Disasters conflict and crisis management
advertisement

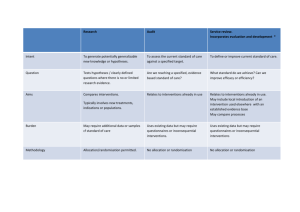
Disasters conflict and crisis management It is not unlike disaster recovery and risk management Disasters, conflict and crisis management How to approach the different interventions required: conceptual aspects, definition problems and purpose of the interventions Are they different sides of the same coin: crisis managements associated with disasters and / or conflict? Conceptual quagmire Methodological problems: needs assessments vs. Causal analysis Operational problems: setting priorities and differentiating emergency from urgency: simultaneity and sequencing Policy problems: positive vs. negative intervention; resource allocation vs. policy change promotion Vicious circle: Insecurity, conflict and mistrust Human actions progressively deteriorate the socio-economic fabric Conflict persistence affects stability (positively / negatively) Impact of instability and insecurity deteriorates governance and potential for recovery BREAKING THE CYCLE OF CONFLICT AND RESUMING THE PATH OF DEVELOPMENT The World Bank’s Conflict Prevention and Reconstruction Team, SDV SEQUENCE OF EFFECTS SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION PREVENTION the “before” actions Actions (programmes, projects) with the objective of anticipating and counteract the negative consequence an event may have (avoidance of conflict) It implies namely operational and organisation actions to build communication, trust and mutual respect, training of potentially affected groups and population to promote consensus building through mutual trust. SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION (2) MITIGATION encompasses actions “before”, “during” and “after” Actions (programmes, project) with the objective of counteracting (reducing the negative impact) of an occurrence. Includes allocation of resources to reinforce structures, redesign or alter existing elements to reduce vulnerability in addition to training and organisation (including at the community level) Ownership of actions is fundamental to build trust SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION (3) VULNERABILITY calculation made on the basis or exposure to the recurrence of conflict Risk factors or exposure to danger of existing institutional framework such as: Marginalisation, Informality, Pauperization, Conditions of human settlements and localisation of productive activities (primary, industrial, tertiary or services) and their linkage among them and with the environment. SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION (4) CONFLICT REDUCTION encompasses actions “before”, “during” and “after” Actions (programmes, project) with the objective of reducing vulnerability and exposure to risk Implies trust in functioning institutional arrangements and community involvement Difficulty in setting limits of outside intervention vs. local “sovereignty” or “ownership” SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION (5) RISK MANAGEMENT (actions to be carried out “before” with consequences “during” and “after”) Pro-active strategy (in contrast to re-active response) to reduce vulnerability and counteract risk factors Its objective is conflict reduction Is not a sector action but a global set of actions encompassing all sectors, beginning with sound environmental management Is not a conservation policy per-se but requires sustainability criteria both in terms of natural resources and human intervention. SOME DEFINITIONS IN CONFLICT RESOLUTION (6) CONFLICT MANAGEMENT actions to be carried “during” and the immediate (short-term) “after” The response strategy (re-active strategy) to, after the occurrence of a disaster, intends to counteract its more immediate negative impact and prevent more severe effects in the short term. Includes emergency actions (search and rescue, immediate assistance, shelter, sanitary and health campaigns, rehabilitation of lifelines, assessment of emergency needs and first appraisal of reconstruction requirements). Proposed courses of action Comparison of post-disaster and post conflict analysis / interventions Comparison of post-disaster and post conflict analysis / interventions (2) Comparison of post-disaster and post conflict analysis / interventions (3)