OVER-EXFOLIATION
advertisement

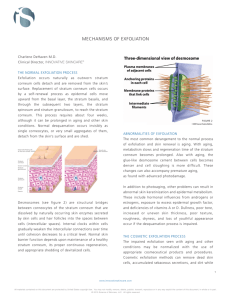
OVER-EXFOLIATION Dr Des Fernandes The Shirnel Clinic Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa. In order to understand the intricate ramifications of exfoliation, one needs to know some details about the epidermis. The epidermis is that superficial layer of the skin that lies on the deeper dermis. In the dermis there are fibroblasts, collagen and elastin fibres, nerves and blood vessels all lying in a jelly-like substance called the intercellular matrix. The epidermis is about 0.1 to 0.2 mm thick and comprises four distinct layers (see diagram 1): 1. The stratum germinativum: the basal layer of cells (keratinocytes) that are in contact with the dermis and from which virtually all the cells of the epidermis arise. The cells are anchored to the basement membrane (that divides the epidermis from the dermis) by minute clusters of fibres called hemi-desmosomes. These cells are either keratinocyte stem cells, that serve the function of creating more keratinocytes, or differentiating keratinocytes that will lose their hemi-desmosomes and gradually migrate towards the surface of the skin. These are the functional cells of the epidermis and their destiny is to die and thereby create the protective film that is totally responsible for the health of the skin. Another form of protection comes from the melanin in the cells, which is produced by the melanocytes that lie in close relationship to the basal keratinocytes. 2. The stratum spinosum: as the basal cells are replaced by new cells, they move upwards and become larger. This layer is called the spiny layer because of the apparent spines joining the cells together. In fact these are the fibres connecting cells together and they are called desmosomes. Desmosomes have the function of keeping the cells in contact with each other. Stratum spinosum cells are metabolically active and they are nourished by the dermis via the fluid between the cells. As the cells get closer to the surface, their nourishment becomes compromised and they also change shape and become flatter. At the same time important changes occur which are all essential for the ultimate development of effective cells in the stratum corneum. The nuclei of the cells are modified and virtually disappear by the time the cells reach the stratum granulosum. 3. The stratum granulosum: the cells are now spindle shaped and they have distinct granules at their periphery, which distinguishes them from the other layers of the epidermis. These granules are in fact the agglutination of compounds (e.g. ceramides) that will give protective and waterproofing properties when they are extruded from the cell as it migrates into the stratum corneum. These extrusions are called lamellar bodies and contain replicated layers of water and oil soluble chemicals, which we call lipid bi-layers. 4. The stratum corneum: the corneocytes1 are flattened and surrounded by lamellar bodies, which coalesce to create an envelope around each cell. This is the active chemical and waterproofing complex that fills the space between the cells and prevents substances from easily getting into the skin. It is particularly effective against water-soluble chemicals. This barrier also prevents water from evaporating from the body through the skin. If it weren’t for this layer then we would melt in water and evaporate in hot climates. There are significant changes in the corneocytes as they migrate up to the surface to prepare them for the confrontation with the harsh, dehydrating environment. In the beginning, corneocytes are well anchored to each other by desmosomes to ensure that this protective film is secure. Finally, when they are on the surface, the desmosomes break and the cell can be desquamated. By then the cell is extremely flat and no longer functional. It generally takes about three to four weeks for a cell to grow from the basal layer till the time that it is desquamated. In darker skinned people the horny layer cells maintain their melanin and, as a result, increase the natural photo-protection of the skin (equivalent to about SPF 14 on average). Because of the density of the layers of cells and the lipid bi-layers, the horny layer also has a photoprotective effect even in pale-skinned people equivalent to about SPF 2. The thickness of the horny layer also reduces the depth to which UV rays may penetrate the skin. The horny layer also protects us from physical injury and reduces the force by acting as a mini shock absorber. With this knowledge it is easy to understand that we all need a healthy, reasonably thick horny layer to keep environmental toxins out, reduce the danger of solar irradiation and also maintain the normal hydration of the skin and, eventually, of the body. Now all of this happens in the space of about 0.01 to 0.02 mm and about 14 layers of cells! WHEN SHOULD WE EXFOLIATE? There is a serious and widespread misconception about the value of exfoliation. Most people believe the surface of the skin is composed of dead, useless cells that make the skin look dull, prevent the skin from “breathing” and can clog up the follicles. In reality these “dead” cells are the mature functional cells of the skin. They are there for a special purpose. There is no doubt that desquamated corneocytes do mix with sebum and can create plugs in the follicles that can then cause comedones and acne. In people with photo ageing the stratum corneum becomes excessively thickened, and the skin takes on a dry, rough texture. The cells are kept on contact with each other for a prolonged time by the desmosomes. It seems that the basal keratinocytes respond to the irradiation by setting up processes whereby the total growth cycle is lengthened by the horny cells staying on the surface of the skin for as much as three weeks longer than usual. This is obviously an unhealthy state of affairs and to treat this problem we have to first of all stop the abuse from of sunlight, and secondly, to reduce the thickness of the stratum corneum. This is a good indication for exfoliation of the horny layer. This thickened horny layer will also interfere with the penetration of any of the therapeutic preparations (containing vitamin A and antioxidants chiefly) to treat photo ageing. So if you intend to treat someone with a photo-damage, it is sometimes useful to start off with a mild exfoliation so that the active ingredients of your therapeutic skin care can penetrate and exert their effects. However, once the initial exfoliation has been done, then it should be repeated with great care for this may actually aggravate the damage and also exaggerate the side effects of the therapeutic skin care regime. Once a scientific skin care regime is started, the horny layer will return to normal thickness of its own and needs no further exfoliation. In cases of acne, one needs to reduce the surface flaking cells that line the follicles that may mix with the sebum and cause comedones and, hence, acne. The horny layer itself does not need exfoliation. The client should be instructed to gently massage the involved areas with an ultra mild exfoliant, which should just remove the very surface cells and allow them to be washed away before they can fall into the follicles and aggravate the condition. Alternatively, a mild AHA product may be used to “polish” the surface of the skin. HOW CAN WE BEST ACHIEVE SAFE EXFOLIATION: I believe we should avoid the harsh scrubbing exfoliants that seem to be found in most skin care ranges. They destroy too much of the horny layer and may even expose the stratum granulosum. Remember that the stratum corneum is only 2 hundredths of a millimetre thick so it is easily removed. A simple scratch on the skin surface may remove almost all the stratum corneum. It is bewildering to think of how fragile this layer is and yet the health of our skin is totally dependant on it. I also believe that harsh peeling systems should be avoided except under special circumstances. If the therapist want to do exfoliation by using a peeling system, then I believe simple “soft” chemical peels (e.g. low dose TCA, alpha or beta hydroxy acids etc) are superior to strong concentrations of acid or the harsh granular plant peels that mechanically abrade away the skin as well as peel it chemically. If the therapist does a manual exfoliation then they should make sure that the abrading granules are barely perceptible and the client always feels comfortable during and after the treatment. Steam or heated towels are also useful. The client may do the exfoliation themselves and again I would suggest the mildest abrading packs, or simple light alpha or beta-hydroxy creams or gels. One should stress to the client that this should not be done excessively, and also not forever and ever! The concomitant use of topical vitamin A helps to minimise the potential negative effects of over-exfoliation by promoting both the growth of the epidermis, as well as increasing the hydration of the skin. We have all seen the examples of chronic over-exfoliation by well-known therapists and clients using AHAs : their skin looks thin, lifeless and un-natural even though it might be smooth! Many therapists make the mistake of suggesting exfoliation to clients with normal skin with the belief that the client’s skin can be made more radiant and look fresh. We all know that immediately after exfoliation, the client will have a healthy pink glow with a lovely well-moisturised appearance and the client will be complimented on their skin. It looks great and indeed, some well-known skin care “experts” heartily endorse weekly exfoliation to maintain the best appearance. However, let’s look at reality. The client did not have an excessively thickened horny layer and so the exfoliation has removed some important mature functional cells with their surrounding lipid bi-layers. The healthy pink moisturised cells that we see on the surface after exfoliation are actually cells that have not yet been properly prepared to encounter air and the environment. The client may be pleased, but the cells are shocked by this sudden exposure to the horrible environment. They cannot truly perform their function of protection because they themselves require protection! More water is lost through the skin and these cells cannot rapidly adapt to this new, harsh environment and after a few days the skin feels dry and the surface lacks lustre. Bearing in mind how good the skin looked immediately after the exfoliation, it seems that the obvious answer is to repeat the exfoliation and remove these offending dead cells! And so it goes on. What else has happened? Well, the horny layer is thinner, so the physical protection has been removed and the photo-protective effects have been diminished: the skin is more vulnerable to damage. The waterproofing barrier has been compromised and so water can easily evaporate through the skin and as a result the deeper layers of the epidermis become de-hydrated. The chemical “messages” from the surface to the deeper layers of the epidermis beg for the cells to make a thicker horny layer to preserve the normal degree of hydration! This impaired horny layer also means that chemicals may get into the skin easier and so, for example, if the client decides to use a spray at home with an insecticide or some other noxious chemicals, then those harmful chemicals will get into the skin in greater concentrations. The same is true for any other environmental pollutant. Do you want to expose your client to that unseen danger? The net result of repeated or over-exfoliation of healthy skin is, despite the healthy appearance, significant exposure to environmental toxins, free radicals, dehydration and interference with the normal physiology of the skin. No only that, but the inevitable exposure to light makes the skin more likely to become photo-damaged. As skin care therapists, are we not supposed to make our clients skin healthier, well hydrated and more durable to exposure to light and environmental pollutants? I believe that the intelligent use of exfoliation is important but that exfoliation should be an uncommon way to treat skin and should not be part of the routine care of healthy well-nourished skin. A sensible skin care range actually makes exfoliation unnecessary and we should rather concentrate on treating our clients and ourselves in a scientific way to keep the horny layer as thick and smooth as it normally should be. 1 The cells of the stratum corneum (horny layer of the epidermis).