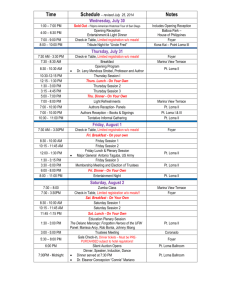
1. Historical Imagination: Mentally imagine that you are in the past
advertisement

Point Loma High School United States History Mr. McElhaney In Small groups discuss the following terms and decide which are most useful in learning history (top 5). Identify the top 5 and why you believe the term is more important than the others. You will be tested on the definitions and use of these terms. Create a poster display of your assigned Term; Include the following: TERM: Definition of term across the top of page (write neatly) Create and visual depiction of the term. This can be a diagram, image, chart, graph, or symbols In your own words write a brief explanation of how this term may be useful for students of history. Point Loma High School United States History Mr. McElhaney How do historians study history? What tools do historians use to reconstruct the past? 1. Historical Imagination Mentally imagine that you are in the past, consider the events or situations, as people at the time would have. Place yourself in the time period and give it perspective. 2. Multicultural Perspective: View historical events and issues from the perspective of different cultures and groups. 3. Point of View: Understand that people see issues and events differently. While studying history try to recognize whose point of view is being presented. 4. Compare and Contrast: Examine events, situations, or points of view for their similarities and differences. Comparing two issues is to find similarities. Contrasting is to find differences in two issues. 5. Cause and Effect: Think about the relationship between an event. The cause leads to an event. Effect is the consequence of the cause. 6. Analyzing: The process of breaking something down into parts and examining the relationships between these parts 7. Distinguishing Fact From Opinion: Separating the fact about something from what people say and believe. A Fact can be proved or observed An Opinion is a personal belief or conclusion. 8. Evaluating: Assessing the significance or overall importance of an issue, event, person or period. 9. Political History: History of politics, governments, laws, international relations, etc. 10. Social History History of groups, peoples, cultures (e.g. Women, teenagers, “Rock n Roll”, workers) 11. Military History: History of war and warfare, tactics, battles, industry of war… Point Loma High School United States History Mr. McElhaney 12. Comparative History: Comparing of historical subjects between one another (e.g., societies, and civilizations… English Colonial development compared to Spanish Colonial development) 13. Economic History: The study of economic trends through history, money, trade, business… 14. Interpretation An explanation of a historical event, person, trend based on specific evidence, arguments, and perspective… “The U S dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima to test atomic weapons and deter the Russians from taking territory.” Historians use facts to create explanations (interpretations) 15. Bias/ Subjectivity Prejudice; to make conclusions or interpretations with preconceived beliefs that influence the interpretation and understanding of a historical event, person, or period. Republicans see most actions of the Bush administration as correct. Democrats see most actions of the Bush administration as wrong. 16. Evidence Documents, artifacts, statements used to prove and make assertions. Example: An eyewitness account is evidence. 17. Primary Source See handout 18. Artifact An item that remains from another time. George Washington’s teeth are artifacts stored in the Smithsonian Institution. 19. Context The situation or circumstances surrounding an event; what happened before, during, and after; the environment that an event takes place in. When students study history they should consider the context of events, documents, and or decisions. 20. Objective; Objectivity: 21. Historiography Uninfluenced by emotions or personal prejudices: The opposite of prejudice or bias The study of how history is written, the study of different interpretations for historical events, people, and issues. Point Loma High School United States History Mr. McElhaney 22. Frame of Reference A set of ideas and beliefs, as of philosophical or religious doctrineby which other ideas are interpreted or understood. 23. Credibility: Everyone has a frame of reference that is the sum of all of their experiences; Each person’s frame of reference influences how they approach issuesHistorians each have a frame of reference that they must consider when studying an event or topicStudents of history must consider the frame of reference of authors, documents, and views being presented. A capacity for belief: Students of history must ask themselves if the explanation, account, or story is credible or believable. Students can judge credibility by investigating sources, evidence used to support conclusions, and author’s standing in the community. (It depends on bias, frame of reference, and how other experts view the explanation) Point Loma High School United States History Mr. McElhaney History Study Terms Test Match the definition or statement in column A with the term in column B 2 points each. A B 1. Comparing historical subjectsA. Economic History Societies and Civilizations, etc. B. Military History 2. Mentally imagine or visualize, place yourself in the time period. 3. Break it down for a better C. Social History D. Political History understanding. E. Distinguish Fact from Opinion 4. An explanation regarding an event or topic in history. 5. The situation that an event occurs. F. Cause and Effect G. Compare and Contrast 6. The history of groups in society. H. Point of View 7. Understand historical events seen through different cultures. 8. Assessing the significance or overall I. Evaluating J. Multicultural Perspective importance. 9. Look at resources, trade, taxes 10. George Washington was the first President of the U.S. George K. Historical Imagination L. Comparative History M. Analyzing Washington was a bad president. 11. Do your homework and "A" in the class. 12. History of government, laws, leaders. N. Interpretation O. Primary Source P. Frame of Reference 13. War and warfare, weapons. 14. Venn diagrams show this. 15. The Declaration of Independence, the Constitution of the United States 16. Not subjective Q. Objectivity R. Context