3 study
advertisement

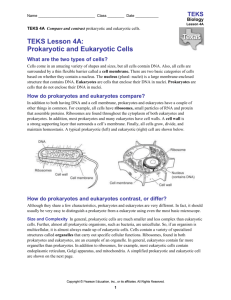
Chapter 3 Study Guide Microbiology (Bauman 2007) Objectives As you work through the activities and practice quizzes for this chapter, keep the following learning objectives in mind. Once you have mastered this chapter, you should be able to: * Describe the major processes of life and their presence in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and viruses. * Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the cell shapes and arrangements of bacteria, with examples as discussed in lecture. * Describe the composition, function, and relevance to human health of glycocalyces. * Distinguish between capsules and slime layers. * Discuss the structure and function of prokaryotic flagella. * List and describe four prokaryotic flagellar arrangements. * Compare and contrast the structures and functions of fimbriae, pili, and flagella. * Compare and contrast the cell walls of Gram-positive and Gram-negative prokaryotes in terms of structure and Gram staining. * Describe the clinical implications of the structure of the Gram-negative cell wall. * Compare and contrast the cell walls of acid-fast bacteria with typical Gram-positive cell walls. * Contrast types of archaeal cell walls with one another and with bacterial cell walls. * Diagram a phospholipid bilayer and explain its significance in reference to a cytoplasmic membrane. * Explain the "fluid mosaic" model of membrane structure. * Describe the functions of the cytoplasmic membrane as they relate to permeability. * Compare and contrast the passive and active processes by which materials cross the membrane. * Define osmosis and distinguish among isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions. * Describe prokaryotic cytoplasm and its basic contents. * Define inclusion and give two examples. * Describe the formation and function of bacterial endospores. * Describe the structure and function of ribosomes and the cytoskeleton. * Describe the composition, function, and importance of eukaryotic glycocalyces. * Compare and contrast prokaryotic cell walls and cytoplasmic membranes. * Contrast exocytosis and endocytosis. * Describe the role of pseudopodia in eukaryotic cells. * Compare and contrast the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. * Identify non-membranous and membranous organelles. * Compare and contrast the structure and function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella. * Describe the structure and function of cilia. * Compare and contrast eukaryotic cilia and flagella. * Describe the structure and function of ribosomes, cytoskeletons, and centrioles. * Compare and contrast the ribosomes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. * List and describe the three filaments of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. * Discuss the function of each of the following membranous organelles: nucleus, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, peroxisome, vesicle, vacuole, mitochondrion, and chloroplast. * Label the structures associated with each of the membranous organelles. * Describe the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and eukaryotic cells. Vocabulary Characteristics of life Growth Reproduction Responsiveness Metabolism Cellular structure Prokaryotes eukaryotes cocci diplococci streptococci tetrad staphylococci Neisseria gonorrhea Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococus pyogenes Staphylococcus aureus Rods (bacilli) Escherichia coli Bacillus anthracis Bacillus cereus Spiral Vibrio Spirochete Axial filament Vibrio cholerae Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme Disease) Treponema pallidum (syphilis) Glycocalyces Capsule Slime layer Flagella Monotrichous Peritrichous Serotype E. coli O157:H7 Chemotaxes Phototaxes Motility Fimbrae Pili Bacterial cell wall Gram positive wall Gram negative wall Peptidoglycan NAM NAG Teichoic acid Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) endotoxin O-polysaccharide Lipid A Periplasm Archae Cytoplasmic membrane Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution Hypotonic solution Lysozyme Penicillin protoplast lysozyme spheroplast Active Transport Group Translocation Nucleod Chromosome Plasmid Ribosomes 70s vs. 80s Inclusions Reserve deposits Volutin: Corynebacterium diphtheria Sulfur granules: Thiobacillus Carboxysomes: Cyanobacteria Endospores Sporulatin Germination Bacillus Clostridium