Electrochemistry Worksheet: Equilibrium & Corrosion
advertisement

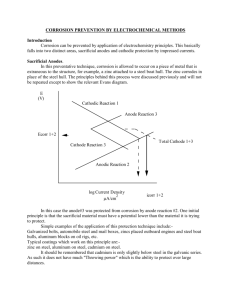
Chem 160 In-Class Worksheet 21 Feb 2008 A. A cell has a standard emf of +0.177 V at 298 K. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction if 1. n = 1? at 25oC, log K = nEo/0.0592 V log K = (1)(0.177 V)/0.0592 V = 2.99 K = 102.99 = 977 2. n = 2? log K = (2)(0.177 V)/0.0592 V = 5.98 K = 105.98 = 9.54 * 105 3. n= 3? log K = (3)(0.177 V)/0.0592 V = 8.97 K = 108.97 = 9.33 * 108 B. At 298 K, a cell reaction has a standard emf of +0.17 V. The equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is 5.5 * 108. What is the value of n for the cell reaction? Again, at 25oC, so we can use the equation log K = nEo/0.0592 V n = log K (0.0592 V/Eo) =log (5.5 * 108) (0.0592 V/0.17 V) = 3 3 mol electrons are transferred in this reaction. C. Magnesium metal is used as a sacrificial anode to protect underground pipes from corrosion. What is a “sacrificial anode”? Used to protect a metal from oxidation. As long as there is an electrical connection between the metal being protected and the sacrificial anode, it serves as an anode/electron donor so that the electrons in the oxidation process will come from the sacrificial anode rather than from the metal itself. You want to be sure that the metal used as the sacrificial anode is oxidized more easily than the metal you want to protect. An iron object is plated with a coating of cobalt to protect against corrosion. Does the cobalt protect iron by cathodic protection? Explain. No, it does not. Comparing the reduction potential of cobalt (-0.29 V) with the reduction potential of Fe2+(-0.41 V), the iron is oxidized more easily. Since this is the case, the iron will be oxidized first, and it would not be protected by the cobalt.