ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: The chemistry of carbon compounds
advertisement

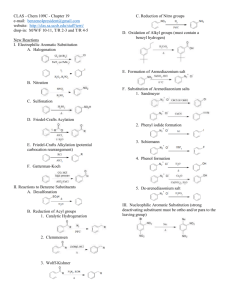
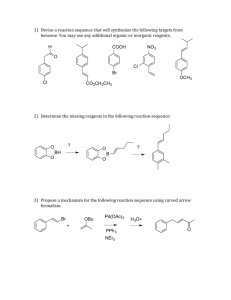
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEST 2 REVIEW answers 1. This is the: carbonyl group H2C O 2. This is the: carboxyl group HC O OH 3. -OH is the: hydroxyl group 4. In ____the carbonyl group is at the end of the chain. aldehydes 5. ___aldehydes have sharp, irritating odors. smaller 6. larger __aldehydes have flowery odors and are diluted for perfumes. 7. What is produced in the human body when ethanol is oxidized? ethanal 8. Aromatics are: benzene and its derivatives. 9. The general formula for an alcohol is: R - OH 10. Benzene is a member of the _____ homologous group. aromatic 11. Alcohols must have this group attached. hydroxyl 12. Longer-chained alcohol like octanol are: not soluble in water and are nonpolar 13 This compound is produced from benzene and is used in making a type of nylon: cyclohexane 14. The radical formed from a benzene ring is the______ radical. phenyl 15. When alcohol is attached to a benzene ring, you have a sore throat spray called: phenol 16. Benzene is considered stable because it has: an even distribution of valence electrons throughout. 17. Of the following compounds which one is not an aromatic compound: (a) ASA (aspirin), (b) Benzocaine (a local anesthetic), (c) Cyclohexane (used in making nylon), (d) Amphetamines (stimulates the nervous system), (e) Adrenaline ( a hormone that stimulates the nervous system). 18. This German chemist proposed a cyclic structure for benzene: Kekule. 19. The common name for methylbenzene is: Toluene. 20. When benzene is not the parent chain it is called a _____ group. Phenyl. 21. The OH group is called a____ group. Hydroxyl 22. When a halide such as chlorine is attached to hydrocarbon it is called: chloro. 23. Rubbing alcohol is: isopropanol (2-propanol) 24. Wood alcohol is: methanol. 25. Acetylene (used for welding) is: ethyne. 26. The treatment for methanol poisoning is to drink lots of: ethanol. 27. What is used to detect the presence of an alkene? Br2 28. Tetrahydrourushiol (Poison Ivy) and Thymol (Hookworms) are examples of: phenol 29. Many organic molecules demonstrate that the what governs their biological properties? structure and shape. 30. Antifreeze is: 1,2-ethanediol. 31. Alcohol tends to boil at___ temperatures than hydrocarbons of similar molecular mass. higher 32. [1-butene ethyne + ethane] is an example of: (a) Cracking, (b) Reforming, (c) combustion, (d) hydrogenation, (e) substitution. 33. Two benzene rings fused together is: napthalene. 34. Ethers are important as: anesthetics. 35. What is used as a “non-surgical” procedure to remove gallstones. (a) dibenzene, (b) diphenylene, (c) phenylbenzene, (d) phenol, (e) methyl tertiary-Butyl ether 36. In ____the carbonyl group is at the end of the chain. aldehydes 37. __________is used to produce acetic acid. Ethanal. 38. What is produced in the human body when ethanol is oxidized? ethanal 39. What does the drug disulfiram do? Slows down the decomposition of ethanal, 40. Which one of the following is not an isomer of dimethylbenzene, which is a xylene. (a) acetone, (b) varsol, (c) paint thinner, (d) polyclens. 41. The modern method of preparing methanol is: (a) Fermentation of methanal, (b) CO + Hydrogen methanol, (c) C6H12O6 + Oxygen methanol, (d) Ethanol cracking methanol. 42. Glycerin is: (a) 2-propanol, (b) 1- propanol, (c) methanol, (d) acetone, (e) 1,2,3-propanetriol. 43. Methoxyethane is an example of a(n): (a) ethers, (b) ketones, (c) aldehydes, (d) esters, (e) carboxylic acid. 44. Ethanal is an example of a(n): (a) ketones, (b) ethers, (c) carboxylic acid, (d) esters, (e) aldehydes. 45. Methanal is commonly known as: (a) acetone, (b) formaldehyde, (c) acetic acid, (d) formic acid. 46. Propanone is commonly known as: (a) formic acid, (b) formaldehyde, (c) acetic acid, (d) acetone. 47. Fehling’s diagnostic test is a test for the presence of: (a) an alcohol, (b) an ester, (c) an aldehyde, (d) a ketone. (1) List four properties of benzene. (2) List and describe 3 examples of common organic halides. Draw the following: handouts