Biology Syllabus
advertisement

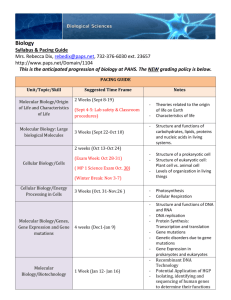
Biology Syllabus & Pacing Guide Mrs. Izamar Vargas-Lassalle, izamvargas@paps.net, 732-376-6030 ext. 23657 This is the anticipated progression of biology at PAHS. The NEW grading policy is below. PACING GUIDE Unit/Topic/Skill Molecular Biology/Origin of Life and Characteristics of Life Molecular Biology: Large biological Molecules Cellular Biology/Cells Suggested Time Frame 2 Weeks Notes - 3 Weeks (Sept 22-Oct 10) 2 weeks (Oct 13-Oct 24) - Cellular Biology/Energy Processing in Cells Molecular Biology/Genes, Gene Expression and Gene mutations 3 Weeks Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration - Structure and functions of DNA and RNA DNA replication Protein Synthesis: Transcription and translation Gene mutations Genetic disorders due to gene mutations Gene Expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Recombinant DNA Technology Potential Application of HGP Isolating, identifying and sequencing of human genes to determine their functions DNA manipulation techniques: PCR , Gel electrophoresis, and DNA 4 weeks - - 1 Week Structure and functions of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids in living systems. Structure of a prokaryotic cell Structure of eukaryotic cell: Plant cell vs. animal cell Levels of organization in living things - - Molecular Biology/Biotechnology Theories related to the origin of life on Earth Characteristics of life - - - Cellular Biology/Cell Reproduction Organismic Biology/Mendelian Genetics and Inheritance patterns 3 Weeks 4 Weeks o o o o o o o o o o o - - - Organismic Biology/Evolution and Population Genetics 3 Weeks (March 9-March 27) - fingerprinting Bacterial DNA Transformation Stem Cells Cell cycle Mitosis Meiosis Chromosomal number mutations Karyotype analysis Heredity and traits Monohybrid and dihybrid cross Human Genetics Inheritance pattern of sexlinked diseases Pedigree analysis Non-Mendelian pattern of inheritance: Incomplete and codominance History of Life ( a brief introduction by looking at patterns (clades)) Lamarck’s theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection Adaptations in organisms Types of SelectionDirectional, Stabilization, Disruptive Mechanisms of selection: Descent with modification Mechanism of Change; Mutation, Migration, Genetic drift, Natural Selection Genetic Variation: Mutation, Gene Flow and Sex Natural Selection, sexual selection and artificial selection Coevolution: Predatory/prey and parasite/host, Competitive species, Mutualistic Species Types and mechanisms and - Organismal 4 weeks (April 13-May 8) Biology/Ecology - - GRADING POLICY causes of speciation Macroevolution Evidence of common descent Population genetics, Hardy Weinberg equation and how natural selection alters the frequency of heritable traits. Ecosystems and Cycling of matter. Interdependence of organisms Flow of matter Interactions of organisms and their environment : Populations, communities and ecosystem, competition and symbiotic Relationships Biogeochemical cycles (carbon cycle, nitrogen Cycle, phosphorous cycle and water cycle) Negative impact of human activities on the environment 60%: TESTS (unit tests, quarterly exams, individual lab reports, large or long term projects, lab practicals) 30%: QUIZZES (quizzes, labs, group lab questions, short-term projects, webquests, small writing assignments) 10% PARTICIPATION (do-now assignments, homework, classwork, test review questions, classroom website blog assignments)