Unit Essentials-Thinking Like a Historians
advertisement

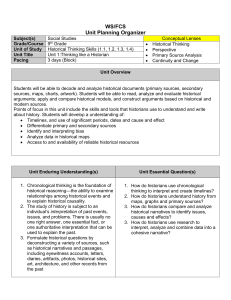
UNIT ESSENTIALS “Thinking Like a Historian” Subject(s) Grade/Course Unit of Study Unit Title Pacing Social Studies 9th Grade Historical Thinking Skills Unit 1:Thinking like a Historian 3 days Key Concepts Historical Thinking Perspective Primary Source Analysis Continuity and Change Unit Overview Students will be able to decode and analyze historical documents (primary sources, secondary sources, maps, charts, artwork). Students will be able to read, analyze and evaluate historical arguments; apply and compare historical models, and construct arguments based on historical and modern sources. Points of focus in this unit include the skills and tools that historians use to understand and write about history. Students will develop a understanding of: Timelines, and use of significant periods, dates and cause and effect Differentiate primary and secondary sources Identify and interpreting bias Analyze data in historical maps Access to and availability of reliable historical resources Unit Enduring Understanding(s) 1. Chronological thinking is the foundation of historical reasoning—the ability to examine relationships among historical events and to explain historical causality. 2. The study of history is subject to an individual’s interpretation of past events, issues, and problems. There is usually no one right answer, one essential fact, or one authoritative interpretation that can be used to explain the past. 3. Formulate historical questions by deconstructing a variety of sources, such as historical narratives and passages, including eyewitness accounts, letters, diaries, artifacts, photos, historical sites, art, architecture, and other records from the past Unit Essential Question(s) 1. How do historians use chronological thinking to interpret and create timelines? 2. How do historians understand history from maps, graphs and primary sources? 3. How do historians compare and analyze historical narratives to identify issues, causes and effects? 3. How do historians use research to interpret, analyze and combine data into a cohesive narrative? Topics Essential Factual Content Lesson Essential Questions Atlas Map Political map Physical map Cardinal directions BC/AD: BCE/CE What is geography? Timeline/ Chronology Cause & Effect Cause & Effect What makes an event significant? What is History? Political Economic Social Technology Culture Primary Source Secondary Source Context Theory Model Research Analysis How do historians evaluate the past? World Map Determining Bias &Historical Theory How is time measured? How do context and perspective effect interpretation of past events?