Name the acid part of the ester as the anion of the acid, the -ic ending of the name of parent acid is changed to –ate.
Once you have name for the acid portion, simply write the name the alkyl group of the ester’s alcohol portion in front of it.