o The father of Genetics.
advertisement

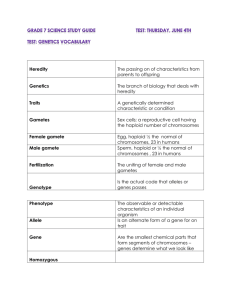
GENETICS Genetics- __________________________________. Heredity- the passing down of traits/_________________ from one generations to the _________. o o o o o o o o o _______________ ____ ___L The father of Genetics. ______________________. Worked with _______________. Not fully appreciated until _____________________. Born _______________________. 1st Scientist to put ________and _________ together. Why Pea Plants? Short Life Cycle…____________. No ________________ traits. They could ______________or be ___________________ by hand. o o Gametes____________. Like an egg or sperm Haploid Cell is a cell that only contains __________________________________…like gametes!! o _______________- has a full number of chromosomes. Like every cell in your body EXCEPT your gametes. Pea Plants A Pea plant has both the _________and _________ gametes enclosed within the flower. ________ grains are the _______ haploid cells. ________ are the female haploid cells. o The __________ can fuse together to make a viable offspring called a ____________ in a process called ______________________. o Or the gametes can be bred by hand….called __________________________. EXPERIMENTS Mendel began his experiment by allowing a given variety to self-fertilize for several generations. This assured what he called a purebreed. He crossed a : tall X tall = all tall Then he would take and cross Tall X Short (also a purebreed) = All Talls in the F1 generation. Through this he discovered what are called _________________…which is the trait observed in a ________. ____________________-a trait that is _____ observed in hybrid. MENDEL’S PEA PLANTS After many experimental crosses Mendel determined that many traits of the pea plants were ________/_______________. He established a _______ that is stilled ___________ used today. Copy the chart in its entirety. Dominant Traits will be represented by ____________ Letters. Recessive Traits will be represented with ___________ ___________ letters. TRAITS o o o You determine which letter to use by taking the ____________ of the _____________trait REMEMBER- ___________________represents _____ trait (Height is one trait so it includes tall and short…still one letter) If you _______ letters than you change __________. CONCLUSION o o During Mendel’s work he concluded that each trait was controlled by something he called a __________…we know today he was talking about _________. He then continued by saying that each trait is really controlled by ______ “factors”,alleles, or genes…________________________________. o Therefor the gametes of an individual contain ______ factor for a _______. REMEMBER: names. ________,_________, and “factors” are all the same thing…just different. GENOTYPE GENOTYPE- the _____________________________ of an organism. PHENOTYPE PHENOTYPE- the form of the trait that is ________________________. TT tt HOMOZYGOUS An organism where the _______ _________ for a trait are the same. Can be ____________ or recessive. Tt Also called Pure Breed HETEROZYGOUS o An organism where the two alleles for a trait are ______________. ___________. Also called a Mendel’s Law The chromosomes of homologous pair are made of __________ sequences called ________…therefor they have _______copies of a gene for any given trait. The Law of Segregation-That each pair of alleles separates during Meiosis o The Law of Dominance-When two alleles for a given trait are different (hybrid) one allele will be dominant over the other. o Law of Independent Assortment - The alleles/gene pairs separate into gametes randomly and independently of each other. (Those alleles located on different chromosomes). Randomly- You have no control. Independently- One trait has no control on another. PROBABILITY PUNNETT SQUARE A ______for _____________ genetic information. RULES FOR THE PUNNETT SQUARE o Determine the __________of the __________. Put one parent on _____ one parent far left. Do not _______ Parents Combine __________ inside the grid. Determine ____________ and ______________ Ratios PRACTICE TIME DO THE FOLLOWING CROSS Cross a heterozygous tall pea plant with a short pea plant. Tt X tt RATIO Phenotypic Ratio: 2:2 (reduce down) Tall:short Genotypic Ratio: Tt:tt 2:2 (reduce down) PUNNETT SQUARE o MONOHYBRID CROSS- Cross that involves only __ trait. Simple Punnett square. o DIHYBRID CROSS- Cross that involves __ traits. A Punnett square that has 16 squares.