Making and Testing Gases
advertisement

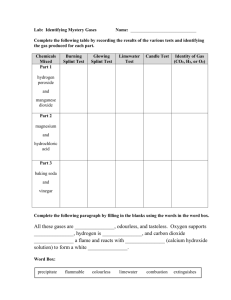
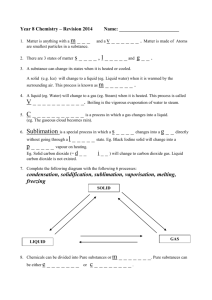
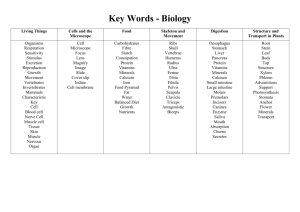
Making and Testing Gases Carbon dioxide gas Making carbon dioxide gas To make carbon dioxide, you need two ingredients - a carbonate of some sort (a carbonate has carbon dioxide trapped in it as part of its structure) like marble chips (calcium carbonate), and an acid to react with the carbonate, which lets the carbon dioxide out. We can also use kitchen chemicals – vinegar (acid) and baking soda (sodium bicarbonate). Carbon dioxide is heavier than air so it isn't too hard to trap some carbon dioxide in a test tube. Chemicals used to make carbon dioxide gas Testing for carbon dioxide gas The easiest way to test carbon dioxide gas is to mix it with some limewater. Limewater is usually clear. When carbon dioxide is added, the limewater goes a milky white colour for a short while (if you keep adding carbon dioxide, the limewater goes back to colourless again so watch out for that). This test is also known as the 'limewater test'. Hydrogen gas Making hydrogen gas You just need a small piece of metal (tin, zinc or magnesium work really well) and some acid, such as hydrochloric acid. Put them carefully together in a test tube and you'll see the liquid fizzing as the hydrogen gas gets released -the metal disappears as it gets used. The colour of limewater for a positive result Testing for hydrogen gas Hydrogen gas is explosive so if we bring the gas near a flame, it makes a squeaky pop. This test is also known as the 'pop test'. Why is hydrogen gas useful? It burns easily and so makes a good fuel - liquid hydrogen can mix with liquid oxygen to make rocket fuel. In fact, hydrogen is the fuels that stars use to produce their heat and light, although they don't burn it, rather they get much more energy out of it by making a nuclear reaction called fusion. Magnesium metal and hydrochloric acid Oxygen gas Making oxygen gas The easiest way to make oxygen gas in a lab is to use two ingredients - hydrogen peroxide (a colourless liquid that looks like water but is much more reactive), and manganese dioxide. (Note that the blackish brown powder called manganese dioxide (MnO2) that is very good at leaving a messy stain on your equipment!) The easiest way to capture some oxygen gas is Chemicals used to make to use a technique known as "the downward oxygen gas displacement of water". The downward displacement of water means that if your test tube is upside down and full of water (in a big container of water too) then as the oxygen floats up into the test tube from the end of your delivery tube, it displaces the water downwards by pushing it down and out of the way, until all the water is outside in the big container of water. We also used this technique for the other gases. Testing for oxygen gas The easiest way to test oxygen uses the fact that flames burn really well in pure oxygen, better than they do in air. We light a small, thin piece of wood called a splint, and then we blow it out so that it's just glowing orange a little, but not actually got any flames left (like an incense stick). Then we put the glowing end of the splint into our gas sample. If the gas is pure oxygen, then the oxygen feeds the fire and a flame starts up again or relights. If the gas sample isn't oxygen, or if your sample has too much air in it, then the glowing orange end does nothing or goes out completely. This test is also known as the 'glowing splint test'. Testing for oxygen gas Read Year 9 text book, pages 44 to 53, for more information Uses of Gases Use textbook to find at least 2 uses Oxygen Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Summary of Gases Name of Gas How we made it Test for gas & expected result Two important ways the gas can be used.