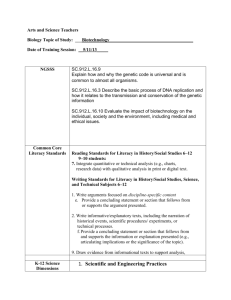
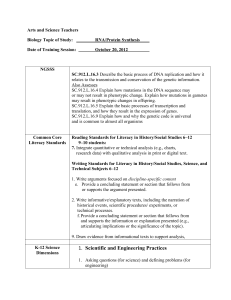
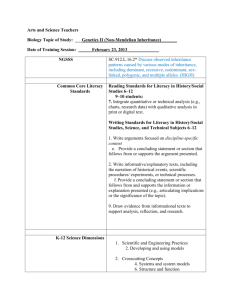
Example assessment & marking criteria Assessment type: Text
advertisement

Assessment type: Subject: Subject learning objectives: (NB: this will change to learning outcomes in 201430): Assessment task: Task description: Example assessment & marking criteria Text analysis and designing learning sequences EML306 English Curriculum: Pedagogies in the primary years This subject will develop and consolidate students’ understanding of English content knowledge in the strands of language, literature and literacy with a focus on the Primary years of schooling. Students will engage in learning experiences that promote their ability to critically analyse texts for content, structure and language features. They will engage more deeply with contemporary theories of literacy learning and teaching, and learn a range of pedagogical strategies, including the use of technological innovation for comprehending, critiquing and constructing multimodal and digital texts in classrooms. Students will learn how to design sequences of learning which reflect a balanced approach to literacy teaching and draw on the NSW K-10 English Syllabus. Students will critically engage with, discuss and apply theories of literacy learning and teaching. Students will explain connections between relevant theory, current issues and pedagogical practices. Students will utilise a range of technologies, digital tools and ICTs to design sequences of learning and to communicate their own learning. Students will utilise a range of curriculum and syllabus documents, resources, and pedagogical strategies to design balanced literacy learning sequences that address the needs of learners from diverse backgrounds. Students will demonstrate knowledge of the language structures and features for a range of more complex texts. Designing Literacy Learning For Primary Students (Years 3-6) In this task students will select and analyse three texts appropriate for primary learners (years 3-6), and use one of these texts as the basis for designing a sequence of learning that develops meaning making and text construction, and reflects the principles of a balanced literacy program. Part 1: Choosing and Analysing Texts Students must choose three different text types (e.g. narrative, persuasive text, information report, explanation, poetry) and three different text modes (e.g. written text, graphic text, film or video, etc). These texts must reflect the cross-curriculum priorities of the National Curriculum (Sustainability, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures and histories, Asia) and be appropriate to the interests and abilities of learners in years 3-6. The texts will be analysed for their structural and language features, for their content, and for their potential for teaching literacy across the curriculum. The analysis will include: 1. An explanation of the structural and language features (including visual) of the text using an annotated extract to exemplify points made. 2. A critical and comprehensive discussion of the content of the text. 3. A discussion of how the text could be used as part of a balanced literacy program and in a cross curricular context. 4. Reference to relevant language and literacy learning theory, including the Four Resources Model and Multiliteracies (where appropriate). Part 2: Designing Learning Sequences Using one of the texts as a starting point, students will design a sequence of three 45 minute lessons that develop learners’ understanding of the text (its structural and language features, and its content) and text construction skills. Students will also write a short 800 word justification of their planning decisions in which they will discuss how they have incorporated multimodality, support for EALD students, and assessment. This justification must be supported with references to subject content and readings. The lessons will include: 1. The intended learning outcomes (related to NSW K-10 English Syllabus). 2. The resources needed to support learning and teaching. 3. The use of appropriate approaches and models for teaching and learning literacy (e.g. The Four Resources Model and the Curriculum Cycle for text construction). 4. A description of the explicit teaching strategies and learning activities, including those to support learners from diverse backgrounds and those who have English as an additional language or dialect (EALD). 5. An assessment plan identifying specifically what will be assessed (linked to the learning outcomes), and how it will be assessed (i.e. the tool that will be used). 6. A clear progression of understanding and skills across the three lessons. Marking criteria Part 1: Choosing and analysing texts Structural, language and visual features are accurately identified and described. Discussion of text content reflects critical engagement. Discussion of text use reflects understanding of balanced literacy teaching and cross-curricular potential. Understanding of relevant theory is apparent and explicitly referred to. Part 2: Designing Learning Sequences Lesson plans include appropriate learning outcomes for the text and level, appropriate resources, and an assessment plan. An understanding and application of appropriate approaches/models is apparent. Lessons include appropriate teaching strategies and learning activities to develop learners’ understanding of text features and skills in meaning making and text construction. Lessons include explicit support for EALD learners. Lessons demonstrate progression of skills and knowledge of text features and skills in meaning making and text construction. Justification clearly discusses teaching decisions with reference to subject readings. Marking criteria & standards of performance Criteria HD DI CR PS A range of complex structural language and visual features are consistently and accurately identified across different text types. The features are described using complex meta-language that is sustained across most text types. Text content is analysed using more sophisticated critical literacy practices. The practices are coherently synthesised in the discussion. A range of simple and more complex structural, language and visual features are accurately identified for most types of text. Few errors in identification are evident. The features are described using more complex metalanguage. Text content is analysed using a number of simple critical literacy practices. These are used discretely in the discussion. Simple structural, language or visual features relevant to the text type are identified. Some errors in identification are evident for some text types. The features are described in basic terms with the use of appropriate metalanguage. Text content is described rather than analysed. There is limited use of critical literacy practices resulting in a more superficial discussion of the text. Description of 2-3 teaching ideas for using the text. Some evidence of links to elements of balanced literacy, and to at least one KLA beyond English. Accurately identify and describe the structural, language and visual features of a range of types of text. A range of complex structural, language and visual features are consistently and accurately identified across all text types. The features are clearly described with consistent control of complex meta-language. Analysis of text content reflects critical literacy practices. Text content is analysed using a range of sophisticated critical literacy practices. These have been skilfully synthesised in the discussion. Discussion of text use reflects knowledge of the principles of balanced literacy teaching, and describes the crosscurricular potential. Sophisticated and confident understanding of balanced literacy teaching is apparent in a comprehensive range of suggestions for text use. Potential for integrating literacy learning in multiple KLAs is discussed. Metalanguage from the subject content is skilfully and confidently used. Theoretical concepts are synthesised and skilfully integrated into the discussion. A range of relevant references are cited. Wide range of suggestions for text use reflects a sound understanding of balanced literacy. Suggestions include some ideas for including literacy learning in more than 2 KLAs beyond English. A range of ideas for using the text is described. These ideas reflect an understanding of balanced literacy and relate to more than one KLA beyond English. Metalanguage from the subject is confidently used and attempts at synthesis are evident. Theoretical concepts are mostly successfully integrated into the discussion. A range of relevant references are cited. Metalanguage from the subject is used with some control. Theoretical concepts are discussed discretely with support from more than 3 different references. Citations are accurately formatted. All lesson plans have appropriate learning outcomes that reference the English Syllabus. Wide range Most learning outcomes are appropriate and reference the English Syllabus. Resources are varied, meet the lesson Most lessons have more than one appropriate learning outcome and most reference the English Syllabus. Relevant theory is explicitly referred to. Lesson plans include appropriate learning outcomes for the text Discussion of the text appropriately uses some metalanguage from subject content to demonstrate engagement with theoretical concepts. Draws on at least 3 different references with accurate referencing formatting. Each lesson plan has at least: one appropriate learning outcome that references the NSW English K-10 of resources that reflect differentiation and meet the lesson focus. The assessment plan identifies multiple assessment opportunities, and includes considered and detailed information about what is assessed and how information will be gathered and recorded. The Curriculum Cycle and Four Resources Model are skilfully and explicitly used to frame teaching points and learning activities for text construction and making meaning from texts. focus and some reflect differential needs of children. The assessment plan identifies a range of opportunities with clear information about what will be assessed and how information will be recorded. Resources are varied in type and are appropriate for the level and lesson focus. The assessment plan identifies one assessment opportunity per lesson, with some information about what is to be assessed and how information will be gathered and recorded. All lessons explicitly develop the Curriculum Cycle for text construction. All lessons incorporate evidence of the Four Resources Model in the choice of teaching points and learning activities. All lessons explicitly demonstrate the use of the Curriculum Cycle for text construction and some elements of the Four Resources Model for making meaning in teaching points and learning activity choices. Lessons include appropriate teaching strategies and learning activities to develop learners’ understanding of text features and skills in meaning making and text construction. All lessons include clearly described strategies and activities that are varied, engaging and appropriate for the lesson outcomes and demonstrate skilled application in a planning context. Lesson choices demonstrate a thorough understanding of text features and skills needed for both making meaning and text construction. All lessons include a variety of strategies and activities to engage learners, and achieve lesson outcomes. Teaching points are clearly described and link to lesson outcomes. There is clear evidence that text features and skills required for making meaning and text construction are fully understood. Most lessons include a range of strategies and activities that are clearly described, and appropriate for the age level and lesson outcomes. A sound understanding of text features and skills needed for making meaning and text construction is apparent in planning choices. Lessons include explicit support for EALD learners. Multiple strategies and learning activities that reflect culturally responsive pedagogies are skilfully Multiple strategies and learning activities that reflect culturally responsive pedagogies are integrated Incorporation of at least one strategy and one learning activity that reflect culturally responsive pedagogies. and level reflecting Syllabus documents, appropriate resources, and an assessment plan. An understanding and application of appropriate approaches/models is apparent. Syllabus, at least 4 suitable resources, and an assessment plan that identifies at least one opportunity for assessment with some information about what is to be assessed and how information will be gathered and recorded. At least two lessons explicitly demonstrate the incorporation of elements of the Curriculum Cycle for text construction, and some elements of the Four Resources Model for meaning making in some teaching points and learning activities. All lessons incorporate at least 1 teaching strategy and 1 learning activity that describe what teacher and learners will be doing in the lesson. Strategy and activity choices are appropriate for the age level and the outcome of the lesson, and demonstrate a basic knowledge of text features and skills needed for making meaning and text construction. At least one teaching strategy or learning activity demonstrates familiarity with culturally and Lessons demonstrate progression of skills and knowledge of text features and skills in meaning making and text construction. Justification clearly discusses teaching decisions with reference to subject readings. integrated into all lessons. An understanding of how to differentiate learning is apparent. Clear and carefully designed progression of skills and knowledge is evident within and across all lessons. Planning and teaching decisions are clearly discussed and justified with a high level of insight into the theoretical understandings and applications that underpin the decisions. A range of pertinent references are accurately cited. into most lessons. Some attempt to differentiate learning is has been made. Clear progression of skills and knowledge is evident within and across most lessons. There are some lapses in continuity and connection between some elements of lessons. Planning and teaching decisions are discussed and justified with relevant examples. Relevant theoretical underpinnings are discussed with sound understanding. A range of pertinent references are accurately cited. linguistically responsive pedagogies. Some progression of skills and knowledge is evident within and across 2 lessons. There are lapses in continuity and connection within and between some lessons. A progression of knowledge or skills is evident in teaching strategies and learning activities within at least 2 lessons and across 2 lessons. A range of planning and teaching decisions are identified and justified. Some linking to relevant theory and examples from lessons. More than 3 accurately formatted and relevant references are used to support ideas. The student can identify and justify some planning and design decisions made. Some examples from the lesson plans are used to demonstrate identified decisions. The justification draws on at least 3 accurately formatted references for support.