Study Guide
advertisement
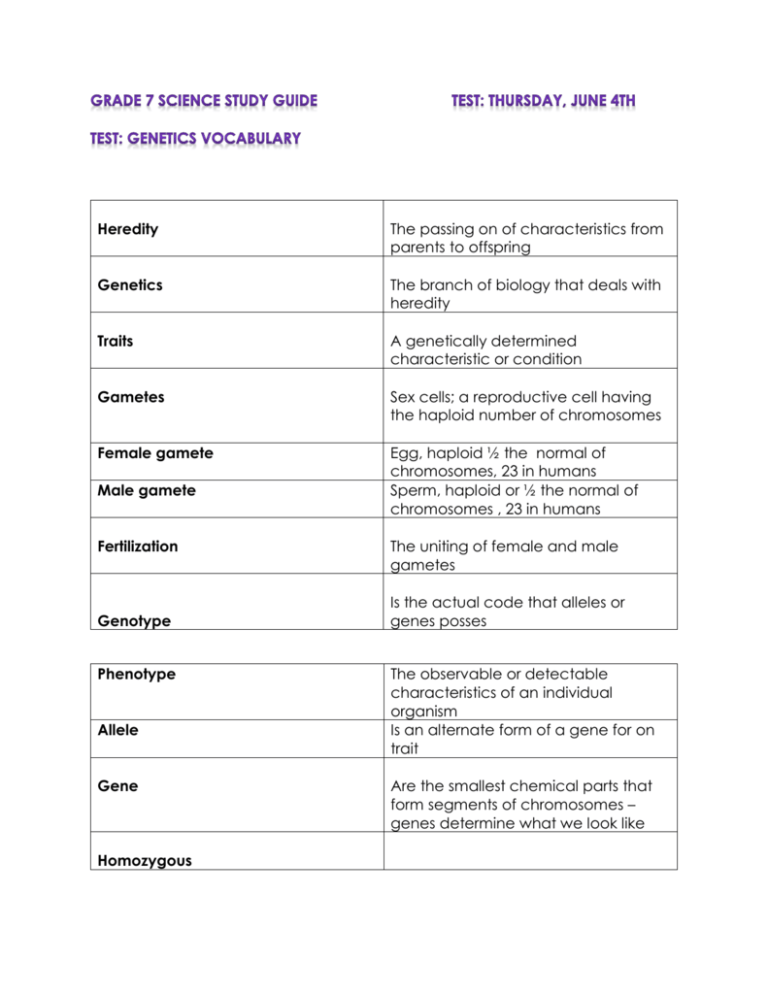
Heredity The passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring Genetics The branch of biology that deals with heredity Traits A genetically determined characteristic or condition Gametes Sex cells; a reproductive cell having the haploid number of chromosomes Female gamete Egg, haploid ½ the normal of chromosomes, 23 in humans Sperm, haploid or ½ the normal of chromosomes , 23 in humans Male gamete Fertilization Genotype Phenotype Allele Gene Homozygous The uniting of female and male gametes Is the actual code that alleles or genes posses The observable or detectable characteristics of an individual organism Is an alternate form of a gene for on trait Are the smallest chemical parts that form segments of chromosomes – genes determine what we look like A genotype consisting of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait Heterozygous Dominant A genotype consisting of two different alleles of a gene for a particular trait Observed trait of an organism that mask the recessive allele of a trait Recessive A trait of an organism that can be marked by the dominant form of a trait Punnett Square A simple graph method of showing all of the potential combinations of offspring genotypes that can occur and their probability given the parent genotypes. Probability The likelihood that a specific event will occur Mendel’s experiment -An Austrian monk who is often called the “father of genetics” -He tested some 28,000-30,000 pea plants over 7 years -He found the dominant and recessive traits -He disproved the theory of blending and replaced it with his 4 laws Mendel’s laws- #1The rule of unit factor #2: The rule of dominance each organism has 2 genes for each of its traits Only one trait was visible in the generation, the dominant trait #3: The law of segregation The two alleles for each trait must separate when gametes are formed #4: The law of independent assortment The alleles for one trait behaved independently of alleles for other traits during gamete production











