Earth Science
advertisement

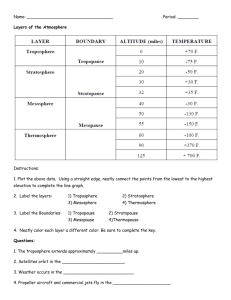
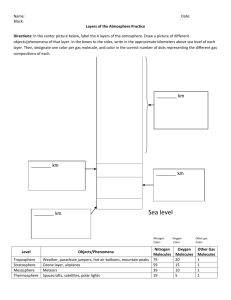
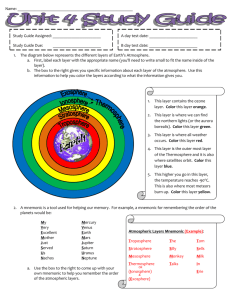
Earth Science Chapter 15 Section 4 A. Layers of the Atmosphere: The four main layers of the atmosphere are classified according to changes in temperature. Theses layers are the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere and the thermosphere. 1. The Troposphere: The lowest layer of the atmosphere. Tropo means, turning or changing. Conditions in the troposphere are more variable than any other of the layers of the atmosphere. The troposphere is where all weather takes place. The depth of the troposphere varies from between 16 Km at the equator to 9 Km at the poles. The shallowest of all the layers, the troposphere contains almost all of the mass of the whole atmosphere. The temperature within the troposphere decreases with altitude at a rate of 6.5 degrees C per 1000 m or 1 Km. At the top of the troposphere, the temperature begins to steady at about – 60 C. 2. The Stratosphere: The stratosphere extends from about 12 Km to about 50 Km above the Earth’s surface. Strato means layer or spreading out. The temperature in the lower stratosphere is about – 60 C. The temperature in this layer increases with altitude to about – 10 C at the top of the layer. Near the top of the stratosphere is the ozone layer. The ozone layer protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. 3. The Mesosphere: The mesosphere ranges from 50 Km to about 80 Km, where temperatures reach about – 90 C. Meso means middle The mesosphere has the coldest temperatures in the atmosphere. 4. The Thermosphere: The thermosphere extends from about 80 Km outward into space. There is no definite outer limit. Thermo means heat. The temperature within the thermosphere can reach 1800 C. The thermosphere is divided into two layers. a. The ionosphere: Ranges form 80 Km to about 550 Km. Energy from the sun causes gas molecules in this layer to become electrically charged, becoming ions. Radio waves bounce back to earth off the ions in the ionosphere. The Aurora borealis – occurs in this layer due to particles from the sun striking oxygen and nitrogen atoms causing them to glow. b. Exosphere: Exo means outer. This layer extends from about 550 Km to thousands of Km into space. Communication satellites orbit in this layer.