Microscopic Features of Nephron & Collecting Ducts
advertisement

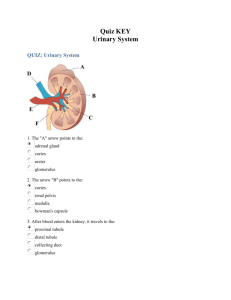
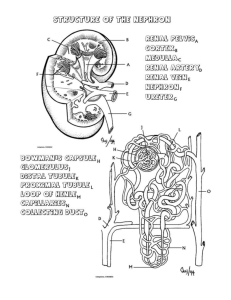
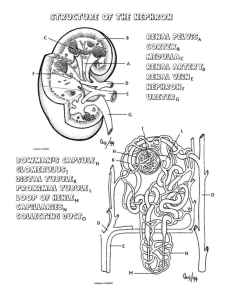
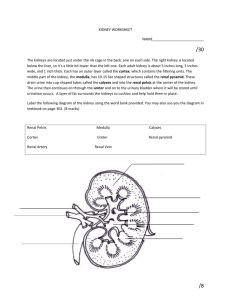
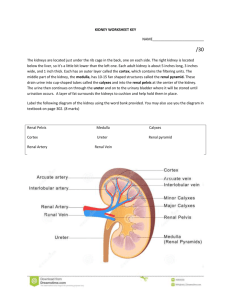
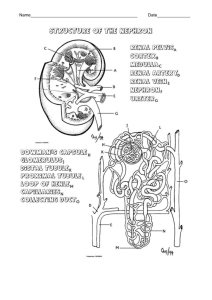
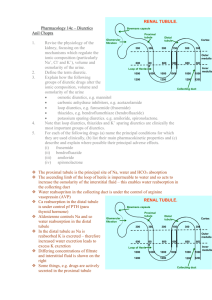
KIDNEY (Histology) Learning Objective: At the end of the lecture student will able: To define the functional unit of the kidney. To describe the different histological of the nephrons. To describe the vasculature of the the kidney. Kidneys Kidneys are reddish brown paired organs, situated along the posterior abdominal wall. They are covered by thin capsule, which is easily removed The cut surface shows outer cortex and internal medulla. Inside the medulla there is renal sinus containing cup shaped major and minor calycies The renal medulla consists of pale, striated, conical renal pyramids. Their bases are peripheral while their apices converging to the renal sinus where they project into minor calyces as papilla. . Each pyramid is capped by cortical tissue to form renal lobe. The renal cortex is subcapsular; it also extends towards the renal sinus as renal columns. The medullary tissue extends into the cortex as medullary rays. Cortex close to the medulla is sometimes termed juxtamedullary cortex. Microscopic Features • Kidney is composed of many tortuous closely packed uriniferous tubules, bound by little connective tissue in which run blood , lymphatics and nerves. • Each uriniferous tubule consists of two embryologically distinct parts. 1. The secreting Nephrons which elaborate urine and 2. Collecting tubule which convey urine to the calyceal system. Kidney and Urineferous Tubule Nephron • Each kidney consists of about 1,000,000 nephrons, • The nephrons begins as double walled epithelial cup (Bowman’s capsule), which surrounds a tuft of capillaries, the glomerulus. • Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus together form the renal or Malpigian corpuscle. Bowman’s capsule consists of two simple epithelial layers; an inner or visceral layer covering the glomerulus and an outer parietal layer. The region where the vessels enter or leave the glomerulus is the ‘vascular pole of the corpuscle. ‘Urinary pole’ of the corpuscle is roughly opposite the vascular pole; here the parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule becomes continuous with proximal tubule. The Nephron and Renal Corpuscle Malpigian corpuscle (Diagrammatic) The cells of the visceral epithelium are specialized, called ‘podocytes’. The nucleus and surrounding cytoplasm protrude into the capsular space and rests on the processes that extend from the cell body, branching one or more times to form a series of slender processes on basal lamina. The terminal processes or pedicles interdigitate with the pedicles of neighboring podocytes; leaving a series of slits between them. Podocyte Parietal Layer of Bowman’s capsule Parietal layer of bowman’s capsule is lined by simple squamous epithelium. This layer becomes continuous with the lining of proximal convoluted tubule. Tubular Part of Nephron The tubular portion of nephrons is composed of A) proximal tubule B) thin segment and C) distal tubule. Parts Of Nephrons Both proximal and distal tubules have a convoluted portion and a straight portion. The straight portion of the proximal tubule and distal tubule together with the thin segment are arranged in a hairpin loop extending a variable distance into the medulla. These three segments together are called ‘loop of Henle’. The convoluted portion of the distal tubule joins the arched collecting tubule which begins system of the ducts or ‘ collecting tubules’. Proximal Tubule The proximal tubule is the longest section of the nephron (about 14 mm). The convoluted part of the proximal tubules coils close to the glomerulus in the cortex. The diameter of proximal tubules is ~65 µm. Their walls are formed by a low columnar epithelium. The eosinophilic cells of the epithelium have a wide brush border They almost completely reabsorb substances of nutritional value from the glomerular filtrate (glucose, amino acids, protein, vitamins etc). In the proximal tubules the volume of the glomerular filtrate is reduced by about 75%. Sodium ions are actively resorbed from the glomerular filtrate. They are followed by passively diffusing chloride ions and the osmotic absorption of water. The straight portion of the proximal tubule descends towards the medulla. The straight portion of the proximal tubule merges with the intermediate tubule the thin segment of the loop of Henle. A flattened, only ~1-2 µm high epithelium (simple squamous) forms the intermediate tubule, which is only ~15 µm wide. Distal Tubule: The diameter of the distal tubule expands to ~35 µm. The distal tubule, is formed by low cuboidal cells without a brush border. Basal infoldings and all the cell organelles are present. Function of Distal convoluted tubule Epithelial cells in distal tubules cells transport chloride (active) and sodium ions (passive) into the surrounding peritubular space. . Cells in the distal tubules are sensitive to the hormone aldosterone. Juxta-glomerular Complex The distal tubule contacts the glomerulus forming a specialized section of tubular epithelium, the macula densa. At the point of contact with the glomerulus, the distal tubule is always in close contact with the efferent and afferent arterioles of the glomerulus. The juxtaglomerular cells surround the afferent arteriole (they are modified smooth muscle cells), which produce and secrete renin. Third component of the juxtaglomerular complex is extra-glomerular mesangial cells JG Copmplex Function of Renin Renin activates angiotensinogen, a precursor found in the blood stream, leading to the formation of angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is the most potent vasoconstrictor known. Renin also stimulates the secretion of aldosterone Blood supply of kidney Renal artery is a branch of abdominal aorta. Near the hilum it divides into anterior & posterior branches. These branches further divide into segmental arteries apical upper, middle lower & posterior. Renal vasculature Renal artery 1. Interlobar arteries 2. Arcuate arteries 3. Interlobular arteries 4. Afferent arteriole 5. Glomerulus 6. Efferent arteriole 7. Vasa recta. Cortical and medullary capillaries →interlobular vein →arcuate vein→renal vein Renal vasculature