Teacher/Librarian Collaborative Unit Planning
advertisement

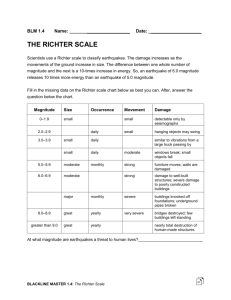
Teacher/Librarian Collaborative Unit Planning Suzanne Carmody –Teacher Rachel Finch – Teacher Librarian Earth Science - Geology Widefield High School Unit of Study Standards Addressed: Earth Science –(Standard 3) The theory of plate tectonics helps to explain geological, physical, and geographical features of the earth. (Standard 8) Natural hazards have local, national and global impacts (volcanoes, earthquakes, tsunamis, hurricanes, thunderstorms, etc.. ISTE – (Standard 2) Students use digital media and environments to communicate and work collaboratively, including at a distance, to support individual learning and contribute to the learning of others. (Standard 3) Students apply digital tools to gather, evaluate, and use information. (Standard 4) Students use critical thinking skills to plan and conduct research, manage projects, solve problems, and make informed decisions using appropriate digital tools and resources. Resources (include URLs): Virtual Earthquake www.sciencecourseware.org Geology labs online United States Geological Survey (USGS) www.usgs,gov Content Area Essential Questions, Goals & Objectives: Students will analyze and synthesize data. Students will determine earthquake location. Students will calculate epicenter using triangulation. Students will determine Richter’s magnitude. Students will read latitude and longitude from a map. Students will evaluate information from a recent earthquake. Description of Culminating Task: Students will work cooperatively to complete the virtual earthquake activity, explaining how epicenters are determined (triangulation). Students will work independently on an earthquake simulation to calculate how epicenters are determined. Students will take an online quiz to assess understanding. Students will complete a worksheet evaluating information from the USGS. Assessment: Earthquakes Epicenters and Magnitudes worksheet Online quiz Haiti Earthquake worksheet Extra Credit activity Responsibilities: Teacher Reserve computer lab and laptops. Assist students Assess Earthquakes Epicenters and Magnitudes worksheet. Oversee administration account to view student assessment. Responsibilities: Librarian Complete simulation online Edit Earthquakes Epicenters and Magnitudes worksheet. Create Haiti Worksheet. Assist students Assist in assessment of worksheet and quiz. Proposed Learning Activities: Virtual Lab Cooperative learning Independent work Internet exploration and evaluation on recent earthquake. Instructional Strategies: Cooperative learning Independent study of reading, interpreting charts/graphs. Following instructions Computer skills Resource Distribution: Lab reservations Laptop computer reservations Earthquakes Epicenters and Magnitudes worksheet. Haiti Worksheet Planning Times: February 3 8:20 – 9 a.m., February 8 8:25 – 9 a.m. Lab Time Needed: 1 class period Computer on Wheels needed for 1 class period Evaluation Being an elementary teacher I was stretching myself teaching high school science, but I thoroughly enjoyed the experience. Suzanne Carmody and I worked very well together and made a great team. The students were actively engaged in the laptop simulation of an earthquake and worked well in cooperative learning groups. The second day the students completed the quiz and analysis independently and seemed to enjoy the tasks. Many of the students chose to complete additional simulations for extra credit. Below are the objectives and assessment results from the quiz: Learning Objectives Learning Outcome 1 Estimating distance between epicenter and recording station GOOD . Overall, students scored 86%* on this objective. 97% of students could read S-P lag time on a seismogram (Question 1) 97% of students could interpret a travel time curve (Question 3) 69% of students understood the relationship between distance and S-P lag time (Question 9) 2 Determining Richter's magnitude GOOD . Overall, students scored 86%* on this objective. 94% of students could read wave amplitude on a seismogram (Question 2) Students achieved 73% success in using Richter's nomogram (Questions 4, 5, & 6) 91% of students understood the relationship of distance and amplitude to magnitude (Question 10) 3 Reading Latitude and Longitude from a map EXCELLENT . Overall, students scored 91%* on this objective. 100% of students could read wave points to the nearest degree (Question 7) 83% of students could estimate the minutes between degree lines (Question 8) Below is Suzanne Carmody’s evaluation of the collaborative lesson: The geology lesson using computer technology to explore, analyze, and evaluate earthquakes and their epicenter location was taken to a much higher level this year because of Rachel. I feel that the students were able to understand the basic and advanced version of "Virtual Earthquake" much better this year than in years past. The students were able to take the knowledge gained and applied through the technology and research and better understand the recent Haiti earthquake. The students' experiences through the entire lab process was more advanced and knowledgeable than in past years with similar lessons. Suzanne Carmody Science Department 719-391-3157 Widefield High School Name________________________________________________Period______Date_______________ Lesson: Earthquakes, Epicenters, and Magnitudes (San Francisco Virtual Earthquake) Page # Question 1A What type of seismic wave arrives first? How many seconds does each line on the graph represent? Explain how you can tell this from the graph. What is meant be the ‘S-P’ interval? What are the S-P intervals? Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Approximately how many kilometers does a S wave travel in one second? 1B 1C 1D 3 4A 4B 4C 4D 5B What is the value of each line of distance on the graph? How can you tell? What are your distances? Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 What are the units for distance on the graph? Look at the map of the epicenter. Do your three circles intersect in exactly the same spot? Should they meet in one place? Why? 5C When the three circles meet at one spot, what is the spot called? 5D What factors may affect the accuracy of this method? 7A What is the magnitude of an earthquake? 7B How big does an earthquake measured on the Richter scale have to be to be felt by people? How would you describe maximum amplitude? 4E 5A 7C 7D 8A 8B 8C 9A Can maximum amplitude be below the zero line as well as above it? What magnitude is a standard Richter earthquake? How much amplitude does a “Standard” earthquake have? If the Richter magnitude goes from 3 to 4, by how many mm does the maximum amplitude increase on the seismogram? How much is each horizontal line worth for the amplitude? 9B 10 What is the maximum amplitude for each of your stations? (Don’t forget to estimate between lines.) Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 What is your value? (Type in your value and CLICK on [Confirm Magnitude]. *If your Richter magnitude is correct, you will get a message congratulation you. If it is incorrect, you will have to remeasure and reenter your figures. Extra Complete the other Virtual Earthquakes and submit your certificates. (Southern Credit California, Japan Region, and/or Mexico) Recent Eathquakes in BAJA – California. Retrieved 5 Feb. 2010. http://pasadena.wr.usgs.gov/images/cahist_eqs.gif Name_____________________________________________________Date_______________Period________ Haiti Earthquake Directions: 1) Go to www.usgs.gov and type Haiti in Search USGS. 2) Click Magnitude 7.0 HAITI REGION 3) Read information on the tabs: Details, Summary, and Map. Complete the following questions/activities. 1) What was the magnitude of the Haiti earthquake?_______________________________ 2) Where was the epicenter of the earthquake? Lattitude__________________________________Longitude__________________________________ 3) List the locations of the four stations and the distances from the earthquake. Station Location Distance from earthquake (km) 4) How many people were Killed?_____________________________Injured?___________________________ Displaced?____________________________________ 5) What two plates did the Haiti earthquake occur between? ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 6) According to the USGS how many aftershocks were located and at what magnitude did they range? Aftershocks____________________ Magnitude_______________________ 7) Click on the Map tab and then the ShakeMap. Complete the chart below, reading the Intensity Scale. City Santo Domingo Saint Marc Port-Au-Prince Perceived Shaking Potential Damage