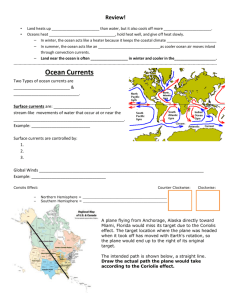
______ currents – streamlike movements of water
advertisement

___________ currents – streamlike movements of water - influenced by: o ________________________________ o ________________________________ o ________________________________ - help people predict where objects in the open ocean will be carried ___________ currents – streamlike movements of water - influenced by: o ________________________________ o ________________________________ o ________________________________ - help people predict where objects in the open ocean will be carried _________ currents – horizontal, streamlike movements of water that occur at or near the ocean surface - controlled by three factors: o ________________________________ o ________________________________ o ________________________________ - ex. Gulf Stream _________ currents – horizontal, streamlike movements of water that occur at or near the ocean surface - controlled by three factors: o ________________________________ o ________________________________ o ________________________________ - ex. Gulf Stream Global Winds - Near the equator winds blow ocean water _________________________________ - Near the poles ocean water is blown __________________________________ Global Winds - Near the equator winds blow ocean water _________________________________ - Near the poles ocean water is blown __________________________________ Coriolis Effect - Curving of moving objects from a straight path due to __________________________________________ - causes surface currents in the Northern Hemisphere to turn _________________________________ - causes surface currents in the southern hemisphere to turn _________________________________ Coriolis Effect - Curving of moving objects from a straight path due to __________________________________________ - causes surface currents in the Northern Hemisphere to turn _________________________________ - causes surface currents in the southern hemisphere to turn _________________________________ Continental Deflections - when surface currents meet continents, the currents ___________________________, or change direction Continental Deflections - when surface currents meet continents, the currents ___________________________, or change direction Current Notes Ocean currents – stream-like movements of water - influenced by: weather, Earth’s rotation, position of the continents - help people predict where objects in the open ocean will be carried Surface currents – horizontal, stream-like movements of water that occur at or near the ocean surface - controlled by three factors: global winds, Coriolis effect, continental deflections - ex. Gulf Stream Global Winds - Near the equator winds blow ocean water east to west - Near the poles ocean water is blown west to east Coriolis Effect - Curving of moving objects from a straight path due to Earth’s rotation - earth’s rotation causes wind and surface currents to move in curved paths - causes surface currents in the Northern Hemisphere to turn clockwise - causes surface currents in the southern hemisphere to turn counterclockwise Continental Deflections - when surface currents meet continents, the currents deflect, or change direction Deep Currents – streamlike movements of ocean water located far below the surface - not directly controlled by wind. Form in parts of the ocean where water density increases. - Density – the amount of matter in a given space - Density of ocean water is affected by temperature and salinity - Salinity – a measure of the amount of dissolved salts or solids in a liquid - Decreasing the temperature of ocean water and increasing the water’s salinity increase the water’s density