Cellular Respiration
advertisement

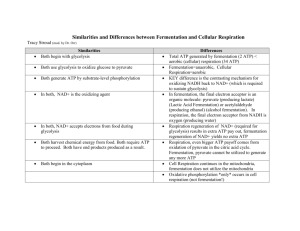
Overview of Respiration - aerobic = requires oxygen to occur (ex: cellular respiration) vs. anaerobic = does not require oxygen to occur (ex: glycolysis and fermentation) Organic Compounds Glycolysis Oxygen Present Cellular Respiration (aerobic) ATP ATP Oxygen Absent Fermentation (anaerobic) No ATP Glycolysis - takes place in the cytoplasm of cells - always occurring and does not require oxygen - occurs before cellular respiration or fermentation - 2 ATP are used to start process - breaks down glucose into a net of 2 ATP, 2 pyruvate, and 2 NADH - Why is there a net of 2 ATP? - products (pyruvate and NADH) enter either cellular respiration or fermentation - Efficiency = 3.5 % (only 2 ATP are made) Overview of Cellular Respiration = releases chemical energy from sugars and other organic compounds to make ATP when oxygen is present - occurs in the mitochondria of cells Cellular Respiration – 2 Stages - occurs in the mitochondria 1) Krebs Cycle = produces molecules that carry energy to the second stage of cellular respiration - occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria - pyruvate from glycolysis is broken down - some ATP and other energy forms are made - carbon dioxide is given off as a waste product 2) Electron Transport Chain - occurs in the inner membrane of a mitochondria - made of proteins - uses energy from Krebs cycle and oxygen to make ATP - water and heat are given off as waste products Efficiency of Cellular Respiration = 66% (38 ATP are made) Equation for Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + (sugar = glucose) 6O2 (oxygen) 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) Fermentation - starts with glycolysis - does not make ATP (but allows glycolysis to continue) Types 1) Lactic Acid Fermentation - occurs in your muscle cells - produces lactic acid, results in muscle fatigue and cramps - produces NAD+ that goes back to glycolysis 2) Alcoholic Fermentation - produces alcohol (ethyl) and carbon dioxide - produces NAD+ that goes back to glycolysis Lactic Acid Fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation Importance of Fermentation - produces food products we use (bread, cheese, yogurt) - allows glycolysis to continue - microorganisms in digestive tract break down food (allows more nutrients to be absorbed)