INSTRUCTIONS TO AUTHORS FOR THE PREPARATION
advertisement
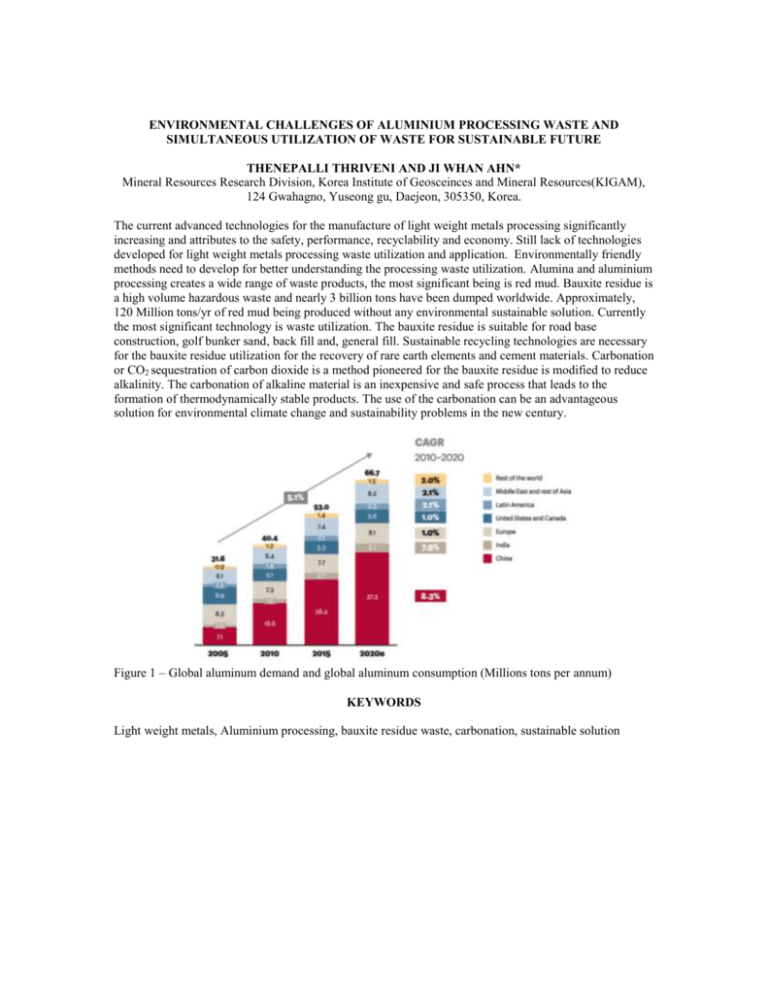
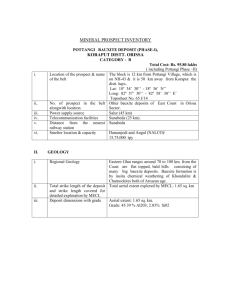
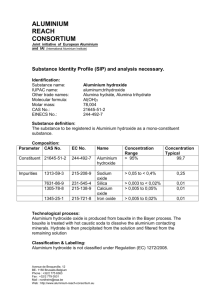
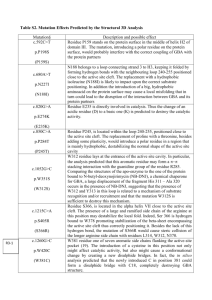
ENVIRONMENTAL CHALLENGES OF ALUMINIUM PROCESSING WASTE AND SIMULTANEOUS UTILIZATION OF WASTE FOR SUSTAINABLE FUTURE THENEPALLI THRIVENI AND JI WHAN AHN* Mineral Resources Research Division, Korea Institute of Geosceinces and Mineral Resources(KIGAM), 124 Gwahagno, Yuseong gu, Daejeon, 305350, Korea. The current advanced technologies for the manufacture of light weight metals processing significantly increasing and attributes to the safety, performance, recyclability and economy. Still lack of technologies developed for light weight metals processing waste utilization and application. Environmentally friendly methods need to develop for better understanding the processing waste utilization. Alumina and aluminium processing creates a wide range of waste products, the most significant being is red mud. Bauxite residue is a high volume hazardous waste and nearly 3 billion tons have been dumped worldwide. Approximately, 120 Million tons/yr of red mud being produced without any environmental sustainable solution. Currently the most significant technology is waste utilization. The bauxite residue is suitable for road base construction, golf bunker sand, back fill and, general fill. Sustainable recycling technologies are necessary for the bauxite residue utilization for the recovery of rare earth elements and cement materials. Carbonation or CO2 sequestration of carbon dioxide is a method pioneered for the bauxite residue is modified to reduce alkalinity. The carbonation of alkaline material is an inexpensive and safe process that leads to the formation of thermodynamically stable products. The use of the carbonation can be an advantageous solution for environmental climate change and sustainability problems in the new century. Figure 1 – Global aluminum demand and global aluminum consumption (Millions tons per annum) KEYWORDS Light weight metals, Aluminium processing, bauxite residue waste, carbonation, sustainable solution