lecture

The Romantic Age
1798 – 1832
I.
“Romance” and “Romanticism”
II.
Historical and political background a.
American Revolution b.
French Revolution i.
Reign of Terror ii.
Napoleon c.
Industrial Revolution i.
“Two Nations: ii.
“Laissez – faire”
III.
The five major poets a.
Wordsworth b.
Coleridge c.
Byron d.
Shelley e.
Keats
IV.
Poetic theory and poetic practice a.
Spontaneity b.
Nature poetry c.
The commonplace d.
The supernatural e.
Individualism, infinite striving, and nonconformity
V.
The familiar essay, drama, and the novel
Restoration decorum level of diction conservative respect for order
Romanticism enthusiasm revolution x3 language of the common man democrative sympathies
Epic
Tragedy
Comedy
Satire
Pastoral
Lyric
The Romantic Period
1798 – 1832
I.
Introduction
Following the common usage of historians of English literature, we shall denote by the Romantic Period the span between the year 1798, in which William
Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge published their Lyrical Ballads, and in 1832, when Sir Walter Scott died, and when the passage of the first Reform bill set in motion the Victorian era of cautious readjustment of political power to the economic and social realities of a new industrial age.
Before we look at the main features of this period, we need to thing about the words Romantic and Romanticism. The names we apply to broad periods of literary and cultural history can often be misleading, and this is especially true of the “Romantic”
Age and “Romanticism.” The word romance (French roman ) was a broad term in origin and was applied indiscriminately to any long narrative in French verse – for example, the
Roman du Rou , a chronicle of Normandy; the Roman de la Rose , an allegory of aristocratic courtship; the
Roman d’Alexandre
, the history of Alexander the Great. By the end of the Middle Ages, however, the word roman , or romance , had become restricted to something like its modern meaning: a tale of knightly prowess, usually set in remote times or places and involving elements of the fantastic or supernatural.
Therefore, the word romance originally referred to the highly imaginative medieval tales of knightly adventure written in the French derivative of the original Roman (or romance ) language, Latin. (That these tales often involved amorous encounters between a knight and his lady is partly responsible for the modern meanings of romance and romantic.
) When we speak of the Romantic Period, we are using the word romantic in this older sense. We are referring indirectly to an interest in the charming, magical world of medieval “romance,” and more generally to the rich imaginative activity displayed in that world, which is deeply characteristic of the late eighteenth and early nineteenthcentury writers. To avoid confusion, we should remember that “romance” as “freely imaginative perfection-seeking fiction,” not “romance” as “love between men and women,” is the true basis for the terms “Romantic Age” and “Romanticism.”
II. Historical and Political Background
The eighteenth century was a time of great prosperity and confidence for the upper and middle class in England, but toward the end of the century two major political revolutions disturbed the established sense of security and well-being in the country.
Although both revolutions occurred outside England, they nevertheless affected the late eighteenth and early nineteenth-century thinking.
First, there was the revolt of the English colonies in America against the uncaring and unjust economic policies of the mother country under the blundering leadership of
George III. The victory of the American movement for independence was certainly a blow to English confidence, but practically and philosophically it was less threatening than the second revolution, which took place in France in 1789.
Unlike the American Revolution, which was merely a rejection of authority and control by a distant and unorganized group of colonies, the French Revolution was a complete overthrow of the government of a great European power from within. This seeming change in the balance of power sparked the feeling in English liberal and radicals that, in the spirit of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and the storming of the
Bastille to liberate political prisoners, England was now primed for a triumph of popular democracy. (Historical accounts suggest that the Bastille liberation was more symbolic than actual.)
Later, however, English sympathizers dropped off as the revolution followed its increasingly grim and violent course. When revolutionary extremists gained control of the government in 1792, they executed hundreds of imprisoned nobility in what became known as the September Massacres. The year 1793 saw the execution of King Louis XVI and the establishment under Robespierre of the Reign of Terror, during which thousands of those associated with the old regime were guillotined. Most disturbing of all to the
English mind was, perhaps, the invasion of the Rhineland and the Netherlands by the army of the French Republic, and the French offer of armed resistance to all countries desiring to overthrow their present governments. This threat of internal rebellion spurred the existing conservative parliament into war against France, which after savage reprisals against those who had held power during the Reign of Terror, produced Napoleon as dictator and eventually as emperor of France. Once a champion of the Revolution,
Napoleon became a tyrannical despot who strove to conquer Europe and establish a hew dynasty.
The reaction of the supporters of the Revolution was on of disillusionment and hopelessness in France as well as England. In England, the government and ruling classes, in reaction to the fear that the early democratic principles of the revolution might spread to their own country, introduced severe measures. Public meetings were prohibited, habeas corpus was suspended for the first time in over a hundred years, and advocated of even modest political change were charged with high treason. The disillusionment of the liberal and democratic thinkers seemed to reach its deepest when
Napoleon, still regarded by some as a song of the Revolution, was defeated by British forces as Waterloo in 1815. This defeat by on despotic power over another, rather than showing democratic progress and reform, seemed to have consolidated the power of the wealthy and reactionary ruling classes.
Though less sudden and obvious in its consequences that the political revolutions in America and France, the Industrial Revolution was ultimately more important in transforming European society, and its own way more violent in its impact of human life.
This was a turbulent period, during which England experienced the ordeal of change from a primarily agricultural society, where wealth and power had been concentrated in the landholding aristocracy, to a modernized industrial nation, in which the balance of economic power shifted to large scale employers, who found themselves ranged against an immensely enlarging and increasingly resistive working class. The result of this industrialization of Britain’s cities was to depopulate the countryside by forcing workers to seek employment in the various city mills. Working and living conditions in these cities were terrible; women and children as well as men labored for long hours under intolerable conditions. More than ever before the population was becoming increasingly polarized into what Prime Minister Disraeli called the “Two nations”- the two classes of capitol and labor, the large owner or trader, and the possessionless wageworker, the rich and the poor.
No attempt was made to regulate the shift from the old economic world to the new because of the pervasive social philosophy of laissez- faire.
This theory of “let alone” allowed corrupt, or at least insensitive, employers to abuse their employee’s rights
without government interference. Subsequent reports done on the conditions of the mining industry where five to ten years old children were forced to pull carts on their hands and knees read like passengers from Dante’s
Inferno.
In summary, the Romantic Age was a time of vast and largely unguided political and economic change. Most of the writers of this period were deeply affected by the promise of subsequent disappointment of the French revolution, and by the contorting effects of the Industrial revolution. In many ways, both direct and indirect, we can see the historical issues we have just been surveying reflected in the main literary concerns of romantic writers.
Much as the French Revolution signaled an attempt to break with the old order and to establish a new and revitalized social system, romanticism sought to free itself from the rules and standards of eighteenth-century literature and to open up new areas of vision and expression. The democratic and insistence on the rights of the individual, which characterized the early states of the French revolution, have their parallel in the
Romantic writer’s interest in the language and experience of the common people, and in the belief that writers and artists must be free to explore their own imaginative worlds.
The main consequences of the industrial revolution – the urbanization of English life and landscape, and the exploitation of the working class – underline the Romantic writer’s love of the unspoiled natural world or remote settings devoid of urban complexity, and his passionate concern for the downtrodden and oppressed.
III.
The Five Major Poets of the Romantic Age
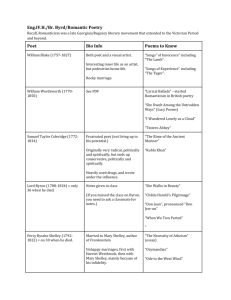
William Wordsworth (1770 - 1850)
Although Wordsworth is the least colorful of the major Romantic poets, he is recognized by many as the greatest. Wordsworth’s reputation is based on his collaborative efforts in Lyrical Ballads and his autobiographical masterpiece the
Prelude, the greatest and most original long poem since Milton’s Paradise Lost.
Wordsworth is remembered as the poet of the remembrance of things past, or as he himself put it, “of emotion recollected in tranquility.” Where an object or event in the present triggers a sudden renewal of feelings he has experienced in youth; the result is poetry that exhibits a discrepancy between who he is aat the present and who he once was.
Samuel Taylor Coleridge (1772 - 1834)
Coleridge, Wordsworth’s co-collaborator on
Lyrical Ballads, is most famous for his mysterious and demonic poetry, including The Rime of the Ancient
Mariner, Kubla Khan, and Christabel. Coleridge was regarded by his friends as one of the greatest intellectual minds of the day; albeit, a mind that should have produced more, and one that suffered the dehabilitating effects of opium addiction.
George Gordon, Lord Byron (1788 - 1824)
Byron cuts one of the most fascinating personalities of the Romantic Age.
He Achieved great fame during his lifetime and was rated as one of the greatest poets through the nineteenth century, but is now viewed as the least consequential of the major Romantic poets. Interestingly, none of the major poets, bar Shelley, thought highly of Byron or his work; while Byron spoke slightingly of all the major poets except Shelley. Byron felt that all his contemporaries were focused on the wrong subject matter he chose the favorite of the neoclassicists, satire against modern civilization, in his masterpiece Don Juan.
Byron’s chief claim to be considered an arch-Romantic is with the personage of the “Byronic hero.” This persistent character is that of a moody, passionate, remorse-torn, but unrepentant wanderer; in essence, a reflection of himself. The literary descendants of this
Byronic hero are Heathcliff in Wuthering Heights, Rochester in Jane Eyre, and
Captain Ahab in Moby Dick. Byron died at the age of thirty-six in Greece, where he is regarded today as a national hero for his efforts in training Greek soldiers during the Greek/Turkish wars.
Percy Bysshe Shelley (1792 - 1822)
Shelley’s writing is the most passionate and intense of all the romantics. Eccentric in manners and in religious and political beliefs, “mad
Shelley” was expelled from Oxford for the publication of an article called
The
Necessity of Atheism. Like Byron, Shelley felt himself to be an alien and outcast from his own country and society; subsequently, Shelley lived out the latter years of his life in Italy. Shelley’s greatness as a poet is seen in hi philosophical masterpiece Prometheus Unbound, and for his great “Ode to the West Wind,”
among others. Shelley, like Byron and Keats, died at a young age. Only twentynine, Shelley was killed in a boating accident in 1822. Shelley’s body was thereby cremated by a group of friends, including Byron, and his ashes buried in the
Protestant cemetery in Rome.
Mary Shelley (wife) – Frankenstein; daughter of Mary Wollstonecraft- A
Vindication of the Rights of Women
John Keats (1795-1821)
The brevity and intensity of Keats’ career are unmatched in
English poetry. At the age of twenty-three, Keats had achieved the culmination of his brief career. Within five years of first trying his hand at poetry, Keats had written The Eve of St. Agnes, La Belle Dame sans Merci, Lamia, all of the “great odes,” as a sufficient number of the sonnets to make him, like Wordsworth, a major Romantic craftsman in that form.
To put Keats’s potential in comparison, it should be remembered that
Wordsworth did not start writing in earnest until he was twenty-seven, and on his death at the age of twenty-five, Keats’ achievements greatly exceeded that of
Chaucer, Shakespeare, or Milton.
IV.
Poetic Theory and Poetic Practice
Although no writer during William Wordsworth’s time considered himself a
“Romantic,” a word not applied until half a century later by English historians, many of then did feel there was a pervasive intellectual and imaginative climate, which some of them called “the spirit of the age.” The Revolution left the feeling that this was a great age of new beginnings when, by discarding inherited procedures and outworn customs, everything was possible, not only in the political and social realm but in intellectual and literary enterprises as well. Remember, the major writers of the day including Robert Burns, William Blake, Wordsworth, and Coleridge were all fervent supporters of the early Revolution. Even after its collapse, writers such as
Shelley and Byron felt when purged of its errors, the Revolution’s example still comprised humanity’s best hope.
As was mentioned, the Romantic Age in England began with perhaps the greatest act of collaboration in all of English Literature; the publishing of William
Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge’s
Lyrical Ballads. In excited daily communions these two men set out to revolutionize the theory and practice of poetry.
Wordsworth undertook to justify the new poetry in the Preface to Lyrical Ballads. In it he set himself in opposition to the literary ancien regime , those writers of the preceding century – Dryden, Pope, and Johnson- who, in this view, had imposed on poetry artificial conventions that distorted its free and natural development. Although
Coleridge did not agree wholeheartedly with all of Wordsworth’s assumptions, he did see the necessity of overturning the reigning tradition. This preface, therefore, deserves its reputation as a turning point in English literature, for Wordsworth gathered up isolated ideas, organized them into a coherent theory based on explicit critical principles, and made them the rationale for his own massive achievements as a poet. a.
Spontaneity
Wordsworth described all good poetry as, at the moment of composition,
“the spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings.” Although there existed varied theories of what Romantic poetry was, all concurred on the crucial point that it was the mind, emotions and the imagination of the poet that were the defining attributes of a poem. The emphasis in this period on the free activity of the imagination is related to an insistence on the essential role of instinct, intuition and the feelings of “the heart” to supplement the judgments of the purely logical faculty, “the head,” whether in the province of artistic beauty, philosophical or religious truth, or moral goodness. b.
Nature Poetry
Because of the prominence of landscape in this period, ‘Romantic poetry” has to the popular mind almost become synonymous with “nature poetry.”
Romantic “nature poems” are in fact meditative poems, in which the presented scene usually serves to raise an emotional problem or personal crisis whose development and resolution constitutes the organizing principle of the poem. Restate: Nature causes the poet to meditate over a problem and resolve it. c.
The Commonplace
Another characteristic of Romantic poetry was the glorification of the common man and rustic life; or according to Wordsworth, “to choose incidents and situations from common life” and to use a “selection of language really spoken by men,” for which the model is “humble and rustic life.” Byron maintained allegiance to both aristocratic proprieties and traditional poetic decorum: “Peddlers,” and “Boats,” and “Wagers’!
Oh! ye shades Of Pope and Dryden, are we come to this? d.
The Supernatural
Also characteristic of this poetry was an interest in the realm of mystery and magic, in which materials from ancient folklore, superstition, and demonology are employed in the distant past or far away locations.
Coleridge’s
The Rime of the Ancient Mariner and Kubla Khan, and Keats’
La Belle Dan sans Merci fit this character. e.
Individualism, Infinite Striving, and Nonconformity
Through the greater part of the eighteenth century, men and women had for the most part been viewed as limited beings in a strictly ordered and unchanging world. The opposite was true in the Romantic period, where a higher estimate was put in human powers. Now a radical individualism surfaced that argued that the human being should refuse to submit to limitations and pursue infinite and inaccessible goals. For example,
Goethe’s
Faust, unlike Marlowe’s Faustus, wins salvation through his persistent striving for more. Also apparent in Romantic poetry is the isolation of the individual, (contrast views of the Restoration). Many of the poets of the day employed a protagonist with an individual vision that was achieved outside of an ordered society. Finally, the theme of exile, of the disinherited mind that cannot find a spiritual home in its native land or society is introduced. This solitary Romantic nonconformist was sometimes also a great sinner, therefore the fascination with Cain, Satan, and Faust—or in Coleridge’s case, his outcast Mariner.
V.
The Familiar Essay, Drama, and the Novel
The “familiar essay” – a commentary on a non-technical subject written in a relaxed and impersonal manner – flourished in a fashion that paralleled the
Romantic poetry. Essayists such as Charles Lamb, William Hazlitt, and Thomas De
Quincey wrote autobiographical, personal essays that sympathized with the lower classes and employed a style that broke free from their neoclassical predecessors.
Because of rigid moral and political censorship the drama was virtually non-existent during the Romantic period.
Two new types of fiction were prominent in the late eighteenth century; the Gothic novel and the novel of purpose. The term “Gothic” derives from the frequent setting of these tales in a gloomy castle in the Middle ages, but has been extended to include a lager group of novels that include stories of decaying mansions with dark dungeons, secret passages, and stealthy ghosts; chilling supernatural phenomena; and, often, persecution of a beautiful maiden by an obsessed and haggard villain.
The second fictional mode popular at the turn of the century was the novel of purpose that was written to give light to new social and political theories current in the period of the French Revolution.
The Romantic period produced two major novelists, Jane Austen and Sir
Walter Scott. Austen is one of England’s greatest novelists. She wrote Sense and
Sensibility and Northanger Abbey, two novels that poked fun at popular Gothic tales.
She also wrote Pride and Prejudice and Emma – novels that dealt with various heroines and their capacity to demonstrate grace under social and financial pressure.
Sir Walter Scott, a contemporary of Austen who admired her work greatly, wrote in fiction that was an extreme from hers. He wrote his fiction in the rich and lively realm of history with characters that represented the middle and lower classes.
Scott’s most famous works include Rob Roy, The Heart of Midlothian, and, Ivanhoe.
With the death of Sir Walter Scott in 1832, and the passage of the First
Reform Bill in that same year followed by Queen Victoria’s accession to the throne in
1837, England entered a new phase in its cultural and literary history. The Romantic concern with the dignity, freedom, and creative potential of the human mind in a
world that was becoming increasingly complicated, an alien, continued to be a major concern of Victorian writers – the next era of British literature.