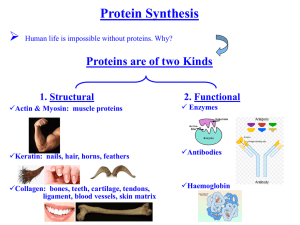
2007-october Admission Exams
advertisement

Structural and Functional Genomics Entrance Exams October 2007 1) Dynamical model of metabolic pathways: describe in some detail a possible approach by means of an example 2) Using microarray analysis to find the targets of a drug treatment 3) Time series analysis and modeling 4) What are the noncoding RNAs? 5) Describe how you would identify differences in gene expression between two tissues 6) Describe the different components of the mammalian transcriptome 7) Eucaryotic transposable elements 8) Regulation of eucaryotic RNA polymerases 9) miRNAs: how are they synthesized and what do they do 10) Technologies useful for conditional mutagenesis 11) Genes patterning the drosophila embryo 12) Epigenetics 13) Is the “ from DNA to RNA to Protein” biological dogma still valid? 14) How many proteins a single gene can code for? 15) Describe examples of how chromatin structure can influence gene expression 16) Describe what type of intermolecular interactions are responsible for the formation of (1) protein aggregates (2) the DNA double strand. 17) Describe a major experimental technique to solve the structure of membrane proteins 18) Structure and function of G-protein coupled receptors 19) The sequence of a new protein has just been determined in your lab. Can you obtain any structural and functional information from it? 20) Beta-strands are secondary structure elements much more common in cytoplasmatic proteins than membrane proteins. Why? 21) Provide an example of the usefulness of molecular simulation approaches for structural genomics. 22) Describe some physical process playing a major role in biological functions 23) Describe optical tools for visualizing cells at the micro and nano-scale. 24) Discuss how and why nanotechnology can help understanding biological problems. 1