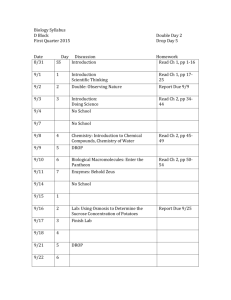
The state educational institution of the higher
advertisement

The state educational institution of the higher vocational training OMSK STATE TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY “Concurred by” Dean of machine-building faculty ___________ YE. N. Yeremin __________________2009. Confirmed by: Pro-Rector for Academic Affairs ___________ A.V. Myshlyavtsev __________________2009. The PROGRAM of entrance tests in the form of interdisciplinary exam (IDE) for training under Master’s degree programmes in a direction 280200.68 - « Environment Protection » The program 280212.68 "Monitoring of quality the environment and ecological instrument making » 2009 1. QUESTIONS OF INTRODUCTORY TESTS Section: «Fiziko-chemistry of solids» 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. The first law of thermodynamics. Its basic formulations. Нeat. Work. Internal energy. Thermal and calorific properties. Application of the first law of thermodynamics to chemical processes. Thermochemistry. Hess' law. The consequences that derive from the Hess' law. Their use for definition the thermal effects of chemical reactions. Dependence of thermal effect on temperature. Kirchhoff's law. The second law of thermodynamics. Its essence and the basic formulations. Mathematical expression of the second law of thermodynamics. Carnot cycle. Entropy. A statistical property. Entropy and thermodynamic probability. Entropy calculations. Absolute value of entropy. Planck's postulate. Characteristic functions - criteria of system balance and a direction of spontaneous processes. First and second order transition. Clapeyron-Clausius equation. Heterogeneous multicomponent multiphase systems. Gibbs' phase rule. Physicochemical analysis. Unicomponent and two-componental systems. Examples. Constitutional diagram. Eutectics. Lever rule and Alekseyev’s rectilinear diameter. Solutions. A general characteristic. Balance: a liquid solution - saturated vapour. Raul and Henry's laws. The ideal and extremely diluted solutions. The osmotic, cryoscopy and ebullioscopy phenomena. The quantitative description. Definition of molecular weight. First class and second-class conductors. Electrolytes (weak, average, strong). Electrolytic dissociation. Arrhenius theory. The Ostwald's dilution law. A central tenet of the theory of strong electrolits Debaj - Hjukkel - Onzagger. Strong electrolytic conductivity. Reversible electrodes. Their classification. Standard electrode potentials. Volta series of metals. Galvanic cells. Electromotive forces. Their measurement. Nernst equation. Galvanic cell thermodynamics. Kinetic classification of chemical reactions. Molecularity and a reaction order. Dependence of chemical reaction velocity on concentration of reacting agents. The mass action law. Elementary chemical reactions. The basic kinetic equations. Difficult reactions (reversible, parallel, consecutive). The overall performance. Dependence of chemical reaction velocity on temperature. Van't Hoff's Rule. The Arrhenius theory of active collisions. 14. 15. The general principles of catalysis: catalysis and chemical balance. Activity and selectivity of catalysts. Catalysis and chemical reaction velocity. The reasons of accelerating action of the catalyst. The homogeneous catalysis theory (Kobozev - Shpitalsky). The acid-base catalysis. Heterogeneous catalysis. Its features. Section: «Surface phenomena» Definition of dispersoidology. Classification of disperse systems according to: -a aggregative state, interphase interaction, dispersion. 2. The phenomena connected with participation of colloidal particles in thermal movement. Diffusion. Molecular movement. Its thermal nature. Einstein and Smoluhovsky's theory. 3. Passage of an optical beam through disperse systems. The theory of dispersion of light and Rayleigh’s equation. Tyndall effect. 4. Research techniques of colloid systems, based on the phenomenon of dispersion of light. Nephelometry. Turbidimetry. Ultramicroscopy. Electronic microscopy. 5. Adsorption on a solution-gas border. A surface-tension. A structure of an adsorbed layer. 6. Surfactant and surface-inactive substances. Influence of a structure and the molecular size of surfactants on adsorption on a solution-gas border. Duclot-Traube rule. 7. Adsorption on a firm body - gas border. Physical and chemical adsorption. Empirical relation and the quantitative description. The equations of an equilibrium isotherm of monomolecular adsorption: Henry, Langmuir, Friendlich-Bedeker. 8. The equation of an isotherm of polymolecular adsorption, its analysis. Definition of a adsorbent specific suppression. 9. Capillary condensation. An overall picture of capillary condensation (according to Zigmondi). 10. Adsorption from solutions. Molecular and ionic adsorption. Ion-exchange adsorption. Its features. Gapon and Nikolsky works. 11. The account of specific adsorption according to Stern. Recharge of DEL. Electrokinetic potential. 12. Volume and weight methods of measurement of adsorption. The Poppy-Ben-Bakr scales and « quartz crystal scales». 13. The electrokinetic phenomena: electro-osmosis, electrical endosmosis, the inverse phenomena. 14. Structure of a double electric layer (DEL). The overall performance and history of development the ideas about DEL structure. 1. 15. A structure of micell. Stability and coagulation conditions of colloids. A coagulation threshold. Critical potential of a surface. Mutual coagulation of colloids. Section: «Environmental chemistry» 1. Sources of chemical pollution and the general laws of distribution of chemical polluting substances in biosphere. Local, regional and global pollution. Stability, transformation and accumulation of pollutants. 2. Physical and chemical processes in atmosphere. A structure and atmosphere composition. An atmospheric dust and aerosols, their classification, sources of formation and the characteristic. Atmosphere pollutants and a thermal mode of a planet. 3. Gases behaviour in atmosphere. Carbonic oxide (II) and carbonic oxide (IV). Formation sources, chemical and biochemical balance of carbonic oxide (IV). Greenhouse gases. A greenhouse effect and its consequences for environment. 4. Ozone. An ozone layer, its role in a planet life. Technogenic changes of an ozone layer. The reasons of occurrence of "ozone holes". Consequences of concentration reduction of ozone in atmosphere. Ozone Depletion Potential and ozone layer protection. 5. Atmosphere in cities. Primary and secondary pollutants. A smog of London and Los Angeles types. The reasons, the mechanism and the chemical reactions leading to occurrence secondary pollutants. 6. Acid rains. Sources of acid deposits. Chemical processes of formation and acid deposition influence on a person and environment. Acid rains prevention. 7. Chemistry of water pollution. Classification and the characteristic of natural water. Impurity, oxidability, rigidity, dry residue. Quantity of the dissolved oxygen, microorganisms in water. 8. Influence of oil and oil-product on the water environment. Ways of receipt and a consequence. Synthetic detergents in water. Pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, organochloride hydrocarbons, phosphorus-containing organic compounds. 9. Nitrogen role in water systems. Nitrification, ammonification, denitrifying process. Phosphorus and its role in water systems. Anthropogenous eutrophication. Water body trophicity. Actions for prevention of eutrophication. 10. A structure and lithosphere composition. Aeration and soil formation processes. Soil - definition, features, structure, physical properties. The salt-water mode and soil buffering power A soil chemical compound and the factors influencing it. Acidity of soil and acidity kinds. 11. Soil salination, the reasons. Secondary soil salination and actions for its prevention. Anthropogenous pollution of soil (acid pollution, heavy metals, pesticides, radioactive elements). 12. The characteristic and recycling of waste. The organisation of solid wastes polygon. Reusing of a waste, recycling of toxic wastes. Cut waste. Dioxin issue, catching and neutralisation of dioxin. 13. Especially dangerous chemical compounds of an anthropogenous origin. The pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, benzapyrenes. Dioxins, orthanilinic acids, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals. Sources of their receiption and transformation in environment. 14. Radioactive isotopes in environment. Sources of an induced radioactivity in environment. Physical and biological half-life periods of a radioactive nuclide. Reactions in body tissue caused by ionising radiation action. 15. Foodstuff and food supplements. Pollution of a foodstuff at conservation and packing. Toxicity of commodity: preparations for dry cleaning and washing, organic solvents, varnishes and hygiene products. Section: «Basis of industrial ecology» 1. Atmosphere protection. Dispersion of impurity in atmosphere. Dry clearing of air and gases (cyclones, dust precipitation chambers). Process parametres of dust collecting. 2. Atmosphere protection. Dry clearing of air and gases: louver dedusters, rotational, dynamic dedusters (smoke exhausters). Their work principle and a scope. 3. Atmosphere protection. Wet clearing of gases (scrubbers). Hollow (scrubbers with atomizers) and packed-bed scrubbers. The device. Work principle, a scope. Bases of calculation of constructions. 4. Atmosphere protection. Wet dedusters: scrubbers Вентури, centrifugal scrubbers. The device, an action principle, a scope, bases of calculation of constructions. 5. Recycling and neutralisation of a gaseous waste. Gas scrubbing devices, their kinds. The device, work principle, a scope, bases of calculation of constructions. 6. Recycling and neutralisation of a gaseous waste. Classification of filters. The device, work principle, a scope, bases of calculation of constructions. 7. Sewage treatment by flotation. Essence of the method, a scope. Ways of sewage treatment by flotation. Flotation with allocation of air from a solution (vacuum, pressure head, airlift flotation). The scheme of pressure flotation installation, a work principle, a scope. 8. Flotation with mechanical dispersion of air. The scheme of flotation installation with an impeller. Flotation by means of porous plates. The device of flotation installation with porous caps. Chemical, biological, ionic flotation. 9. Adsorption sewage treatment. Sorbents. The scheme of adsorption system with consecutive injection of adsorbent. The scheme of counterflow adsorption system. The scheme of adsorption system with continuous action. Concept «a dead layer» of adsorbent. 10. Ion change sewage treatment. Essence of a method, a scope. Mineral and inorganic ionites. Properties of ion exchangers. The nomenclature of pitches. Regeneration of ion exchangers. 11. Schemes of ion exchange plant of periodic and continuous action. A principle of work of periodic installation. The scheme of installation with the alluvial filter. Lacks of installations of periodic action. 12. Extraction sewage treatment. Regeneration of extragent. The scheme of multistage extraction plant. A scope of liquid extraction. 13. A reverse osmosis and an ultrafiltration. Essence of methods, a scope. Reverse osmosis system: the elementary, with consecutive and parallel connection of modules. Method lacks. Membranes. 14. Electrocoagulation. The method characteristic. The technological scheme of sewage treatment by electrocoagulation. A scope, bases of calculation of constructions. 15. Electroflotation. An electrodialysis. Schemes of installations, a scope. Lacks of methods. Section: «Ecological biotechnology with microbiology elements» 1. Morphology of microorganisms. A chemical compound (water, fibers, carbohydrates, mineral substances, lipids). Types of nutrition and breath of microorganisms. 2. Variability of microorganisms (a mutation, dissociation, adaptation, transformation, updating). Influence of conditions of an environment. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Aerobic (spirit, lactic, propionate, oil-sour) decomposition of substances by microorganisms. Aerobic (oxidation of spirit, hydrocarbons, cellulose decomposition) decomposition of substances by microorganisms. Transformation of nitrogenous substances. Nitrification. Denitrifying process. Biological fastening of nitrogen in soil. Transformation of sulfur compounds, phosphorus compounds, iron compounds by microorganisms. Water microbiology. Seas and oceans microbiology. Air and soil microbiology. Mutual relation of microorganisms and plants. Technological bases of bioecological manufactures: prefermentative, fermentative, postfermentative stages. The biological agent, a substratum, environment, a product. Biological methods of sewage treatment. Aerobic processes. Anaerobic processes. Biological methods of a firm waste recycling. Bio-oxidation of gaz-air emissions. Classification of installations. Parametres of of air clearing installations. Biological production of hydrogen. Biofuel elements and bioelectrocatalysis. Biotechnology of metals: microbial leaching, metallurgy. Biosorption of metals from solutions. Beneficiation of ores. Section: «Monitoring of environment objects » 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Monitoring. The purposes and problems. Monitoring: global, national, regional. Features of monitoring programs. Monitoring systems; global monitoring systems on the environment condition (GMSEC); federal monitoring and control system (FMCS) on the environment condition; system of the automated supervision and the environment control (cities atmosphere) - SASEC (CA). Global monitoring systems (GMSEC). Stations of complex background monitoring (SCBM). Placing of stations. Supervision programs at stations. The international mode of potentially toxic chemical substances (IMPTCS) and its purpose for a choice of priority polluting substances. Global and regional polluting substances. Observation network over atmospheric air condition. Stationary sites, route sites, under plume sites. A principle of the choice of stationary sites location. Monitoring of the transboundary. 6. Threshold concentration in environment quality assurance. Sanitary-hygienic and ecological rating. Quality standards (MPC). Temporary standards. Differential and integrated indicators. Stream oriented characteristics of pollution sources: MPE, MPD. 7. The automated systems of SASEC (CA) type. Mobile hydrochemical laboratories (MHL) and their role in information reception for the system of the automated supervision and the environment control of water pollution (ANKOS-WP). 8. Observation network over water objects condition. Categories of observation sites, principles of their placing and the supervision program. Sampling selection. Sampling programs. Representative samples. Time and space representative samples. Ways of concentration averaging. Rules and precautions of air, water, soil, ground adjournment sampling. 9. Rules of snow cover sampling. Advantages of snow cover as air contamination indicator and the subsequent pollution of soils and superficial waters. 10. Chromatography. Spectophotometery and colorimetry. Essence of methods. Comparison of possibilities of methods in the analysis of environment objects. 11. Mobile laboratories of air analysis, their structure and possibilities. Chemical sensor controls-gauges as a basis of creation the new express methods. 12. Bioindication and biotesting methods. The used phenomena of biomagnification for an estimation of the water environment impurity. Bioindication and test objects in hydrobiological service of a network (FMCS). 13. The requirements to complex estimations. Accumulationof errors in a difficult analytical technique. Checking the importance of hypotheses. 14. Establishment of exact characteristics of the measurements executed with the certain technique. An estimation of accuracy of measurements. Definition of detection limits of polluting substance. 15. Estimation of measurement error. An estimation of a systematic component of measurement error. Drift revealing. Revealing of screwup on Q- and τ-criteria. 2. THE BASIC AND ADDITIONAL LITERATURE FOR PREPARATIONS TO ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS IN THE FORM OF IDE Section: « Physicochemistry of a solid substance» The basic literature: Zhuhovitskij A.A., SHvartsman L.A. Physical chemistry. M: Metallurgy, 2001. 2. Krasnov К.С, Vorobev N.K., Godnev I.N., etc. Physical chemistry. In 2 vol. М: the Higher school, 2001. 3. Зимон A.D. Physical chemistry, М: Chemistry, 2000; М: Agar, 2003. 4. Samokhin I.A. Physical chemistry, М: the Moscow State University, 2001. 5. Stromberg A.G. Physical chemistry. М: the Higher school, 2001. 6. Mushkambarov N.N. Physical and dispersoidology. М: GEOTAR-MED 2002. 7. Kireev V.A. A physical chemistry short course. М: Chemistry, 1985. 1. The additional literature: 1. Evstratova K.I., Kupina N.A., Malakhova E.E. Physical and dispersoidology. М: the Higher school, 1990. 2. Golikov G. A. Physical chemistry guideship. М: the Higher school, 1988. 3. Kuznetsov V.V. Physical chemistry and dispersoidology. М: the Higher school, 1976. 4. Glazov V.M. Principles of physical chemistry. М: the Higher school, 1988. 5. Gladkov V.M. Principles of physical chemistry. М: the Higher school, 1988. 6. Kochergin S.M., Dobrenkov G.A, Nikulin V.N, etc. A physical chemistry short course. М: Higher school.1978. Section: « Surface phenomena» The basic literature: Shchukin E.D., Pertsov A.V., Amelin E.A. Dispersoidology. М: the Higher school, 2001. 2. Mishustin A.I., Belousova K.F. Dispersoidology. М: MGUIE, 1999. 3. Kirovskaya I.A. Surface phenomena. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2001. - 180p. 4. Kirovskaya I.A. Dispersoidology. Super microheterogeneous and microheterogeneous disperse systems. Omsk: OmSTU, 2000. 5. Kirovskaya I.A. Chemistry. Colloid solutions. Omsk: OmSTU 2003.-217 p. 6. Kirovskaya I.A. Colloid solutions. Omsk: OmSTU, 2004. - 207 p. 7. Kirovskaya I.A. Adsorptive processes. Irkutsk: Publishing house IGU, 1996.-300p. (classified publication). 1. The additional literature: 1. Senicheva L.V., Argaeva V. A, Yankovets ZH.N. Surface phenomena. Adsorption. Khabarovsk, KhSTU, 1999. Section: «Environment chemistry» The basic literature: 1. Stepanovsky A.S. Applied ecology: Environment protection. Textbook for higher schools. - M. UNITI-DANA, 2003.-750p. 2. The person and environment of his dwelling. Chrestomathy. Textbook for higher schools on speciality 032300 "Chemistry"/ Under the editorship of G.V.Lisichkin, N.N.Chernov. –M. Mir, 2003 with. 3. Korobkin V.I. Ecology. Textbook for higher schools / V.I.Korobkin, L.V.Peredelcky.- Rostov-on-Don. Phoenix. 2003.-575 p. 4. Rozanov S.I. The general ecology. Textbook for higher schools on "Ecology" discipline for technical directions and specialities / S.I. Rozanov. - SPb; Lan, 2003. 288 p. 5. Ecology. Textbook for higher schools / V.V. Deniss, I.N.Lozanovsky, I.A.Lugansky,and others; under the editorship of V.V. Denisov. - M.: Rostov н/Д. March. 2004. -671 p. ' The additional literature: 1. Morli J. Replacement ozone-destroying substances applied as coolants / Morli J., T.Markina: M.: "Rostra-Dej", 2000. № 7. pp. 15,16. 2. Wilkis, Bryan. A strategic direction in a environment protection problem / B. Wilkis: M.: Ecology and the industry of Russia. 2000. - № 5.-pp. 15-16. 3. Menshikov V.V. Methods of an environmental contamination estimation. Studygiude to a lection course. M. Publishing house MNEPU, 2000, 59 p. Section: «Basis of industrial ecology» The basic literature: 1. Gridel T.Ye., Allenbi B.R. Industrial ecology. - М: UNITI-DANA, 2004. - 513p. 2. Golitsin A.N. The basis of industrial ecology. - М: Academy, 2004.-239 p. 3. Chelnokov A.A., Yushchenko L.F. The basis of industrial ecology. - Minsk: Higher schools. - 2001.-366 p. 4. Kalygin V.G. Industrial ecology. A course of lectures. - М: 2000. - 240 p. The additional literature: 1. Potapov A.D. Ecology: Textbook. М: Higher schools, 2004.-pp. 431-445 Section: «Ecological biotechnology with microbiology elements» The basic literature: Gusev M.V. Microbiology: Textbook for higher schools in a direction "Biology", etc. / M.V.Gusev, L.A.Mineev. - 4th edition - М: Academy, 2003. - 461 p. 2. Emtsev V. T. Microbiology: Textbook for higher schools. - М: Drofa, 2005. – 445 p. 3. Zagrebelny S.N. Biotechnology: in 2 vol./S.N.Zagrebelny; Novosibirsk State Univercity - Novosibirsk: NSU, 2001. - 445 p. 4. Lipunov I.N. The basis of chemistry and microbiology of natural and waste waters: Study guide / I.N.Lipunov; Ural timber academy. - Ekaterinburg: 1995.-212 p. 1. The additional literature: 1. A practical work on microbiology: Study guide for higher schools in a direction "Biology", "Microbiology", etc. / A.I.Netrusov, M.A. Egorova, L.M. Zaharchuk and others; under the editorship of A.I. Netrusov. - М: Academy, 2005/- 602p. Section: «Monitoring of environment objects » The basic literature: Ivanov P.V. Environment monitoring. Monitoring and recycling of wastes products. M: VTMITs. 2000. 2. Malyshev V.V., Krasilnikov M. N, Bobronnikov V. M. Satellite systems of monitoring. M:MASS. 2000. 556 p. 3. Scripko T.V. The basis of ecology. The basic laws of functioning of natural systems of a various rank: the course of lectures. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2000.-27p. 4. Scripko T.V. Properties of ecological systems and laws of their functioning: Tests on lectures. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2002.-27p. 5. Scripko T.V. Environment of our dwelling. Anthropogenous influence and its consequence: Study guide. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2005.-96p. 1. Non destructive testing and diagnostics: Reference book /V.V. Klyuyev, F.R.Sosnin, A.V. Kovalev, etc.; Under the editorship of V.V. Klyuyev. - 2 revised edition. - М: Mechanical engineering, 2003. - 656 p. 7. Blinov L.N. Wildlife management. Study guide / L.N.Blinov, I.L.Perfilova, L.V.Yumasheva. - М: Drofa, 2004. - 95 p. 8. Novgorodtseva L.V. Ecological monitoring. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2003. 9. Novgorodtseva L.V. Question and exercises on ecology. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2000. 10. Novgorodtseva L.V. An estimation of harmful substances influence on environment and ecological examination. Manuals. Omsk: Publishing house OmSTU, 2003. – 40p. 11. Tarasova N.P., Kuznetsova V.A, etc. Problem and questions in environment chemistry. M.: Mir, 2002.-368p. 12. Engineering ecology: Textbook for higher schools / V.T.Medvedev, V.V. Skibenko, A.K.Makarov, etc.; Under the editorship of V.T. Medvedev. - М: Gardarika, 2002. - 687 p. 13. Hutorsky M.D., Zvomensky, Rasskazov A.A. Monitoring and forecasting of geophysical processes and natural accidents. M: 1999.- 221p. 6. The additional literature: Protasov V.F. Ecology, health and environment protrection in Russia [Text]: textbook / V.F.Protasov. - 2 edition. - М: the Finance and statistics, 2000. - 671 p. 2. Timonin A.S. Engineering-ecological reference book: Study guide for specialities: 32.07.00-Environment protection and rational use of natural resources; 33.02.00engineering protection of environment/ A.S. Timonin; the Moscow state university of engineering ecology. - Kaluga: N.Bochkareva's Publishing house, 2003.Vol 3. -2003. 1019p. 1. Timonin A.S. Engineering-ecological reference book: Study guide for specialities: 32.07.00-Environment protection and rational use of natural resources; 33.02.00engineering protection of environment/ A.S. Timonin; the Moscow state university of engineering ecology. - Kaluga: N.Bochkareva's Publishing house, 2003.Vol 1. -2003. 914p. 4. Тимонин A.S. Engineering-ecological reference book: Study guide for specialities: 32.07.00-Environment protection and rational use of natural resources; 33.02.00engineering protection of environment/ A.S. Timonin; the Moscow state university of engineering ecology. - Kaluga: N.Bochkareva's Publishing house, 2003.Vol 2. -2003. - 880 p. 3.