Biogeochemical Cycles notes 2
advertisement

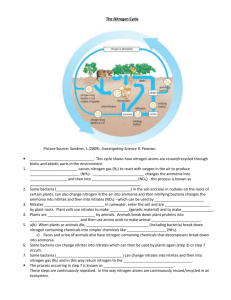
Biogeochemical Cycles COMMONALITIES AMONG THE CYCLES: >exist in the hydro-, litho-, biosphere, & sometimes the atmosphere >there are “pools” or reservoirs >they are changed chemically or biochemically >there are “fluxes”, or movement between pools >transformations (changes) are important & can lead to positive or negative consequences SOURCE – a reservoir that releases more nutrients than it accepts SINK – a reservoir that accepts more nutrients than it releases CARBON CYCLE WHERE USED BIOLOGICALLY: >for structural growth – part of plants & bones >cellular respiration – releases carbon (carbon dioxide) >photosynthesis – removes carbon dioxide >decomposition >largest reservoir is sedimentary rock (fossil fuels & sediments), then oceans (calcium carbonate) WHERE USED GEOLOGICALLY: >volcanic activity >fossil fuels >sedimentary rocks – limestone & carbonate rocks >oceans – calcium carbonate in animal shells CHEMICAL CHANGES TAKING PLACE: >CO2 used to make sugars >CO2 used to make calcium carbonate >sugars broken down & releasing CO2 >dead organisms decomposing or turning into fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) HUMAN INFLUENCE: >burning fossil fuels >clearing/burning forests & rainforests >mining fossils, minerals >planting crops, trees, etc. NITROGEN CYCLE WHERE USED BIOLOGICALLY: >fertilizer for plants >78% of the atmosphere is nitrogen & it is essential for making amino acids & proteins, DNA, RNA >bacterial nitrogen fixation – nitrogen gas changed to nitrites and nitrates >animal waste – ammonia NH3 >bacterial denitrification – release nitrogen gas WHERE USED GEOLOGICALLY: >deposition of nitrogen compounds & animal excretion >decaying organic matter >nitrates move down through soil by leaching, are dissolved in groundwater & may go to ocean sediments CHEMICAL CHANGES TAKING PLACE: >nitrogen gas changed to nitrates & nitrites >ammonia (NH3) changed to nitrates & nitrites >nitric oxide (from combustion of fossil fuels) changed to nitric acid (forms acid precipitation) HUMAN INFLUENCE: >manufacture & use of synthetic fertilizer >fossil fuel use >using natural, organic fertilizer PHOSPHORUS WHERE USED BIOLOGICALLY: >key component of DNA, RNA, & ATP & ADP > in cell membranes, bones, teeth >excretion of urea, bird & bat guano >marine organism use >plants use phosphate dissolved in water WHERE USED GEOLOGICALLY: >most phosphorus is in rocks, ocean sediments, & soil (mostly calcium phosphate) >erosion, weathering, & uplifting releases phosphate >phosphatic rock from ancient seas can be mined for phosphorus CHEMICAL CHANGES TAKING PLACE: > phosphate (PO4) is changed into organic compounds >decomposition returns phosphorus to the soil HUMAN INFLUENCE: >making synthetic fertilizer >using guano for fertilizer TAKE-HOME MESSAGE THE CYCLES WORK TOGETHER, AND CHANGING ONE CYCLE WILL CHANGE THE OTHER THE CARBON, NITROGEN, & PHORPHORUS CYCLES HAVE ELEMENTS THAT ARE ESSENTIAL FOR LIFE ON EARTH HUMAN ACTIVITIES HAVE ACCELERATED GLOBAL CHANGES OF ELEMENTS, RESULTING IN CHANGING CONCENTRATIONS IN THE LAND, ATMOSPHERE, & WATER MANY ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS STARTED DUE TO ACCELERATED BIOGEOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN THE ELEMENTS, WHICH BECOME “POLLUTANTS WHEN THEY ARE OUT OF BALANCE