PRENTICE HALL - CELLS AND HEREDITY
advertisement

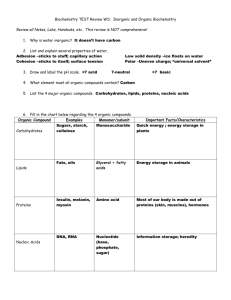
Key Concepts: -What are elements and compounds? -What are the main kinds of organic molecules in living things? -How is water important to the function of cells? PRENTICE HALL - CELLS AND HEREDITY CHAPTER 1 - CELLS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Section 3 – Chemical Compounds in Cells Key Terms and Connections Main Ideas and Visuals Elements and Compounds -Air is a mixture of gasses including both elements and compounds. E.g. Three gasses in the air include oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Element-------------------> Compound----------------> Elements: -An element is any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. -The smallest unit of an element is an atom, and each element is only made up of one kind of atom. E.g. Some elements found in organisms include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Compounds: -A compound is formed when two or more elements chemically combine. -Most elements in organisms occur in the form of compounds. -The smallest unit of many compounds is a molecule. E.g. Water is an QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Questions and Comments example of a compound. Organic and Inorganic Compounds: -Many compounds found in organisms contain carbon. -Most compounds that contain carbon are called organic compounds. E.g. Some important groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. -Since foods you eat come from living things, many of these compounds are found in food. -Organisms also contain compounds that do not contain carbon called inorganic compounds. E.g. Some inorganic compounds include water and table salt. Carbohydrates Carbohydrate-------------> -A carbohydrate is an energy-rich organic compound made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. E.g. Sugars and starches are 2 examples of carbohydrates. -Sugars are produced during the food-making process that takes place in plants (photosynthesis). When these sugar molecules combine, they form complex carbohydrates: large molecules called starches. -Plant cells store excess energy in molecules of starch, thus many foods that come from plants contain starch. E.g. These foods include potatoes, pasta, rice, and bread. -When you eat these foods, your body breaks down the starch into glucose, a sugar that your -What is the distinction between compounds that contain carbon and compounds that do not? Why are compounds containing carbon called “organic” compounds? -How can a compound be energy-rich? What energy does it store? -How can a cell store “energy” in molecules of starch? What form of energy do they store? - Does the mitochondria Lipids-----------------------> -Lipids are very similar to carbohydrates! They are made of the same elements, and are both energy-rich. Proteins--------------------> cells use to produce energy. in cells convert glucose -Carbohydrates are also important components of into cellular energy? some cell parts. E.g. The cellulose that makes up cell walls is a type of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are also found in cell membranes. Lipids -Lipids are energy-rich organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. E.g. Fats, oils, and waxes are all lipids. -Lipids contain even more energy than carbohydrates. -The cell membrane is mainly made of lipids. -Cells store energy in lipids for later use. E.g. During the wintertime, a dormant bear lives on the energy stored as fat within its cells. Proteins -Proteins are large organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and, in some cases, sulfur. E.g. Foods high in protein include meat, eggs, fish, nuts, and beans. Structure of Proteins: Amino acids---------------> -Amino acids are the smaller molecules that make up protein. -The 20 amino acids are like the -Cells combine the 20 types of existing amino acids 26 letter of the alphabet. By in a variety of different ways to produce different combining different letters in kinds of proteins. different orders, thousands of -If proteins are made up of the molecules, amino acids, then aren’t they compounds and not molecules? words can be formed. Enzyme--------------------> Nucleic acids-------------> Functions of Proteins: -Proteins form parts of the cell membrane and also make up many of the organelles within a cell. -An enzyme is also a type of protein that speeds up chemical reactions within living things. -Without enzymes, many chemical reactions necessary for life would either take too long to occur, or would not occur at all. Nucleic Acids -Nucleic acids are very long organic molecules made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. -Nucleic acids contain the instructions cells need to -So are nucleic acids carry out all the functions of life. -The two kinds of nucleic acids are, DNA & RNA. DNA-------------------------> -DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the genetic material that carries out information about an organism, and is passed from parent to offspring. -The information in DNA also directs all of the cell’s functions, thus most of the DNA within a cell is found in the cell’s chromatin. RNA-------------------------> -RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is found in the cytoplasm and nucleus, and it plays an important role in the production of proteins. Water and Living Things -Water takes up about 2/3 of your body, and it plays many important roles in cells. E.g. Most chemical reactions in cells involve substances that are dissolved in water, and water molecules themselves take part in many chemical reactions within cells. *Most chemical reactions within cells could not take place without water. -A cell without water -Water also helps cells maintain their size and would be like a balloon shape. with no air. -Finally, since water changes temperature slowly, it helps keep the temperature of cells from changing rapidly. located within the chromatin of cells? -What is this important role? Doesn’t the cytoplasm do this? Or is the cytoplasm mostly made up of water?