Name Class
advertisement

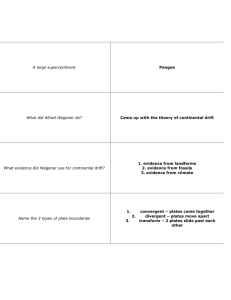
Name _______________________________ Class ______________ NB # ________ DATE ____________________ 1. Label each part of Earth Mantle lithosphere First thin part, Asthenosphere Where convection currents are Inner core Crust Outer core Continental and Oceanic Two “sub layers” 2. Define and give one example of each type of heat transfer. The following three different types of heat transfer are Convection, Radiation, and conduction. Convection is the transfer of heat energy by the movement of a heated fluid. When a fluid, a gas or liquid, becomes heated it becomes less dense and rises. As it rises and loses heat, it will become more dense and sink. This continual process will create a cyclical motion within the fluid creating the convection current. A second type of heat transfer is radiation. Radiation is when heat energy is transferred through empty space. Direct sunlight or UVA, UVB rays to heat the Earth is an example. Lastly, Conduction is the third type of heat transfer. This is when heat energy is transferred through direct contact of particles of matter. An example of conduction would be a pot of soup being heated. If a metal spoon is used to stir the soup and is left in the pot, it will become hot due to the direct transfer of the heat from the original source, through the liquid soup and pot, and to the spoon. 3. Compare and contrast Sea Floor Spreading and Subduction. Be sure to define and detail each. Sea floor spreading is when molten material rises from the mantle adding new crust to the ocean floor. Older material gets pushed to the sides causing the ocean floor to separate or spread. Subduction is when the ocean floor sinks back into the mantle. Older oceanic crust is denser and gravity will pull it down beneath the trench. This will then cause it to become forced into the mantle and melted. Similarities: Sea Floor spreading and Subduction 1. 2. Both involve movement of oceanic crust. Both involve molten lava. Differences: Sea Floor spreading and Subduction 1. 2. SFS is the buildup, Sub is the breakdown of oceanic crust. Crust material at SFS is less dense then crust at Sub. Magma 3. 4. 5. Both involve plate boundaries 3. 4. 5. cools quickly at SFS and creates pillow like rock. SFS is divergent plate movement, Sub is Convergent 4. Using drawings as well as explaining in complete sentences, define the three types of Plate Boundaries. Give one example of each. Three types are Transform boundaries, Divergent boundaries and Convergent boundaries. Transform boundaries are boundaries that slide past one another in opposite directions. Examples would be where earthquakes occur like the San Andreas Fault in Ca. Also Fractures may be formed. Divergent boundaries are two plates that move apart in opposite directions from one another. An example would be SFS or RIFT Valley with volcanoes Convergent boundary is when two plates come together resulting in a collision. Subduction is an example of this. They produce volcanoes, mountain ranges, and deep ocean trenches. 5. List all evidence that supports the idea of sea floor spreading. Harry Hess proposed the idea of SFS. Supporting his idea and evidence of SFS comes from molten material, magnetic strips of the earth and Samples of the oceanic floor. Molten material found along the MOR is pillow shaped rocks that only form when magma erupts and hardens quickly under water. Magnetic poles of Earth have been reversed throughout Earth’s history. As iron in the molten material line up toward the poles, new rock forming records the current magnetic position. This creates band of magnetized rock that match up from each side of the ridge. Lastly, Samples collected from the Earth’s oceanic crust support that samples found further away from the ridge were older than those found close to the ridge. 6. List all the layers of the earth, and briefly describe each. Use diagrams as well as written words to answer. Starting at the outermost layer of the Earth there is the crust. It is composed of both the continental crust and the oceanic crust. Next there is the Mantle which contains a rigid layer, the lithosphere directly under the crust and the asthenosphere which has a thick viscosity of molten material. This material, in the Asthenosphere, gets heated by the Earth’s core and creates the convection currents that drive the plates of the Earth. Below the Asthenosphere, solid mantle extends to the Earth’s core. Below the Mantle is the outer core followed by the inner core. The outer core is a thick liquid material of iron and nickel. The inner core is believed to be a dense ball of nickel and iron due to the pressure of the upper core keeping the material compacted in. The core is believed to be slightly smaller than the size of the moon. 7. Using the diagram below, explain what is occurring in the mantle as well as how this directly relates to continental drift, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes. Incorporate plate boundaries as well. In the mantle there is a constant convection in the Asthenosphere due to the heat from the mantle and core. This constant heating and cooling of the mantle causes the plates of the earth to constantly be in motion. This supported Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift. Continental drift was the theory that one giant continent, Pangaea began to break apart. The pieces of earth slowly moved to where they are today. Wegener used mountain ranges and other features to support this, the way the continent fit together, evidence from fossils and evidence form climate. Today there is proof that when one plate moves, it affects another. This is known as continental drift. When continental drift occurs, plates are moving in various directions and forms. Plates can have convergent, divergent or transform boundaries due to the plate movements. When two plates converge or come together the possibility of mountains and volcanoes being created can occur. This is due to the force of the colliding plates and the rising of the land where one plate rises over another or the buckling of one due to the pressure. Diverging plates are going to separate and possibly allow molten material to rise up such as the mid-oceanic ridge or the Rift valley in Africa. Again, the movement of one plate will affect the others, so as two are moving away, it is going to cause others to shift as well. Lastly, Transform plates are going to be sliding next to one another. These plates will have the greatest chance of creating earthquakes in and around the plate boundaries. California is an excellent example of this as 2 large plates and one smaller plate are all together. This supports the high occurrence of earthquakes in this area. 1. Scientists who study the forces that make and shape the Earth are called. a. Geneticists b. geologists c. Ecologists d. Biologists. 2. Mountains and bodies of water help make up the _____ of the Earth a. Core b. mantle c. Crust d. Asthenosphere 3. Oceanic crust consists of dark dense rock called. a. Granite b. basalt c. marble d. slate 4. All of the following are parts of the mantle EXCEPT. a. Lithosphere b. crust c. Asthenosphere d. lower mantle 5. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: a. Asthenosphere b. Lithosphere c. Inner core d. Continental crust 6. The spinning of the ____, made of iron and nickel, explains why the Earth has a magnetic field. a. Inner Core b. Asthenosphere c. Outer Core d. Lithosphere. 7. The picture is an example of: a. Convection b. conduction c. radiation d. condensation 8. The picture is an example of: a. Convection b. conduction c. radiation d. condensation 9. Convection current form because of a difference of ____ and ____ in a fluid. a. Volume and density c. volume and temperature b. Temperature and density d. Mass and volume 10. In earth, the convection currents are found in the _____. a. Asthenosphere b. Lithosphere c. outer core d. inner core 11. The movement of energy from a warmer object to a cooer object is known as. a. Heat transfer b. Temperature c. chemical reaction d. density 12. During sea floor spreading, magma rises through a_____. a. Trench b. ridge c. mountain range d. fault 13. To prevent the ocean floor from widening, the older rock sinks into the earth at a ________. a. Trench b. ridge c. mountain range d. fault 14. What drives the motion of the earth’s plates? a. Ocean b. Wind c. tectonic plates d. convection currents 15. Plates moving apart will form a ______ a. Trench b. Ridge c. mountain range d. None of the above 16. Continental crust moving together will form a _______ a. Trench b. Ridge c. mountain range d. None of the above 17. When plates slip past each other in opposite directions a _______ a. Trench b. Ridge c. mountain range d. None of the above 18. The magnetic strips found on the ocean floor tell us that: a. There are magnets in the sea floor b. Some parts of the sea floor have magnets in them and others do not c. Some parts of the sea floor were added during periods of magnetic field reversal d. That the magnetic strips cause the reversal of the magnetic field.