Cellular Respiration, Oxidation/Reduction, and
advertisement

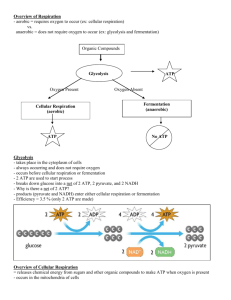
Cellular Respiration, Oxidation/Reduction, and Glycolysis Day 43 Double Cellular Respiration can be divided into three metabolic processes that are, glycolysis and fermentation, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Each of these processes occurs in a different and specific region of the cell. Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol. The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation via the electron transport chain, occurs in the mitochondrial membrane. In glycolysis, the 6-carbon sugar glucose molecule, is broken down into two molecules of a 3-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This change is accompanied by 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules. In the Krebs Cycle, the pyruvate molecules are transported into the mitochondria, and loses carbon dioxide to form acetyl-CoA, a 2-carbon molecule. When acetyl-CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide in the Krebs cycle, chemical energy is released, which is then transformed in the form of NADH, FADH2, and ATP. In oxidative phosphorylation, the electron transport chain allows the release of the large amount of chemical energy stored in reduced NAD+ (NADH) and reduced FAD (FADH2). The energy released is transformed into the form of ATP. NADH + H+ + 3 ADP + 3 Pi + 1/2 O2 → NAD+ + H2O + 3 ATP FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 1/2 O2 → FAD+ + H2O + 2 ATP Fermentation occurs when oxygen is not present. Therefore, the pyruvate is metabolized. In fermentation, glycolysis makes it possible for ATP to be continually produced in the absence of oxygen. By oxidizing the NADH produced in glycolysis, fermentation regenerates NAD+, which can take part in glycolysis once again to produce more ATP. http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cellresp/overview.html http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/bio%20101/bio%201 01%20lectures/cellular%20respiration/cellular.htm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nGRDa_YXXQA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AdtAu5JgOV0 Oxidation/Reduction Redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions include all chemical reactions, in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. This can be either a simple redox process, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide, or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane. Or a complex process, such as the oxidation of glucose in the human body, through a series of complex electron transfer processes. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. There is small riddle that might help you to remember what oxidation is, and what reduction is. "OIL RIG" = Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/biobookenzym.html#Oxidatio n http://chemistry.about.com/od/imagesclipartstructures/ig/Science-Clipart/RedoxReaction-Example.htm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e6Xxz-VBE6s Glycolysis Glycolysis is a sugar break; because glyco=sugar and lysis=break. ATP is used in glycolysis, to break glucose into 2 molecules. It is used in cellular respiration, located in the cytosol. http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/cellresp/simpleover.gif http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5eMW4b29rg 1. Why is cellular respiration necessary? 2. Where does cellular respiration mostly take place? 3. What is fermentation? 4. What is oxidation, and what is reduction? 5. What is the process of glycolysis? 1. All cells use oxygen to convert raw food products into energy they can use for health. In the process they make a bi-product which is carbon dioxide and waste material. If there was no cellular respiration the cell would die, because they would be lacking the oxygen needed for food conversion, and they would have no means of getting rid of their waste products. 2. The mitochondria 3. An anaerobic (without oxygen) cellular process, in which organic foods are converted into simpler compounds, and chemical energy (ATP) is produced. 4. Oxidation is losing of electrons, and reduction is the gaining of electrons. 5. Glycolysis is the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvate. The glycolysis process is a multistep metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol. Vocabulary Cellular Respiration-- A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell, in which biochemical energy is harvested from organic substances, and stored as energy carriers for use in energy-requiring activities of the cell. Oxidation-- A chemical reaction in which there is a loss of electrons. Reduction-- A chemical reaction in which there is a gain in electrons. Glyco-- sugar Lysis-- breaking Glycolysis-- the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvate. It occurs in the cytosol.