syllabus_pharmacy_english
advertisement

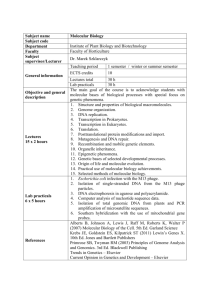
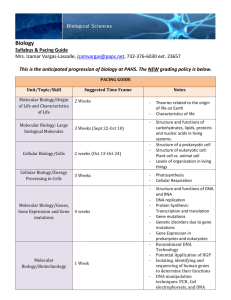
Cellular and Molecuar Biology syllabus for 1st year pharmacy students 1. Subject, place and significance of biology. Basic methods in biology. 2. Molecular organization of life. Organic compounds. Proteins – structure and functions. 3. Nucleic acids. DNA – structure and biological functions. 4. Nucleic acids. RNA – types and biological functions. Self-assembly of macromolecules. 5. Cellular basis of life. Comparative structural and functional characterization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Origin and evolution of cells. 6. The cell as an open biological system: membrane transport, endocytosis and exocytosis. Cell signaling. Cell junctions. Cell receptors. 7. Individual development of cells. Cell senescence. Apoptosis. 8. Cell reproduction. Phases of the cell cycle. Mechanism, phases and consecutive events of mitosis. Cytokinesis. 9. Cell reproduction. Cell cycle control, MPF description. Control of cell proliferation in multicellular organisms. 10. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. Replication (DNA synthesis). Basic modes of replication. 11. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. Mutagenic factors and mechanism of their action. DNA repair. 12. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. Transcription (RNA synthesis). 13. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. RNA processing. 14. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. Genetic code. Translation. 15. Molecular mechanisms of the basic genetic processes. Protein sorting into cellular organelles. Posttranslational modification of proteins. Senescence and degradation of proteins. 16. Organization of the prokaryotic genome. Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells. 17. Organization of the eukaryotic genome. Levels of regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. 18. Submicroscopic structure of chromosomes. 19. Microscopic structure of chromosomes. Human karyotype. Methods of karyotyping and chromosomal analysis. Evolution of karyotype. 20. Laws of heredity. Allelic form of the genes. Interactions between genes. Basic types of inheritance. Penetrance and expressivity 21. Laws of heredity. Inheritance of linked genes. Crossing over. Molecular mechanisms of crossing over. Groups of linked genes in the human. 22. Laws of heredity. Extrachromosomal (cytoplasmic) inheritance in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 23. Heredity and environment. Reaction norm. Phenocopies and genocopies. Genotype variation. Hybrid and recombinational variation. 24. Genotype variation. Mutational variation – chromosomal and genome (numerical chromosomal) mutations. Chromosome diseases. 25. Mutational variation – gene mutations. Molecular diseases. Pharmacogenetics. 26. Genetic engineering at the level of population, organism and cell. 27. Genetic engineering at subcellular level, cloning by transplantation of somatic cell nuclei into oocytes. 28. Recombinant DNA techniques and gene engineering. Specific DNA cleavage, most important enzymes in recombinant DNA techniques. DNA sequencing. Hybridization of nucleic acids with specific probes. 29. Recombinant DNA techniques and gene engineering. DNA and cDNA cloning. Polymerase chain reaction. Gene engineering and gene therapy. 30. Immunological homeostasis. Non-specific (innate) immunity. Complement system. 31. Antigens as inducers of the immune response. Haptens. 32. Antibodies. Structure, classes and function of antibodies, antigenic determinants of antibodies. 33. Antigen – antibody reaction. Immunological methods. 34. Cellular basis of the immune response. Cells involved in immune response. Т lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, phagocytic and antigen-presenting cells. 35. Human alloantigens. ABO(H) system. Lewis system. Lectins. Biosynthesis of the A,B, H and Lewis antigens 36. Human alloantigens. Rhesus system. Immunological conflict between mother and fetus. Origin and biological importance of alloantigens. 37. Cellular interactions during the immune response. Activation of antigenpresenting cells. Activation of T lymphocytes. Activation of B lymphocytes. 38. Phases in differentiation of immunocompetent cells. Primary and secondary immune response. 39. Genetic control of the synthesis of antibodies and T-cell receptors (TCR). 40. Major histocompatibility complex (МНС). Transplantation immunity. 41. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of anti-tumor defense. 42. Regulation and control of the immune processes. Genetic control of the intensity of the immune response. Immune tolerance. Immunity theories. 43. Reproductive biology. Sex determination and differentiation 44. Reproductive biology. Cytological basis of sexual reproduction. Meiosis 45. Reproductive biology. Gametogenesis. Spermatogenesis. Characteristic features of male gametes. Origin of germ cells. 46. Reproductive biology. Oogenesis. Molecular mechanisms of oocyte maturation. Characteristic features of mature ova. 47. Reproductive biology. Fertilization. External fertilization and mechanisms for blocking polyspermy. Completion of fertilization. 48. Reproductive biology. Fertilization. Internal fertilization in mammals. Differences between external and internal fertilization. 49. Reproductive biology. In vitro fertilization. ICSI method. Atypical forms of reproduction. 50. Individual development. Embryonic period in vertebrates. Body plan formation, role of grey crescent in amphibians, cleavage. Regulative and mosaic types of development. 51. Individual development. Formation of the blastula. Gastrulation. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of gastrulation. Embryonic induction. Elements of organogenesis. 52. Individual development. Embryonic development of mammals and human. Stem cells. Differentiation, differences between cells, cell memory. 53. Population biology. Phenotype, genotype and gene frequences. Hardy – Weinberg law. 54. Molecular evolution. REFERENCES MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF THE CELL. Alberts B., A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, P. Walter. 4th Edition. Garland Publ. Inc., New York, 2002. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY. Gilbert S.F. 8th Edition. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 2006. ESSENTIAL IMMUNOLOGY. Roitt I., P. Delves. 10th Edition. Blackwell, 2004. IMMUNOLOGY. Lydyard P., A. Whelan, M. Fanger. 2nd Edition. Garland Publ. Inc., New York, Abingdon, 2004, 2005, 2007. GENETICS. Fletcher H., I. Hickey, P. Winter. 3rd Edition. Taylor & Francis, New York, Abingdon, 2007. MODERN GENETICS. Ayala F.J., J.A. Kiger. 2nd Edition. Benjamin-Cummings, 1984. This syllabus is valid from the academic year 2010/2011 onward.