Supplementary Table 1
advertisement

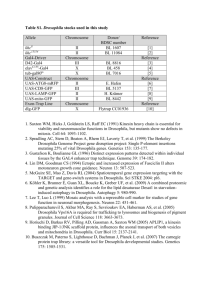
Supplementary Table 1. Species A59T G375R A66S R286S S299R I370T G384S Differences in TXNRD2 orthologs only Differences in TXNRD1 (Tr1), TXNRD2 (Tr2), TXNRD3 (Tr3) and GSR (Gr) orthologs 0/12 0/12 1/12 (Drosophila) 6/12 11/12 11/12 2/43 Drosophila (Tr1 and Tr3) 0/42 22/43 38/45 43/45 41/42 2/12 (Drosophila, Xenopus) 19/42 Legend to Supplementary Table 1: Analyses of the aligned sequences as shown in supplementary Figure 1 representing the number of non-conserved sequences at each position. The specific alignment of ortholog TXNRD2 sequences shows that both A59 and G375 are perfectly conserved across all investigated TXNRD2 sequences, i.e. they are unique to the sequenced TXNRD2 ortholog genes of 11 vertebrates and one invertebrate (Drosophila). Also their degree of conservation across the four classes of homologous oxidoreductases is much higher than any of the other. While the G375 position is perfectly conserved in all 42 investigated sequences, A59 is conserved in 41 sequences out of 43. Notably, in TXNRD1 and TXNRD3 of Drosophila, valine is found in the analogous position to A59, an amino acid with a hydrophobic side chain and similar sterical requirements like alanine, while threonine (observed in our DCM cohort) is polar. This table also shows that Drosophila TXNRD2 harbours leucine at position 66 rather than alanine. The non-synonomous variant A66S (rs5748469) is thus not conserved in all Txnrd2 genes in the same manner as A59 and G375. The lower degree of conservation at this position becomes particularly apparent when glutathione reductases and thioredoxin reductases other than Txnrd2 are included in the comparison. This shows that A66 is conserved in only 21 of 43 sequences ruling out an important role in a function conserved amongst all oxidoreductases like e.g. FAD binding. All other variants are conserved to a lesser degree. For one of the other variants, I370T, it becomes apparent that T370 is the ancient allele which is shared in all 10 other investigated vertebrate TXNRD2 sequences. Drosophila has V370 in this position. This excludes a functionally damaging effect of the T370 allele in the human I370T variant of TXNRD2.