Notes 4 WKSTs Polyatomic Ions
advertisement

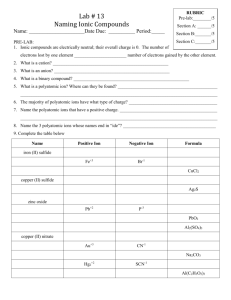
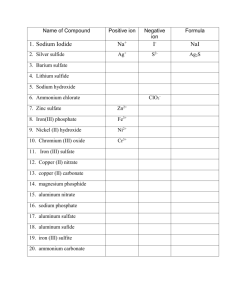
Notes/WKSTs Polyatomic Ions: Names and Formulas Name Date___________ Block_____ As the name suggests, polyatomic ions contain many atoms. A polyatomic ion is an ion consisting of two or more atoms chemically bonded together by covalent bonds and carrying a net electric charge. Remember the definition of an ion: an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more valence electron and has become a charged particle. The ions involved in the binary ionic compounds are single atoms that have become ions. Polyatomic ions are molecules that have become ions. Almost all polyatomic ions carry a negative charge. The original molecules have gained electrons. The exception is the ammonium ion, NH4+1. The ammonium ion is the only polyatomic ion that carries a positive charge. The ammonium ion is formed when an ammonia molecule, NH3, forms a coordinate covalent bond with a hydrogen ion, H+1. The ammonia molecule doesn’t lose electrons but rather gains a positively charged particle: the single proton of the hydrogen ion. It is this “additional” proton – or rather the additional positive charge – that gives the ion its +1 charge. Most of the polyatomic ions we will be using are called oxoanions which consist of oxygen covalently bonded to another nonmetallic element (called the characteristic or central element). For example, the oxoanion carbonate consists of a central carbon atom with three oxygen atoms: CO3-2. Sulfur, for example, forms the oxoanions sulfate, SO4-2 , and sulfite, SO3-2. Two or more different oxoanions of the same central element can be distinguished from each other by suffizes added to the stem name of the central element. The suffix -ate denotes the anion with the greater number of oxygen atoms; the suffix -ite denotes the anion with fewer oxygen atoms. The sulfate ion has four oxygen atoms; the sulfite ion has three oxygen atoms. The oxoanion with the greatest number of oxygen atoms is given the prefix per- and the suffix -ate. The oxoanion with the least number of oxygen atoms is given the prefix hypo- and the suffix -ite. For example: ClO4 –1 perchlorate ion ClO3 –1 chlorate ion ClO2 –1 chlorite ion ClO –1 hypochlorite ion Polyatomic Ions You MUST Know acetate C2H3O2 –1 (named after acetic acid HC2H3O2(aq)) ammonium NH4 +1 cyanide CN –1 carbonate CO3 –2 chromate CrO4 –2 dichromate Cr2O7 –2 hydrogen carbonate HCO3 -1 (also called bicarbonate) hydroxide OH –1 nitrate NO3 –1 nitrite NO2 –1 phosphate PO4 –3 sulfate SO4 –2 sulfite SO3 –2 (do not switch the order of the elements!) Writing Formulas Containing Polyatomic Ions The polyatomic ion behaves as a SINGLE UNIT. Treat the formula of a polyatomic ion as you would an ion of a single atom. Remember, the total number of positive charges must equal the total number of negative charges. There is zero net charge on the ionic compound. NEVER CHANGE THE FORMULA OF A POLYATOMIC ION: do NOT omit or change any subscript in the formula! Na +1 + OH -1 there is one positive charge and one negative charge; therefore, only one of each ion is required: NaOH Notice that the symbols of the ions involved are written with no space between them. Writing Na OH is incorrect. Na +1 + SO4 –2 there is one positive charge, but there are two negative charges; therefore, two positive ions are needed to balance the negative charges: Na2SO4 Again, notice the placement of the symbols of the ions and subscript. The formula is not written Na2 SO4. Be very careful when writing formulas of compounds. Na +1 + PO4 –3 NH4 +1 + Cl –1 there is one positive charge, but there are three negative charges; therefore, three positive ions are needed: Na3PO4 only one of each ion is needed: NH4Cl So far so good. But in the examples above, only one polyatomic ion was involved. How do we write the formula of a compound that requires MORE than one polyatomic ion? Figure out how many total positive and total negative charges are needed, and how many of each ion are needed. Then use parentheses ( ) around the entire polyatomic formula and write the necessary subscript OUTSIDE the parentheses. Ca +2 + OH –1 Al +3 + NH4 +1 + Here we have two positive charges and only one negative charge. Two negative ions are required: Ca(OH)2 OH –1 Here we have three positive charges and one negative charge. Three positive ions are needed: Al(OH)3 S –2 We need two positive ions to balance the two negative charge on the sulfide ion: (NH4)2S And what do we do if the positive ion is a polyatomic ion and the negative ion is also a polyatomic? Nothing different! Use parentheses!! Just remember to treat the polyatomic ions as single units. NH4 +1 + OH –1 NH4 +1 + CO3 –2 only one of each ion is needed: NaOH two ammonium ions are needed to balance the charge on the carbonate ion: (NH4)2CO3 Complete the following table: OH -1 Li +1 Mg +2 Al +3 NH4 +1 Pb +2 Pb +4 Fe +2 Fe +3 Zn +2 NO3 -1 SO4 -2 PO4 -3 C2H3O2 -1 Now that you can write the formulas of compounds containing polyatomic ions, let’s try naming the compounds from the formulas. And then we’ll write formulas from the names of compounds. Name each ion in the formula. Do not include any reference to the subscripts either in the polyatomic ion formula or in the compound formula. Examples: NaOH is sodium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 is calcium hydroxide NH4Cl is ammonium chloride (NH4)2S is ammonium sulfide (NH4)2SO4 is ammonium sulfate Pb(OH)2 is lead(II) hydroxide Pb(OH)4 is lead(IV) hydroxide Al2(SO4)3 is aluminum sulfate Name the following compounds: 1. LiOH ______________________________________________ 2. FeSO4 ______________________________________________ 3. Cu2SO4 ______________________________________________ 4. CuSO4 ______________________________________________ 5. NH4F ______________________________________________ 6. (NH4)3PO4 ______________________________________________ 7. Co(OH)2 ______________________________________________ 8. ZnSO4 ______________________________________________ Write the correct formula for each compound: 1. sodium sulfate ____________________ 2. potassium hydroxide ____________________ 3. copper(I) phosphate ____________________ 4. copper(II) phosphate ____________________ 5. barium hydroxide ____________________ 6. ammonium carbonate ____________________ 7. iron(II) phosphate ____________________ 8. iron(III) sulfate ____________________ 9. magnesium phosphate ____________________ 10. ammonium phosphate ____________________