Syllabus Outcomes Framework – Numeracy Links
advertisement

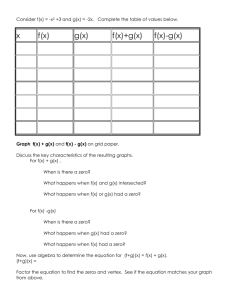
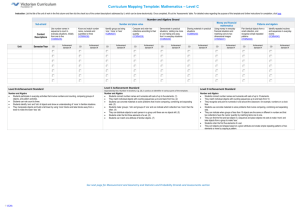
A ES1 Our place Two-dimensional space: - represent two-dimensional shapes using a variety of materials. Use precut shapes to create a picture of a house or a room. Position: - use everyday language to describe position. Locate and describe the position of objects on a walk around the school. B Me Data: - collect data about students. Create picture graphs of physical features such as eyes and hair colour. Length: - identify and describe the attribute of length. Measure body parts such as arm length, head circumference or height to compare lengths. C Changes Time: - sequence events in time. Describe the sequence of events relating to a school day. Time: Syllabus Outcomes Framework – Numeracy Links Stage 1 Stage 2 Local places Local environments Two-dimensional space: Position: -identify and names parallel, vertical - determine compass directions N, S, E, W; and horizontal lines. Identify and NE, NW, SE and SW given one of the name different lines in the directions. Describe the location of natural environment. features in NSW and Australia as a direction Position: from own local area. Three-dimensional space: - describe the position of objects using everyday language, including - name, describe, sort, make and sketch “left’ and “right”. Play action games prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and based on direction. spheres. Make a model of a building. Have several students sketch the building from different viewpoints. Identify the viewpoint from which the drawing was made. Our families Being Australian Two-dimensional space: Time: -identify two-dimensional shapes; - read and interpret simple timetables, identify and name parallel, vertical timelines and calendars. Identify significant and horizontal lines; identify lines of events and record on a timeline. Patterns and algebra: symmetry; create tessellating designs. Investigate badges and flags -generate, describe and record number from different groups; identify shapes patterns using a variety of strategies. and lines within badges and flags; Recognise and describe ostinato patterns in use flag designs to create tessellating music. designs. Time: -identify special days and dates on a calendar; name and order the months and seasons of the year. Growing and changing Data: - gather and record data using tally marks; display data using concrete materials and pictorial representations. Record the growth of © Department of Education and Training, Curriculum K–12 Directorate Mathematics K–6 programming support Effects of growth and change Time: - reads and records time using digital and analogue time Data: -interpret data presented in tables, column Stage 3 Living land Data: -read and interpret graphs with scales of many-to-one correspondence. Analyse information from graphs relating to rainfall and temperature. Length: - convert between metres and kilometres; millimetres, centimetres and metres. Convert measurement units in climate graphs. Identity Length : - record lengths using decimal notation. Investigate the relationship between the lengths of various body parts, such as length of an arm to the length of a finger, or the length of a foot to the height of a person. Fractions and decimals: - model, compare and represent commonly used fractions. Compare fractions parts in the colour and design of flags. Interconnecting growth and change Chance: - orders the likelihood of simple events on a number line from 0 to 1.Write statements predicting events and then order the Page 1 of 3 - name days of the week and seasons; tell time on the hour on digital and analog clocks. Relate events to time and day, ‘we go to library at ten o’clock on Tuesday’. a plant. Length: - use centimetres to estimate and measure length. Use a 10cm length to measure and record the height of a plant at various stages of growth. graphs and picture graphs. Constructs and interprets a column graph to measure lung capacity. D Healthy choices Data: - collect and interpret data. Organise data to represent the food that students eat in a day. Whole numbers: - count forwards to 20 from a given number. Count 20 jumps, hops, steps etc. Getting along Data: -display data using pictorial representation. Use drawings to display data about families. Chance: - recognise the element of chance in familiar daily activities. Use chance words such as’ I might play with my friend after school.’ E Our needs Whole numbers: - use the language of money when buying goods from the class shop. Three-dimensional space: - describe features of threedimensional objects. Choose appropriate containers for holding various objects and justify choice. Products and services Three-dimensional Space: - recognise three-dimensional objects in the environment. Design and construct a container for a nominated product. Volume and capacity: -identify and describe the attributes of volume and capacity. Fill and empty containers using comparative language to describe them as being half full, full or empty. Powering on Length: -use informal units to estimate and measure length. Use blocks to measure distance travelled by rolling Working together Time: - read and record time using digital notation. Write a script for a drama to be videoed and include digital timing for the video sequences. Chance - conduct simple chance experiments e.g. ‘how many different outfits will I have if I take four T-shirts and two pairs of shorts to my school camp?’ Products, services and systems Multiplication and division: - perform calculations with money. Provide students with catalogues to determine the total expenditure when purchasing multiple products. Fractions and decimals: - recognise percentages in everyday situations. Identify the percentages of different materials or ingredients used to manufacture various products. F Moving Patterns and algebra: - create and describe patterns. Create a pattern using different body movements. © Department of Education and Training, Curriculum K–12 Directorate Mathematics K–6 programming support Machines Data: - conduct surveys, classify and organise data using tables. Create a graph to compare different conductors of sound. likelihood of the event occurring on a number line e.g.’ I will be 160 centimetres tall when I am 12’; ‘Our dance group will perform at the Rock Eisteddfod’; ‘I will represent Australia at the Olympic Games’. Patterns and algebra: -describe a pattern in words in more than one way. Explore and describe number patterns through composition in dance and music. Making informed choices Data: - read and interprets graphs with scales of many-to-one correspondence. Investigate and interpret data relating to the electoral process, state and federal government. Global and social Issues Position:- use a variety of mapping skills. Use coordinates as reference points to locate continents, countries and capital cities or landforms. Fractions and decimals: - apply the four operations in reallife situations. Investigate monetary exchange rates of various countries. Physical phenomena Mass: - solves problems involving conversion of measurement units Time: Page 2 of 3 Three-dimensional space: - describe features of threedimensional objects using everyday language. Manipulate objects and describe using language such as, ‘this ball will roll because it is round’. a toy down an incline. Mass: -compare two or more objects according to mass. Make shot-puts from socks filled with sand. Compare the mass of the shot put against the distance that it could be thrown. Our stories Time: -name and order months and seasons of the year. Share stories related to seasonal changes ‘I went skiing in July which is winter’. Patterns and algebra: -create, represent and continue a variety of number patterns. Identify patterns in dance composition. Area: Key idea -estimate, measure, compare and record areas in square centimetres and square metres. Estimate and then measure an area of two square metres for movement and dance sequences. – use a stopwatch to measure and compare duration of events. Measure time as part of a fitness program. Our fleeting past Number: -read, represent and order numbers up to four-digits. Order historical events and dates. Position: - use simple maps to represent position and follow routes. Plot the journey of Captain James Cook on a world map. Traditions and heritage Time: - draw and interpret a timeline using scale. Create a timeline using a scale to represent key figures and events that have shaped Australia’s identity. Position: - use scale to calculate distances on maps where significant events in Australia’s history took place. Symbol systems Patterns and algebra: - describe a pattern in more than one way and determine a rule to describe the nth term in the pattern. Use geometric shapes to create and explain patterns, ‘one hexagon has six sides, and therefore ٱ hexagons will have ٱsides’. Two-dimensional space: -enlarge and reduce shapes and identify shapes that have rotational symmetry. Use understanding of the properties of 2D shapes when designing a product. Physical activity G No COG H No COG Understanding ourselves Time: -identify the day and date on a calendar. Use a calendar to identify days of significance for different cultures. Patterns and algebra: -create a pattern and identify missing elements. Use body movements to create a repeating pattern. Understanding each other Position: - locate objects on maps using coordinates. Use coordinates on maps to locate countries. Data: - create two-way tables to organise data comparing customs and religions of two countries. I Physical activity Physical activity Physical activity © Department of Education and Training, Curriculum K–12 Directorate Mathematics K–6 programming support Page 3 of 3