Honors Biology: Cellular Respiration & Photosynthesis Study Guide
advertisement

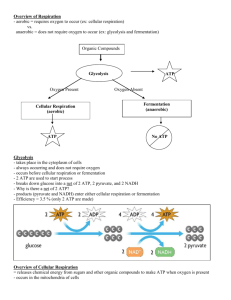
HONORS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 6 STUDY GUIDE Name__________________________________________________Per_____ Label the Mitochondrion. Refer to p. 63 Label: outer membrane Intermembrane space cristae matrix 1._____________________________________ 2._____________________________________ 3._____________________________________ 4._____________________________________ Fill in the blanks. Refer to p. 90 Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Organelle it takes place Reactants Products Type of organisms that do this Comparing Breathing and Cellular Respiration pp.90-1 Write a “B” if the statement refers to breathing and “CR” if it refers to cellular respiration. _____take oxygen into your lungs _____glucose is burned _____bonds in ATP store energy from the breakdown of glucose _____breathe out carbon dioxide _____molecules of C6H12O6 are rearranged FILL IN THE NUMBERS: Cellular respiration can produce up to ________ATP molecules for each glucose molecule, a capture of about ____________% of the energy in the glucose. Why are brains called “glucose hogs?” The average person burns _____________-kcal /day. How many calories (little “c”)?_______________ Honors Biology Chapt. 6 Study Guide p. 2 REDOX REACTIONS: LEO GOES GER What are redox reactions? What does REDOX stand for? What happens to the electrons in oxidation?______________ In reduction?______________ What ion accompanies the transferring e-?______________________ In the two boxes below write if the process is OXIDATION or is REDUCTION. NADH AND ETC p. 92 What do we know about NADH? a. what kind of molecule is it?__________________________ b. what vitamin is it made from in the cells?___________________ c. what is its job?____________________________ d. what is its oxidized form?________________ e. how many electrons can this electron carrier actually carry?______ f. what is a good name for an enzyme that removes hydrogen atoms from a molecule?_____________ What do we know about the ETC? a. what does ETC stand for?_____________________ _____________________ ___________________ b. What would you call a molecule at the top of the staircase?__________________________________ c. what would you call a molecule at the bottom of the staircase?_______________________________ d. What types of reactions pass the electrons from carrier to carrier?______________________ e. What molecule picks up this energy that is given off ?_______________ (HINT: 3 letters) OVERVIEW OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION p. 93 Fill in the chart GLYCOLYSIS Occurs where in cell? Starting molecule(s) Ending molecule(s) Purpose: PYRUVATE OXIDATION CITRIC ACID CYCLE OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION Honors Biology Chapt. 6 Study Guide p. 3 GLYCOLYSIS pp. 94-5 Fill in the missing information Is glycolysis anaerobic or aerobic?___________ Overall Reaction: 2 ADP 6-C molecule: It took ______ATP to start the reaction. ____ATP were formed for a NET of ______ATP made. 4 ADP 2 3-Cmolecules: 2 3-C molecules of: NOTE: This ATP is formed by substrate-level phosphorylation (no membrane needed). There are actually 9 steps from the start to end, but we will not learn all of these. We will simply call these compounds that form between the : _______________________. ENERGY SUMMARY: ENERGY INVESTMENT PHASE: Is ATP needed or made here?__________ Where do the phosphates go? ENERGY PAYOFF PHASE: Is ATP needed or made here?__________ How many ATP are produced?_____net?____ How many NADH are produced?________ Is this considered a high or low yield of energy for a cell? Why? OXIDATION OF PYRUVATE: “Cut and Groom” p. 96 1. What functional group is “cut” from pyruvate?____________ 2. What gas is it released as?_______________ 3. NAD+ is reduced to ________________. 4 The enzyme called ______________-is added (grooms) to the 2-C compound to form ________________________________. 5. What are these steps preparing the pyruvic acid to now be able to go?__________________________ Label: Acetyl-CoA pyruvic acid NADH CO2 Coenzyme A Honors Biology Chapter 6 Study Guide p. 4 CITRIC ACID CYCLE pp. 96-7 Page 97in the You pick the colors Lose H Add H What is the total number of NADH molecules generated during the complete breakdown of glucose to six molecules of CO2? (HINT: glycolysis + pyruvate oxidation +citric acid cycle)_____ Honors Biology Chapter 6 Study Guide p. 5 OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION (USING ETC AND CHEMIOSMOSIS) p. 98 Label the following diagram: intermembrane space ATP H2O matrix P NADH O2 1. What are the two electron carriers?______________________ and ______________________ 2. What is the final electron acceptor?_________________________ 3. What product forms when the electrons and and H+ join this final electron acceptor?_________ 4. As the e- are picked up by the ETC, where do the H+ go?_________________________________ 5. The build-up of H+ ions makes a concentration gradient. The H+ ions then move through what structure to cross the membrane?_________________________________________ 6. This movement causes the ATP synthase to rotate which generates energy for the formation of ADP + P = ____________. Read p. 99 chemicals that disrupt Cellular Respiration Rotenone Oligomycin Where it binds Action is causes Cyanide Honors Biology Chapters 6 Study Guide p.6 TOTALS Read p. 100 Fill in the total ATP’s formed (net) from each process Glycolysis _______ Substrate level phosphorylation_______ Oxidative phosphorylation _______ __________________________________ TOTAL ________ FERMENTATION Read pp. 100-101 1. Is fermentation anaerobic or aerobic?________ NOTE: Fermentation is necessary for it will regenerate NAD+. NAD+ is needed as an electron acceptor, or the reactions of cellular respiration will not proceed. LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION 1. What organs in your body undergo lactic acid fermentation?________________________ 2. Under what conditions would your muscles undergo lactic acid fermentation?_________ 3. How does lactic acid feel in the muscles?_________________ 4. What happens to this lactic acid?___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What would the dairy industry use lactic acid for?_____________________________________ ALCOHOL FERMENTATION 1. What organisms undergo alcoholic fermentation?___________________ 2. What two products are made when these organisms break down pyruvate?_____________________ 3. Why don’t the yeast die of alcohol poisoning?______________________________________________ 4. Why do the yeast die in the wine vat?____________________________________________________ TYPES OF ANAEROBES Contrast obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes READ p. 102 EVOLUTION CONNECTION Because glycolysis is the most widespread metabolic pathway found in Earth’s organisms today, what does this suggest about how long ago this process evolved? Section 6.15 Is glucose the only fuel consumed for cellular respiration?____________ How does the yield of ATP from fats compare to that of carbohydrates?___________